Securing today’s cloud-driven businesses is a challenge, and choosing the right approach can be overwhelming. Two popular frameworks – SASE and CASB which often come up in the conversation.
SASE redefines network security with a unified edge approach, while CASB focuses on protecting cloud apps and data. But which one fits your needs? Let’s break down their key differences of SASE vs CASB to help you make an informed decision.
What is SASE?
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is a next-generation framework designed to address the challenges of today’s digital environments. It combines networking and security services into a single, cloud-based solution, built for businesses operating in a decentralized, cloud-first world.
Why Does SASE Matter?
The way businesses operate has fundamentally changed:
- Data is everywhere. Employees need access to resources from multiple locations such as offices, homes, and on the go.
- Applications have moved to the cloud. Critical tools like Microsoft 365, AWS, and Salesforce are no longer confined to data centers.
- Traditional security isn’t enough. On-prem firewalls and VPNs weren’t built for this level of flexibility.
SASE directly addresses these challenges by:
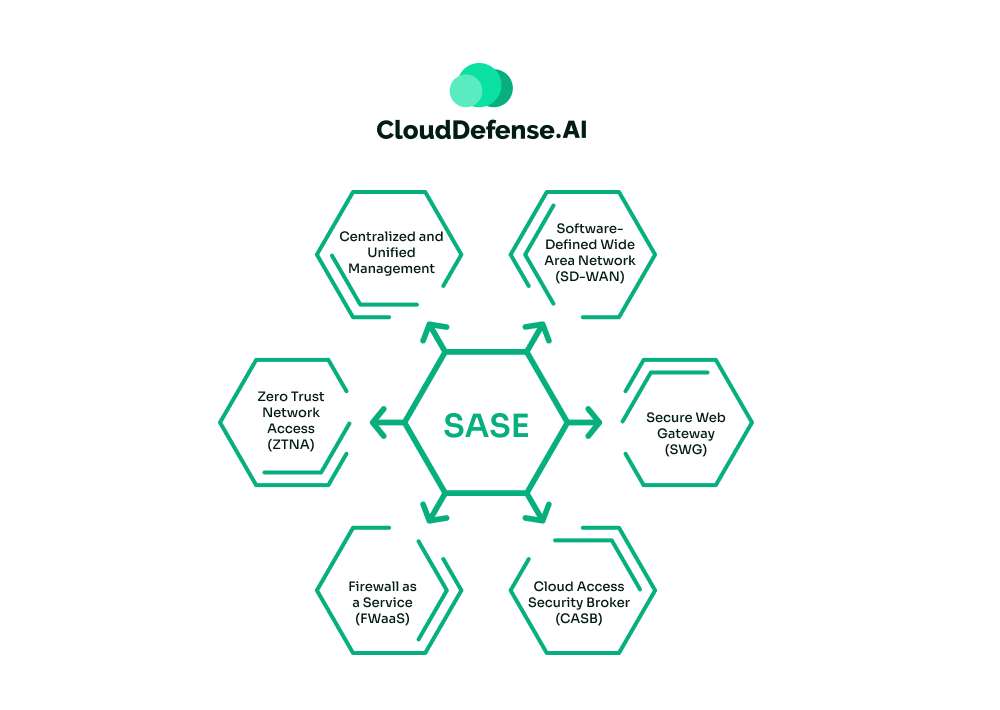
- Merging Networking and Security: It brings SD-WAN (networking) and security features like secure web gateways (SWG), zero trust network access (ZTNA), and cloud-delivered firewalls into a unified service.
- Cloud-Native Delivery: Everything runs in the cloud, ensuring global scalability and efficiency.
- Zero Trust Architecture: It ensures every user and device is verified before granting access, with no shortcuts.
Why Should Businesses Care?
SASE isn’t about following trends, it’s about solving real problems:
- Faster, Secure Access: Traditional tools often slow down user connections. SASE optimizes traffic routing to deliver both speed and security.
- Simplified Operations: By consolidating networking and security tools, IT teams can manage everything through a single platform.
- Future-Proof Infrastructure: Whether scaling up or adapting to new threats, SASE grows with your business without adding complexity.
SASE is more than a solution. It’s a deliberate approach to modernizing network security for businesses ready to meet the demands of a cloud-driven world. Now, let’s see how it compares to CASB.
What is CASB?
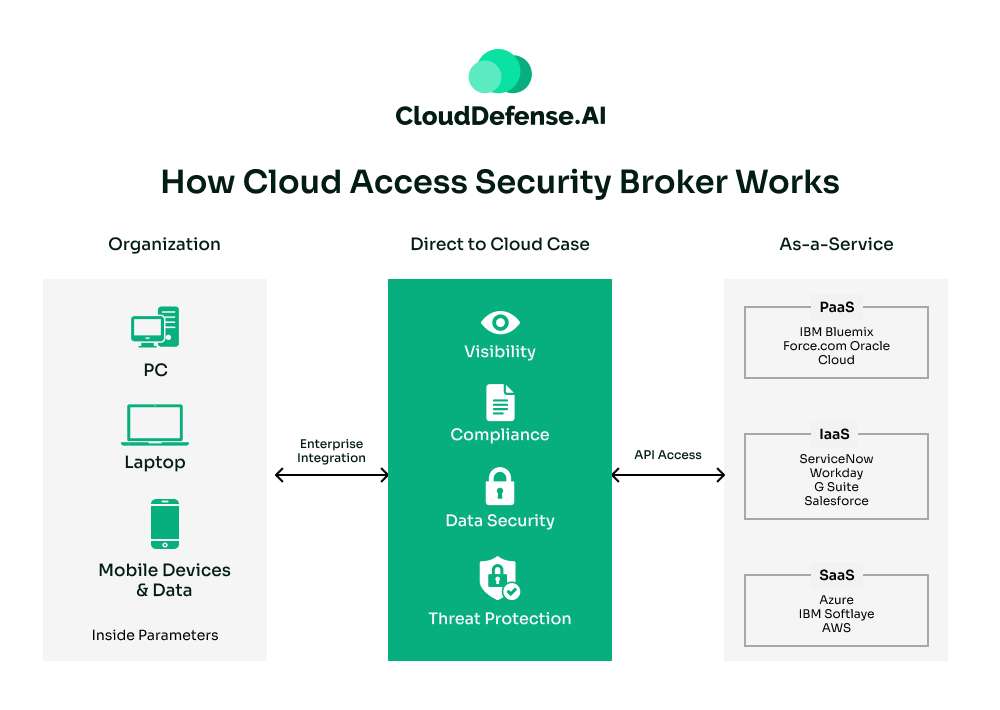
A Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) is a security solution specifically designed to address the unique risks of cloud environments. It acts as a bridge between users and cloud applications, providing visibility, control, and protection for sensitive data in the cloud. Unlike SASE, which is more comprehensive, CASB has a laser focus on securing cloud services.
Even though CASB helps in securing your cloud environment, its capabilities and focus changes according to cloud service models. CASB provides a comprehensive coverage for SaaS models with data loss prevention and shadow IT discovery capabilities.
Whereas the security solution for IaaS models mainly focuses on data security and posture management. The key capabilities include configuration security, data protection and compliance management. CASB for PaaS mostly covers areas like access control and discovery. The capabilities are mostly limited to API security, monitor and policy enforcement.
Why Do Businesses Need CASB?
Cloud applications are powerful but come with risks:
- Lack of Visibility: IT teams often don’t know which cloud apps employees are using (shadow IT).
- Data Exposure Risks: Sensitive information can be shared, uploaded, or misused without proper controls.
- Compliance Challenges: Cloud services often don’t meet regulatory requirements out of the box.
CASB steps in to solve these challenges:
- Cloud Visibility: CASB identifies and monitors all cloud applications in use, giving IT teams full insight into potential risks.
- Data Security: It enforces data loss prevention (DLP) policies, ensuring sensitive information is encrypted or blocked when necessary.
- Access Control: CASB allows businesses to enforce policies on who can access cloud apps, from which devices, and under what conditions.
- Threat Protection: It detects and responds to malicious activity in cloud environments, protecting against account compromises or insider threats.
Why CASB is Critical in a Cloud-First World
- Protecting Sensitive Data: With the rise of SaaS tools, businesses handle more sensitive data in the cloud than ever before. CASB ensures it’s safe.
- Mitigating Shadow IT: CASB identifies and manages unauthorized apps employees use, reducing security gaps.
- Simplifying Compliance: It helps businesses meet regulatory standards by enforcing security policies across all cloud applications.
CASB is not a general-purpose solution, it’s purpose-built to secure cloud apps and data. Whether used on its own or as part of a broader security strategy with SASE, it plays a key role in modern cybersecurity. Up next, let’s compare SASE and CASB directly.
What Are the Differences Between SASE and CASB?
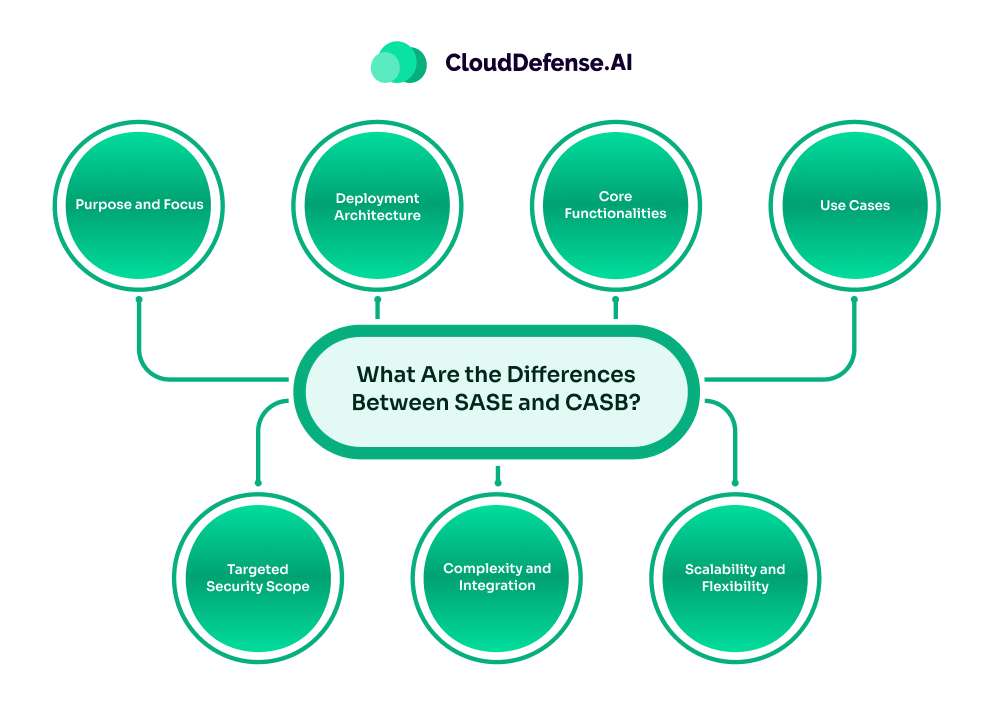
As both SASE and CASB are critical components of modern security architectures, they serve very different purposes and address distinct challenges. Let’s break down the differences across various dimensions to provide a clear understanding.
1. Purpose and Focus
SASE:
SASE is a comprehensive framework that integrates network security and connectivity into a single cloud-delivered platform. It focuses on securing user access to all resources—whether hosted on the cloud or on-prem—while optimizing network performance.
Key areas: Network security, user identity, access control, and traffic optimization.
CASB:
CASB is a specialized solution focused solely on securing cloud applications and protecting data stored or accessed in the cloud. It provides deep visibility into cloud app usage and enforces data protection policies.
Key areas: Cloud app visibility, data protection, access control for cloud apps, and compliance.
2. Deployment Architecture
SASE:
- Delivered via the cloud, SASE integrates multiple components like SD-WAN, Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), and cloud-delivered firewalls.
- It applies security policies at the network level, regardless of whether users access the cloud, on-premises apps, or private data centers.
CASB:
- CASB operates as a middleware between users and cloud services.
- It can be deployed in multiple modes:
- API mode to directly integrate with cloud applications.
- Proxy mode (forward or reverse) to intercept traffic and apply security controls.
3. Core Functionalities
SASE:
- Network Connectivity: Uses SD-WAN to optimize traffic routing across multiple sites and cloud environments.
- Zero Trust Security: Enforces identity verification and contextual access controls for every user or device.
- Traffic Inspection: Monitors all traffic (not just cloud traffic) for potential threats or vulnerabilities.
CASB:
- Cloud Visibility: Identifies and monitors all cloud applications being used, including unsanctioned apps (shadow IT).
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Protects sensitive data by enforcing encryption, blocking risky uploads, or controlling file sharing.
- Threat Protection: Identifies malicious activity within cloud apps, such as compromised accounts or insider threats.
4. Use Cases
SASE:
- Securing remote workforces and hybrid environments.
- Protecting access to multi-cloud infrastructures.
- Replacing traditional VPNs with ZTNA for better performance and security.
CASB:
- Securing data within SaaS applications like Salesforce, Google Workspace, and Microsoft 365.
- Enforcing compliance for data stored in the cloud.
- Mitigating shadow IT risks by identifying and managing unauthorized cloud applications.
5. Targeted Security Scope
SASE:
- Protects the entire network, including cloud applications, on-prem resources, and private data centers.
- Operates across all traffic, including web browsing, internal traffic, and cloud access.
CASB:
- Focused exclusively on cloud applications and their data.
- Operates specifically on SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS platforms.
6. Complexity and Integration
SASE:
- Offers an all-in-one solution that simplifies management by consolidating multiple tools into one platform.
- However, implementing SASE often requires rethinking network architecture, which can be complex for businesses with legacy systems.
CASB:
- Focuses on a narrower problem area, making it easier to deploy in existing environments.
- Integrates seamlessly with specific cloud applications, without requiring major infrastructure changes.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
SASE:
- Designed for organizations with distributed teams and multi-cloud environments.
- Easily scalable for growing businesses or enterprises with global workforces.
CASB:
- Works best for organizations heavily reliant on cloud applications.
- Less focused on scalability for broader network security needs.
Here’s a quick summary that provides a side-by-side comparison to help you understand when and why to use SASE, CASB, or both.
| Feature | SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) | CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker) |
| Purpose | Comprehensive framework for securing network and access to all resources. | Focused on securing cloud applications and data. |
| Primary Focus | Network security, Zero Trust access, and traffic optimization. | Cloud app visibility, data protection, and compliance. |
| Core Functionalities | – SD-WAN for optimized connectivity.- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA).- Secure Web Gateway (SWG).- Cloud-delivered firewalls. | – Cloud app monitoring and shadow IT detection.- Data Loss Prevention (DLP).- Threat protection for cloud apps.- Compliance enforcement. |
| Scope | Protects entire networks, including on-prem, multi-cloud, and private resources. | Focuses exclusively on SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS platforms. |
| Deployment | Delivered via the cloud, integrated into a unified security framework. | Middleware between users and cloud apps; uses API or proxy modes. |
| Use Cases | – Securing remote workforces and hybrid networks.- Replacing VPNs with ZTNA.- Managing multi-cloud infrastructures. | – Protecting SaaS applications (e.g., Salesforce, Google Workspace).- Mitigating shadow IT risks.- Enforcing data compliance policies. |
| Target Audience | Organizations needing comprehensive network security and optimization for global teams. | Businesses heavily reliant on cloud applications. |
| Integration | All-in-one solution requiring rethinking of network architecture. | Integrates with specific cloud apps without major infrastructure changes. |
| Scalability | Scales across distributed teams and global workforces. | Focused on scaling within cloud app environments. |
| Threat Coverage | Monitors all traffic, including web, cloud, and internal communications. | Detects threats specifically within cloud applications. |
| Complexity | Requires architectural changes but simplifies long-term management. | Easier to deploy with less impact on existing infrastructure. |
When to Use SASE vs CASB
Choose SASE if:
- You need a unified platform for both network and security across your entire infrastructure.
- Your workforce is highly distributed, and you require secure, optimized access to resources from anywhere.
- You want to adopt a Zero Trust architecture for all types of traffic.
Choose CASB if:
- Your primary concern is securing data and managing risks within SaaS applications.
- You want deep visibility and control over cloud app usage, including shadow IT.
- Compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA is a top priority.
Overlapping Functions of SASE and CASB
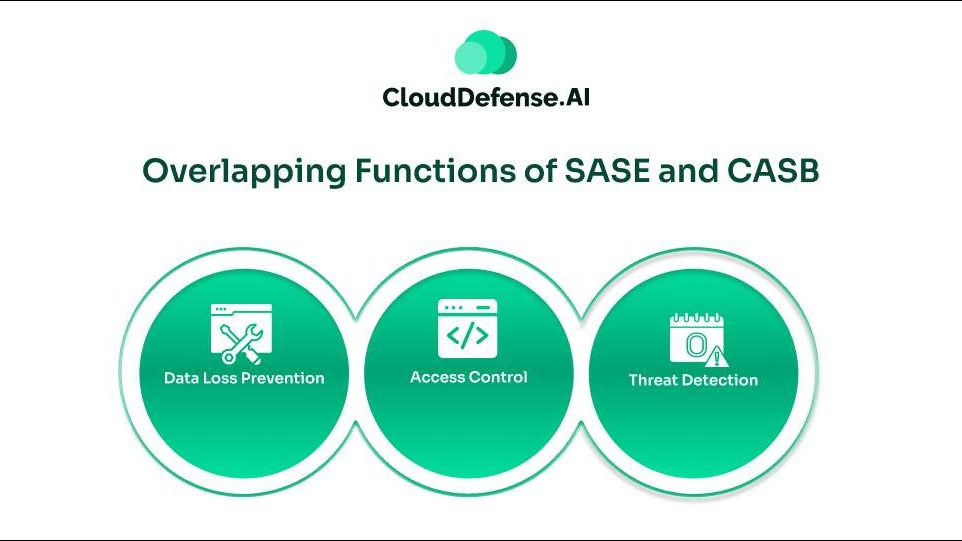
SASE and CASB may differ in various aspects especially with architectural approach but there are functions where both overlap. SASE can embed CASB capabilities and provide a comprehensive approach. Here are three security functions where SASE and CASB overlap:
- Data Loss Prevention: Both SASE and CASB utilizes DLP to curb the loss of sensitive data and unauthorized sharing. SASE leverages DLP for network edges, cloud apps and email to secure all the data that are in transit across the organization’s network. CASB integrates DLP for safeguarding data within the cloud environment. They achieve it by monitoring and regulation of data movement in the cloud services.
- Access Control: SASE makes use of the Zero Trust framework to enforce a stringent access control across the cloud network. It also integrates ZTNA and SD-WAN to provide a complete and identity-centric approach. On the other hand, CASB helps in securing and managing access control to cloud applications and services. They leverage granular access policies to provide access to cloud sensitive data based on user identity, application privilege and device’s security posture.
- Threat Detection: CASB and SASE also integrate various mechanisms to provide threat detection.CASB integrates UEBA to detect any malicious activity within the cloud application. It also identifies cloud specific threats like phishing attacks and provides visibility to user activity. Whereas SASE provides a broader threat detection approach by integrating numerous functions like NGFW. It also provides threat intelligence by utilizing real-time analytics and helps in uncovering any threat on the network edge.
Conclusion
At the end of the day, SASE vs CASB isn’t about choosing one over the other. They’re two sides of the same coin. SASE secures how users connect to resources, no matter where they are, while CASB focuses on protecting the data within cloud apps. If your business relies heavily on cloud services, CASB is non-negotiable. If you’re managing a hybrid or remote workforce, SASE becomes essential.
In reality, most organizations need both. Together, they provide the coverage modern environments demand—strong network protection paired with tight cloud security. It’s not about choosing one; it’s about knowing when to use both.







