Modern AppSec has evolved rapidly in the past few years with the advent of AI. However, a disconnect still exists between application security and developers. Many security tools used by organizations are highly efficient in finding vulnerabilities, providing hundreds of alerts. However, they fail to cover one core aspect that every developer needs- remediation guidance.
For every developer, these alerts are extra work that they need to accomplish apart from their development work. Things get more complicated as all the vulnerability reports only highlight the issue and provide generic remediation advice. To be more effective and bridge all the gaps, organizations need to move from generic suggestions to developer-first remediation guidance.
This approach helps developers with remediation guidance, with context and action that they can easily implement. In this guide, we will dive into how organizations can build a remediation guidance security that developers can actually use.
Why Developers Ignore Many Remediation Guidances
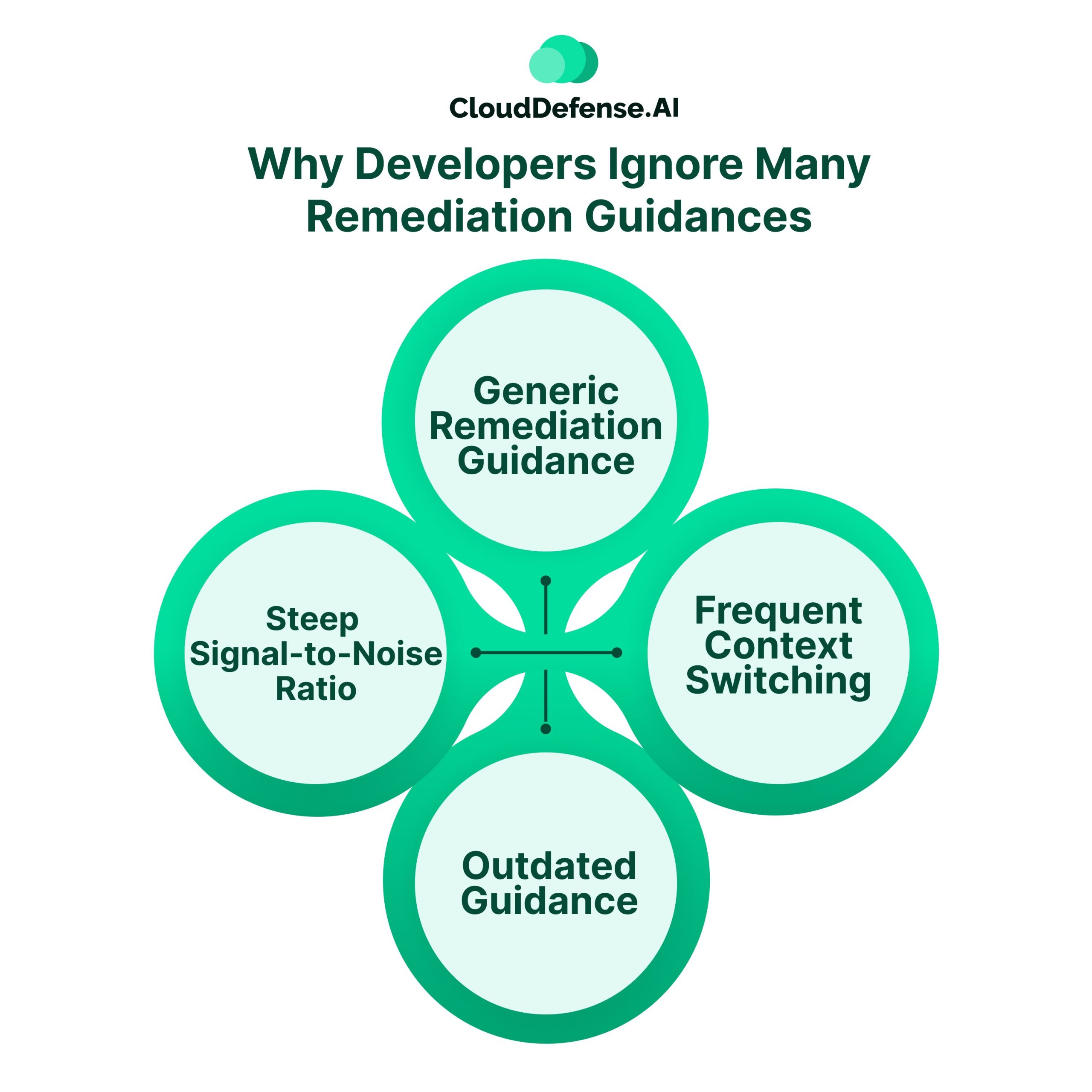
Every organization has implemented remediation guidance for its developers. However, most of these guidelines are never utilized by developers. Why? This guidance doesn’t cater to their requirements.
The main reasons are:
- Generic Remediation Guidance: Most remediation guidance offers generic advice to developers. Most of the guidance lacks context of the code, environment, framework, and many other aspects. As a result, it tells the developers what they can do and not how they can do it. Thus, developers have to test all the possible remediations to avoid breaking the build or making unnecessary changes.
- Frequent Context Switching: All the guidance for patching an issue is located in different dashboards or tickets. The security tools don’t feed the guidance directly into the IDE. Developers have to switch from their IDE or Jira and log in to the dashboard of the security tool to get the remediation support. The constant back and forth between the dashboard not only reduces the MTTR but also breaks the productivity of the developer.
- Steep Signal-to-Noise Ratio: A lot of organizations still rely on traditional security tools like SAST or SCA to identify security threats. A large number of security alerts generated by these tools are false positives, making developers distrust the tools. Developers have to manually triage all of them to find out which alert requires immediate incident response. Eventually, a lot of real alerts get ignored in the process.
- Outdated Guidance: A lot of generic advice that is generated when a security threat is identified is outdated. These preset guidance were often written or updated a few years ago. In most cases, they aren’t applicable to the latest security threats or won’t work with any new framework. As a result, the remediation guidance renders it useless.
Primary Pillars of Developer-First Remediation Guidance Security
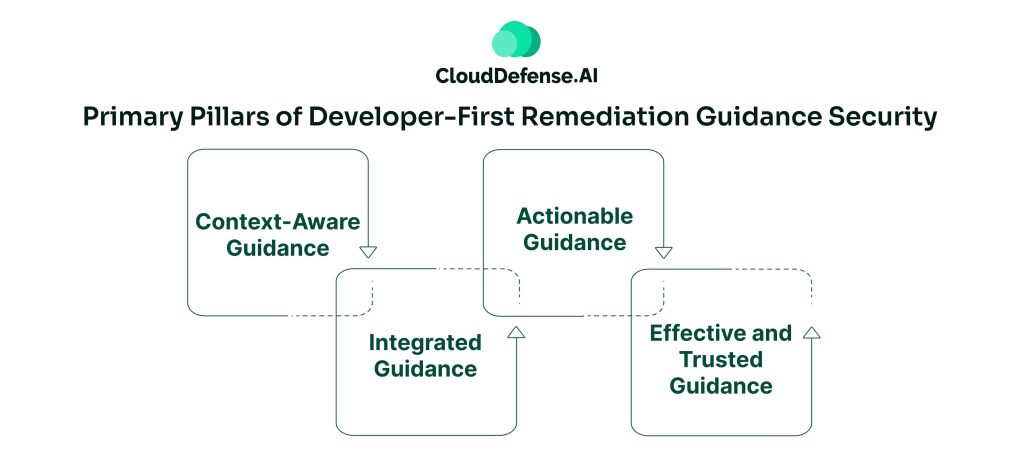
When an organization adopts security tools to identify threats, it is crucial to evaluate the remediation guidance that it has on offer. Not all tools provide actionable guidance. Developers don’t need hundreds of alerts; they need proper guidance.
An effective remediation guidance that developers can use is based on four primary pillars:
- Context-Aware Guidance: The primary aspect that developers look for in a remediation guidance is context-aware patches. The remediation process must be according to the business logic and specific code path. One-size-fits-all fixes won’t work with modern security threats. A context-aware advice will guide developers to fix issues without additional effort.
- Integrated Guidance: Usually, developers have to switch context to use the remediation guidance. The remediation guidance must be available in the section-preferred at IDE where the code is present. It should also be available as chat threads or tickets for easy access.
- Actionable Guidance: Developers need code fixes that are actionable and easy to fix. The remediation guide should include ready-to-implement code fixes or copy-paste code snippets that they can apply. It must be compatible with the specific language and framework of the project.
- Effective and Trusted Guidance: A remediation guidance must prioritise reachability analysis. All the security alerts must pass through reachability analysis to identify whether the threat would cause any impact on the threat. It will not only spare developers from triaging those false positives but also gain trust in the process.
How an Organization Can Transform Remediation Guidance with QINA Pulse
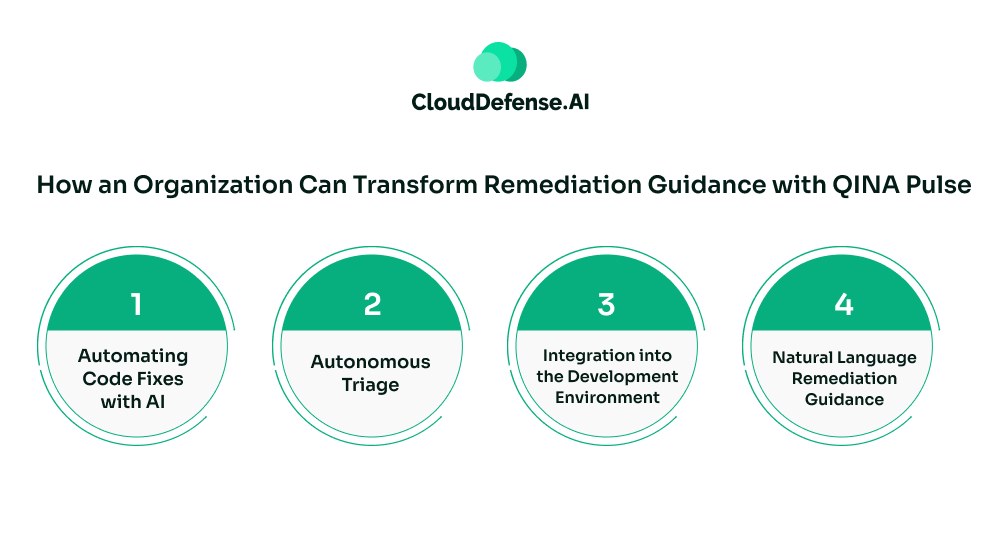
For organizations looking to implement a developer-centric remediation guidance, QINA Pulse is the answer. It is an AI-powered security co-pilot that is designed to orchestrate all the remediation guidance security processes in application security.
This tool acts as an intelligent assistant that not only reports on security threats but also understands the code context and provides fixes accordingly. From detection to remediation support, it supports developers throughout the workflow.
Now the question arises, how can we leverage QINA Pulse to ensure remediation guidance that developers can utilize? Well, here is how QINA Pulse is helping all modern organizations with their remediation processes:
Automating Code Fixes with AI
A major drawback of traditional remediation guidance security support offered by security tools is the lack of specific guidance. It provided generic instructions of “what should be done’ and not how developers can fix it. QINA closed this gap by utilizing LLMs to analyze the context of the vulnerable code and come up with an actionable solution.
It also analyzes the context of the other codes in the surrounding to extract the context. Then it sends a detailed remediation guidance along with secure code snippets needed to solve the threat. In some cases, it triggers automated patches for known vulnerabilities that developers can assess and merge.
Autonomous Triage
When an organization integrates QINA Pulse, it doesn’t send a raw list of all the possible threats. Instead, it utilizes a 4-stage analysis of QINA Clarity to autonomously triage and provide a prioritized security alert.
The detailed analysis involves assessment of data flow, identifying dead code, context extraction, and smart prioritisation of alerts. The reachability analysis enables Pulse to determine whether a user input can trigger the vulnerable code or function.
In this way, it prioritises all the alerts and allows developers to quickly address the vulnerable code of the highest impact. Eventually, it eliminates all the false positives and bolster developer’s trust in remediation support guidance.
Integration into the Development Environment
Frequent context switching for accomplishing security tasks often erodes trust among developers. QINA Pulse integrates directly into the IDEs, CI/CD pipelines, and other development environments.
The main benefit? The chatops of Pulse are directly available in the development workflow. It enables the developers to look for remediation of any identified threat without leaving the development environment. The alerts, along with remediation guidance security support is posted directly as comments into PR.
Native integration also allows developers to easily automate any remediation or apply any security patch. In the end, developers can quickly respond to real threats with proper remediation support.
Natural Language Remediation Guidance
A great aspect of QINA Pulse is that developers can command the tool to remediate a threat through plain English. It completely democratizes security for every developer. The natural language interaction eliminates the need for deep expertise to understand any security threat and ask for remediation guidance.
When a threat is identified, the developers just have to command “Pulse, fix the issue in the database”. It will either trigger an automated process or provide guidance. It provides all the remediation support in plain English, along with step-by-step fixes and security support. This allows developers to address all the security threats without sacrificing development productivity.
Why Organizations Should Leverage QINA Pulse for Remediation Guidance
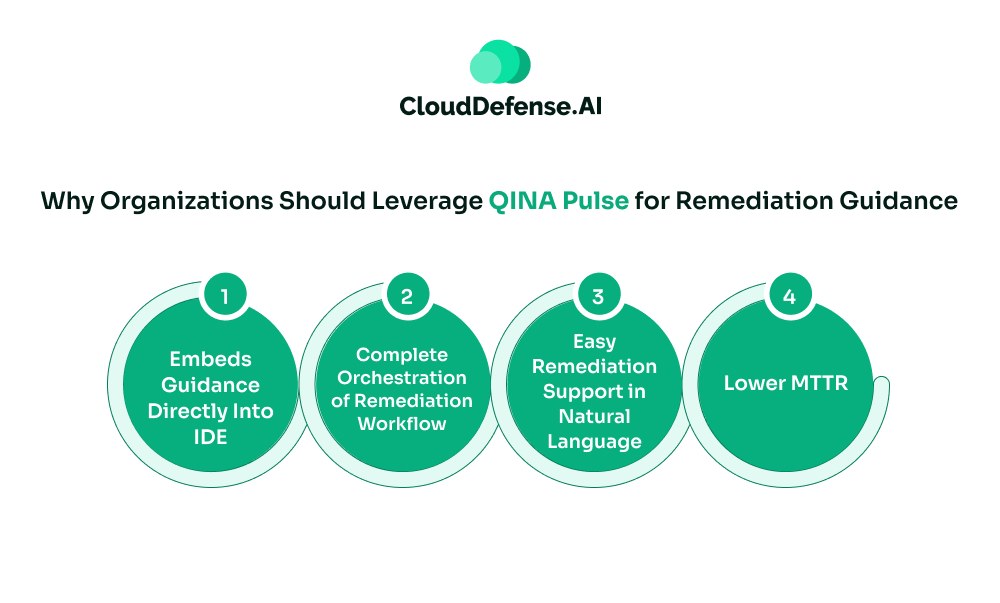
QINA Pulse has emerged as the most appropriate solution for every organization looking to implement a trusted remediation support. But what makes them a crucial tool?
Here are the reasons:
- Embeds Guidance Directly Into IDE: With QINA Pulse, the remediation guidance can be directly integrated into Jira, Jenkins, and PR comments. It enables developers to fix code while carrying on with the development workflow.
- Complete Orchestration of Remediation Workflow: When Pulse is integrated with all the security tools, developers can orchestrate the remediation workflow through simple commands. It can be easily configured to automatically open tickets and suggest fixes based on the context.
- Easy Remediation Support in Natural Language: Pulse communicates with you in plain English. It simplifies all the complex security jargon and enables developers to understand, and implement the remediation process easily.
- Lower MTTR: A major benefit of leveraging QINA Pulse is that it reduces the MTTR by a large margin. The one-click remediation through commands makes fixing patches an easy task for all developers. Lower MTTR ensures better productivity and a faster development cycle.
Bottom Line
Remediation guidance security support plays a key role in the modern development environment. A streamlined remediation support will ensure all the security incidents are patched without sacrificing the speed of development. This is why modern organizations are switching to tools like QINA Pulse. It not only enables them to streamline all remediation tasks through simple commands but also minimizes MTTR to maintain the developer’s velocity. It is eliminating all the friction between security and developers, and helping organizations to maintain a robust application security posture. Organizations looking to integrate QINA Pulse in their AppSec can book a live demo and get to know more about it.







