Since many businesses adopt remote work and cloud-first strategies, the demand for secure and effective access to applications and data has risen dramatically. This shift has brought two key concepts to the forefront: Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and Security Service Edge (SSE).
While SASE combines networking and security into a unified framework, SSE focuses purely on delivering reliable security services. The right choice depends on what your business needs most – efficiency, security, or both.
Here, let’s break down the differences between SASE VS SSE to guide your decision.
What is SASE?
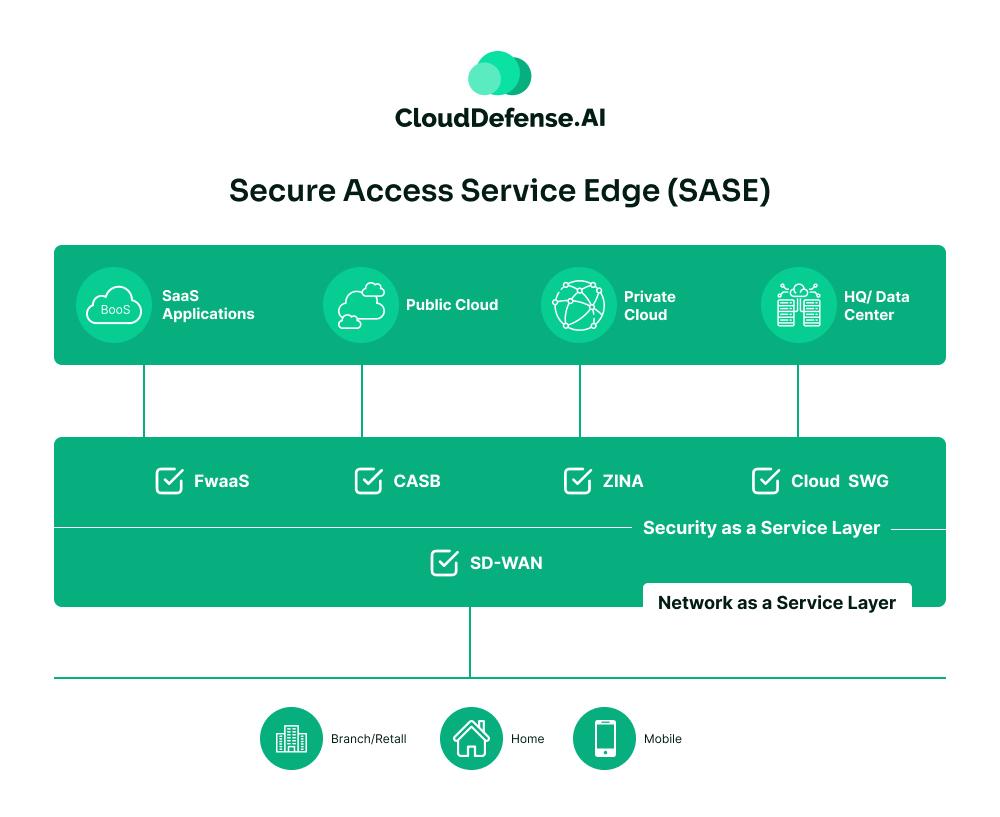
SASE, or Secure Access Service Edge, is a modern approach to solving a real problem – how to secure and connect a distributed workforce efficiently.
The traditional model of routing traffic through a central data center no longer works in a world where applications live in the cloud, and employees work from anywhere.
SASE fundamentally rethinks this by merging networking and security into one cloud-delivered solution.
Here’s how SASE works:
- Unified Networking and Security: SASE combines tools like SD-WAN with advanced security features such as firewalls, secure web gateways, and zero-trust network access (ZTNA). It’s not two separate systems – it’s one platform.
- Cloud-Delivered: Everything is managed in the cloud, making it fast, scalable, and adaptable to your business needs.
- Identity and Context-Based Access: SASE ensures only the right people and devices access the right resources, reducing the attack surface dramatically.
- Global Optimization: With cloud points of presence (PoPs) worldwide, it ensures low latency and fast performance, even for remote users.
Why does this matter?
Because the old ways of managing security and connectivity are failing. Legacy systems are slow, rigid, and built for a world that no longer exists. SASE eliminates these inefficiencies, offering:
- Simplified operations by replacing multiple tools with a unified platform.
- Better security through real-time threat detection and zero-trust principles.
- Faster access for users, no matter where they are.
Ask yourself this:
- Are your systems keeping up with the demands of a cloud-first, remote workforce?
- Are you able to secure data and users effectively without slowing them down?
If you nodded yes, SASE addresses these challenges head-on, giving businesses the flexibility and security they need to thrive in a cloud-first world. It’s more than a tool – it’s a strategic enabler for modern IT.
What is SSE?
Security Service Edge (SSE) is a cloud-delivered security framework that focuses solely on protecting users, applications, and data without altering the existing network infrastructure. SSE takes a more focused approach by isolating the security functions from networking. Unlike SASE, which merges networking and security, SSE concentrates solely on delivering security services through the cloud.
It’s basically designed for organizations that already have a solid networking framework but need to modernize and strengthen their security posture to match today’s cloud-first and hybrid work environments.
Here’s what SSE brings to the table:
- Cloud-Based Security: SSE delivers key tools like Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) directly from the cloud. It removes the need for legacy hardware.
- Zero Trust Enforcement: Access is controlled based on user identity, context, and device compliance. This ensures that only the right people access specific resources.
- Data Protection at Scale: SSE includes advanced data loss prevention (DLP) capabilities to safeguard sensitive information across all workflows – whether data is stored, being shared, or actively used.
- Real-Time Monitoring: It offers centralized visibility and control over user behavior and application activity, making it easier to detect and block security threats instantly.
Where does SSE fit?
- If you already have networking infrastructure like SD-WAN in place, SSE allows you to enhance your security without reconfiguring your entire network.
- If your business relies on SaaS and cloud applications, SSE provides consistent, cloud-native security for remote teams and hybrid environments.
Key benefits of SSE include:
- Simplifies security by consolidating multiple solutions into a single, cloud-managed platform.
- Protects your data and users with cutting-edge threat prevention, specifically designed for cloud-first operations.
- Aligns seamlessly with zero trust strategies to secure access anywhere, anytime.
SSE is a direct response to the growing complexity of securing modern businesses. It’s about addressing today’s challenges – distributed workforces, cloud dependencies, and evolving threats with precision and focus. If your priority is strengthening security while maintaining existing networking systems, SSE might be exactly what you need.
How Does Zero Trust Fit into SASE and SSE?
Zero Trust is a foundational principle in both SASE and SSE frameworks. At its core, Zero Trust means no implicit trust, access is granted based on strict verification of user identity, device compliance, and contextual factors like location and behavior.
It’s about continuously validating access requests, whether they come from inside or outside the organization.
Here’s how Zero Trust integrates into these two frameworks:
In SASE:
- Zero Trust is implemented across both networking and security layers.
- Ensures secure access to resources across a distributed network.
- Combines identity-based access controls with secure traffic routing to reduce risk while optimizing performance.
- Protects hybrid environments by integrating Zero Trust with SD-WAN for seamless, secure connectivity.
In SSE:
- Zero Trust is focused purely on security, ensuring granular access control for cloud applications, data, and services.
- Enables secure, policy-based access to SaaS and cloud resources without requiring a VPN.
- Reduces attack surfaces by enforcing “least privilege” access for every user and device.
- Supports real-time monitoring to continuously evaluate access requests.
Why Zero Trust is essential:
- Traditional security models trusted internal users by default, which doesn’t work in today’s remote and cloud-first environments.
- Zero Trust removes that gap by verifying every access request, no exceptions. This ensures robust security without creating friction for legitimate users.
Both SASE and SSE use Zero Trust as a cornerstone, but how they apply it depends on whether your organization prioritizes a combined networking-security solution (SASE) or a focused security upgrade (SSE).
Regardless of the approach, Zero Trust is non-negotiable for organizations aiming to stay secure in an increasingly complex threat landscape.
SASE vs SSE: Key Differences
While SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) and SSE (Security Service Edge) share the goal of enhancing security for modern, cloud-driven organizations, their scope and focus set them apart. Both frameworks leverage cloud-native technologies, but their design and intended use cases are fundamentally different. Let’s dive into the distinctions in greater detail:
Core Purpose
SASE (Secure Access Service Edge):
SASE is a comprehensive framework that combines networking and security into a single cloud-based solution. Its goal is to simplify IT operations by integrating these traditionally separate domains into one platform. With SASE, enterprises can ensure secure and optimized access for distributed users, devices, and branch offices, no matter where they are.
- It provides secure connectivity across hybrid environments, merging security with networking tools.
- Best suited for organizations aiming to modernize their entire IT infrastructure to align with remote work and multi-cloud environments.
SSE (Security Service Edge):
SSE narrows its focus to security only, delivering critical security capabilities like Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). Unlike SASE, SSE doesn’t address networking concerns like SD-WAN; instead, it builds on an organization’s existing networking setup by adding advanced, cloud-native security capabilities. It’s designed for organizations that want to strengthen their security without overhauling their networking infrastructure.
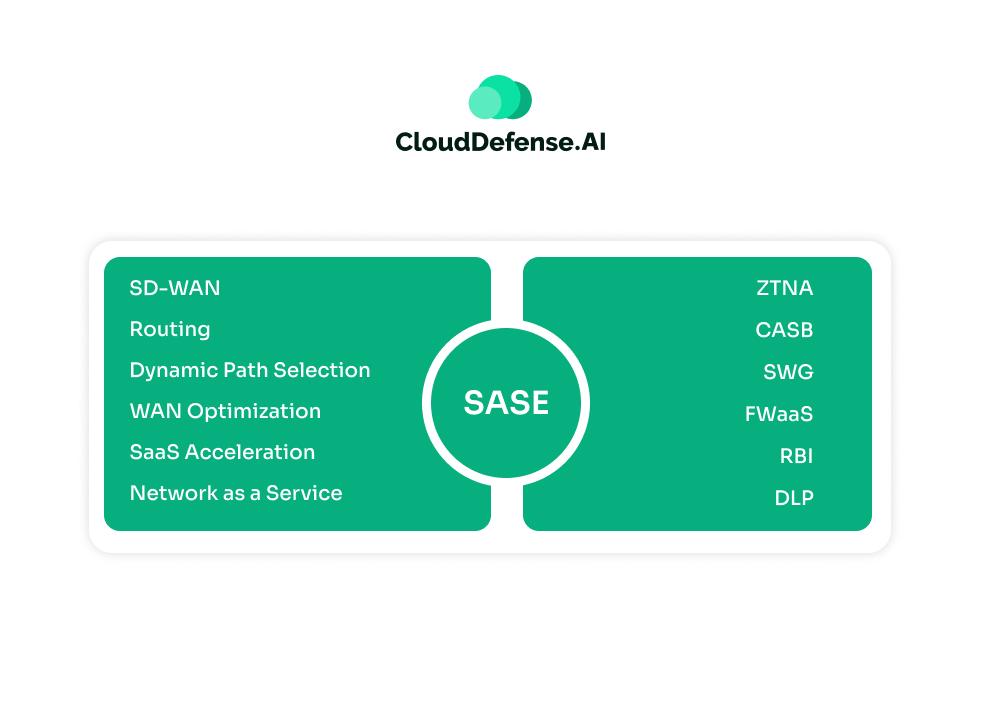
SASE Components:
SASE includes a combination of:
- SWG (Secure Web Gateway): Protects users from web-based threats and enforces acceptable web usage policies.
- CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker): Monitors and controls access to cloud applications, ensuring data protection and threat prevention.
- ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access): Ensures access to internal applications based on strict user identity and device verification, replacing VPNs with a more granular access model.
- FWaaS (Firewall-as-a-Service): Delivers firewall capabilities such as traffic inspection, threat prevention, and policy enforcement directly from the cloud.
These components are deeply integrated to provide end-to-end management of both networking and security functions.
Key Difference from SASE
- SSE focuses on security services.
- SASE combines SSE (security) with networking features like SD-WAN to deliver a complete secure networking framework.
Deployment Approach
SASE Deployment:
- SASE is an integrated solution that can be easily deployed in a phase wise approach. Vendors can help by starting with implementation of SSE components- like Zero-Trust network access and secure web gateways for immediate security needs.
Then gradually they can introduce SD-WAN capabilities which deliver the needed integrated and network management. This phased approach not only helps organizations to achieve complete SASE framework over time but also addresses any urgent security concerns.
SSE Deployment:
- SSE is designed to integrate with existing networking infrastructure, making it faster and easier to deploy. Organizations that already have an SD-WAN or other network solutions in place can simply layer SSE on top to enhance security without disrupting their current operations.
Target Audience
SASE:
- Ideal for businesses that want a holistic solution addressing both networking and security.
- Particularly valuable for companies with distributed teams, remote workforces, or hybrid cloud setups.
SSE:
- Best for organizations that already have a solid networking infrastructure but need a scalable, cloud-native security solution to protect their data, applications, and users.
Use Cases
SASE:
- Enterprises undergoing a full-scale digital transformation or moving to cloud-first architectures.
- Businesses with branch offices or remote workers that need secure, high-performance connectivity.
- Organizations that require a seamless combination of networking and security to simplify IT operations.
SSE:
- Companies looking to modernize security without replacing their networking infrastructure.
- Businesses with a focus on securing SaaS applications, cloud platforms, and remote users.
- Organizations that want to adopt Zero Trust principles to ensure granular, identity-based access control.
Flexibility and Focus
SASE:
- Offers a unified solution for organizations that want to manage networking and security from a single platform.
- However, its broader scope can lead to less flexibility for businesses that only need specific components.
SSE:
- Provides a targeted approach to security, allowing organizations to maintain flexibility in their networking choices.
- It’s ideal for businesses that don’t want to commit to a complete overhaul but still require modern security measures.
For your easy understanding, here’s a clear, side-by-side comparison of SASE and SSE to help you better understand their distinctions:
| Aspect | SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) | SSE (Security Service Edge) |
| Core Purpose | Combines networking and security into a unified solution for secure and efficient access. | Focuses exclusively on security, enhancing cloud-native protection without addressing networking needs. |
| Scope | Includes both networking (e.g., SD-WAN) and security (SWG, CASB, ZTNA). | Limited to security tools like SWG, CASB, and ZTNA. Does not include networking features. |
| Components | SD-WAN- Secure Web Gateway (SWG)- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)- Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) | Secure Web Gateway (SWG)- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) |
| Deployment | Requires a complete overhaul of networking and security systems for integration. | Easily integrates with existing networking infrastructure, making deployment simpler. |
| Primary Use Cases | Organizations seeking a complete networking and security solution.- Businesses with distributed teams or hybrid cloud environments.- Companies undergoing digital transformation. | Businesses that want to modernize security without replacing their networking setup.- Focused on securing SaaS applications, cloud platforms, and remote users. |
| Flexibility | Unified solution may limit flexibility for organizations needing only specific components. | Offers greater flexibility, as it doesn’t enforce changes to networking infrastructure. |
| Target Audience | Enterprises looking for an all-in-one solution to streamline both networking and security. | Companies with solid networking setups, needing scalable, cloud-native security. |
| Adoption Complexity | Higher complexity due to the integration of networking and security systems. | Lower complexity, as it overlays security tools on top of existing networking systems. |
| Focus | Holistic, addressing both secure connectivity and data protection. | Security-first, ensuring granular control and protection without impacting networking. |
So, the key take away here is: the decision between SASE and SSE boils down to your organization’s specific needs:
- If you’re looking for a single, all-encompassing solution that merges networking and security into one streamlined framework, SASE is the way to go.
- If your focus is solely on enhancing security while retaining your existing networking infrastructure, SSE will deliver the results you need.
Checklist: Difference Between SSE and SASE
The checklist offers a quick reference guide for organizations comparing pure security solutions (SSE) versus fully integrated networking and security solutions (SASE).
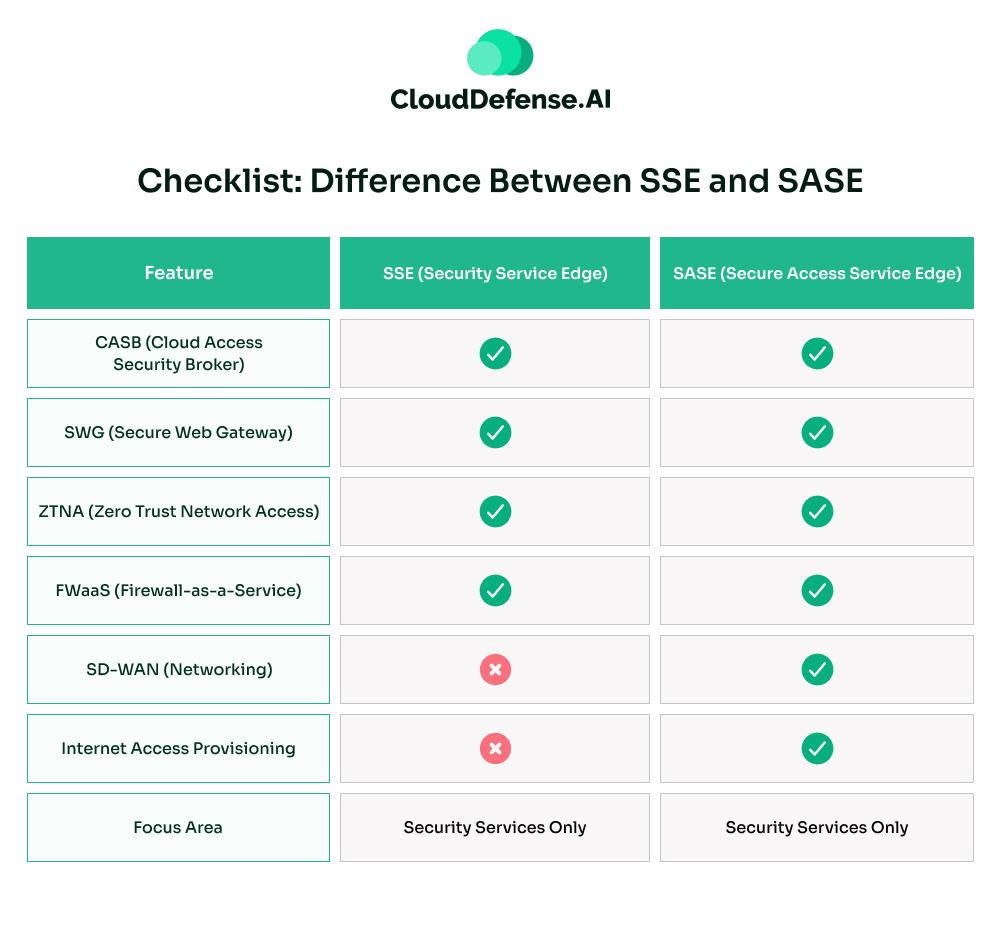
In short,
- SSE = Security-focused only (CASB, SWG, ZTNA, FWaaS).
- SASE = SSE + Networking (SD-WAN, Internet Access).
Final Thoughts
The choice between SASE vs SSE comes down to what your organization needs most. If you’re looking for an all-in-one solution that combines both networking and security, SASE might be the right fit. On the other hand, if your network is already solid and you just need a robust security layer for cloud and remote work environments, SSE makes more sense.
Both approaches align with the principles of Zero Trust and are designed to address modern security challenges. The key is to evaluate your current infrastructure, growth plans, and security priorities. With the right strategy, you can ensure secure and seamless access for your teams while staying ahead of emerging threats.







