Have you ever received a phone call claiming your bank account is compromised, your computer has a virus, or the IRS is taking legal action? If so, you might have been the target of a vishing attack.
Vishing, a cunning blend of “voice” and “phishing,” is a cybercrime where attackers use phone calls to impersonate legitimate entities and steal personal information. This information, like credit card numbers or social security details, can be used to drain your accounts, commit identity theft, or even launch further attacks.
But fret not! In this article, we’ll shed light on vishing tactics, common scams, and essential tips to protect yourself from falling victim to this sneaky cyber threat.
Let’s dive right in!
What Is a Vishing Attack?
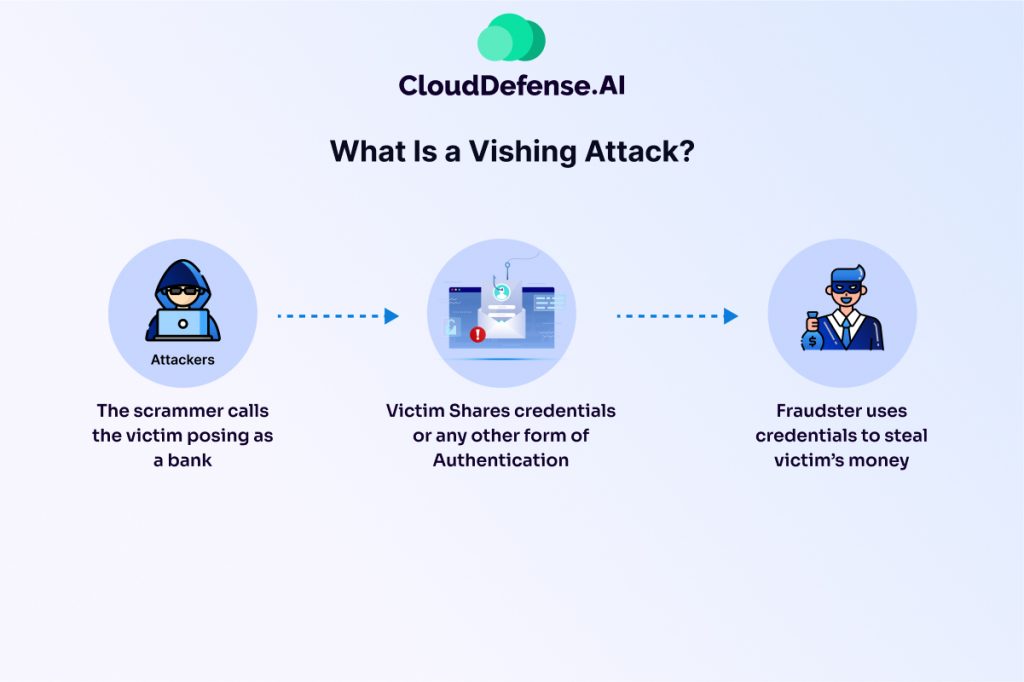
Vishing, a portmanteau of “voice” and “phishing,” is a type of social engineering attack where criminals use phone calls (or sometimes voicemails) to impersonate trusted entities and manipulate victims into revealing sensitive personal information. These entities can range from familiar institutions like banks and credit card companies to government agencies and even tech support providers.
The vishing call typically follows a script designed to create a sense of urgency, fear, or helpfulness. Attackers might claim your account has been compromised, suspicious activity has been detected, or there’s an urgent issue that requires immediate action. They may even sound professional and use official-sounding language to heighten believability.
Once they’ve gained your trust, vishers will try to trick you into divulging confidential details in several ways:
- Requesting verification: They might ask you to “verify” your identity by confirming your account number, password, or Social Security number.
- Directing you to a fake website: They might instruct you to visit a fraudulent website that looks legitimate and convince you to enter your login credentials there.
- Downloading malware: They might trick you into downloading malicious software disguised as a security update or application needed to resolve the fabricated issue.
The stolen information is then used for various malicious purposes, including:
- Financial Fraud: Draining bank accounts, making unauthorized purchases.
- Identity Theft: Creating fake identities for further criminal activity.
- Account Takeover: Gaining access to online accounts like email or social media.
Why Are Vishing Attacks Performed?
Vishing attacks are primarily motivated by financial gain. The stolen information can be used for various malicious purposes, including:
- Direct financial theft: Attackers can use stolen credit card numbers or bank account details to make unauthorized purchases or transfers.
- Identity theft: Stolen personal information like Social Security numbers and birthdates can be used to open new accounts, obtain loans, or commit other crimes in the victim’s name.
- Account takeover: Using stolen login credentials, attackers can gain access to the victim’s online accounts like bank accounts, email, or social media profiles, causing further damage and financial loss.
Vishing attacks can also be used for non-financial reasons. For instance, attackers might aim to compromise business email accounts to launch further phishing attacks within a company network.
The ease with which vishing scams can be launched and their potential for significant rewards make them a popular tool for cybercriminals. By understanding their tactics and staying vigilant, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to a vishing attack.
How Vishing Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Vishing attacks unfold in a series of calculated steps designed to exploit trust and urgency. Here’s a breakdown of the typical vishing operation:
1. Preparation:
- Data Collection: Attackers might gather information about potential victims through various means. This could involve purchasing data breaches on the dark web, social media profiling, or malware infections that steal personal details.
- Spoofing Caller ID: Criminals often use technology to manipulate the caller ID to display a seemingly legitimate number, such as that of a well-known bank or government agency.
- Scripting the Call: Attackers prepare a script tailored to the chosen impersonation. This script will typically involve a fabricated scenario designed to create urgency or fear, prompting the victim to take action.
2. Initiating the Call:
- The Contact: The visher makes a phone call to the targeted victim’s number. The caller might sound professional and courteous, further enhancing the illusion of legitimacy.
3. Building Trust and Urgency:
- The Pitch: The visher launches into their pre-written script, explaining a fabricated issue requiring immediate attention. This could involve a compromised account, suspicious activity, an overdue payment, or a technical problem.
- Emotional Manipulation: The attacker might use scare tactics, threats of legal action, or appeals to authority to pressure the victim into cooperating.
- Creating a False Sense of Security: Often, vishers will offer seemingly helpful solutions, further solidifying their trustworthiness in the victim’s eyes.
4. Extracting Information:
- The Ask: Once trust and urgency are established, the visher directly asks for sensitive information. This may include account numbers, passwords, Social Security numbers, or one-time verification codes.
- Alternative Tactics: In some cases, vishers might direct victims to fraudulent websites or trick them into downloading malware disguised as legitimate software needed to resolve the non-existent issue.
5. Concluding the Call:
- Ending the Interaction: Once they have the information they need, attackers will typically end the call abruptly, leaving the victim with no time to question the legitimacy of the interaction.
What Is the Difference Between Vishing and Phishing?
While both vishing and phishing aim to steal personal information, they differ in the methods they employ. Here’s a breakdown of the key distinctions:
- Delivery Method: Vishing attacks rely on voice calls or voicemails to impersonate trusted entities. Phishing scams, on the other hand, use electronic communication like emails, text messages (smishing), or social media messages to deliver their deceptive messages.
- Sense of Urgency: Vishing attacks often create a sense of urgency or panic through phone calls, pressuring victims into acting quickly without thinking critically. Phishing emails might also create a sense of urgency, but they typically rely on deceptive tactics like fake deadlines or limited-time offers.
- Interaction: Vishing scams involve direct interaction between the attacker and the victim. Phishing attacks are generally one-sided, with the attacker sending emails or messages and hoping the victim clicks on a malicious link or discloses information unknowingly.
- Technical Sophistication: Phishing scams can involve sophisticated techniques to create convincing emails and fraudulent websites. Vishing attacks, on the other hand, often rely on social engineering tactics and the human element of trust to manipulate victims.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | Vishing | Phishing |
| Delivery Method | Voice Calls, Voicemails | Emails, Text Messages, Social Media |
| Interaction | Direct | One-Sided |
| Urgency | High | Can be High or Low |
| Technical Sophistication | Lower | Can be High |
Most Common Vishing Attacks
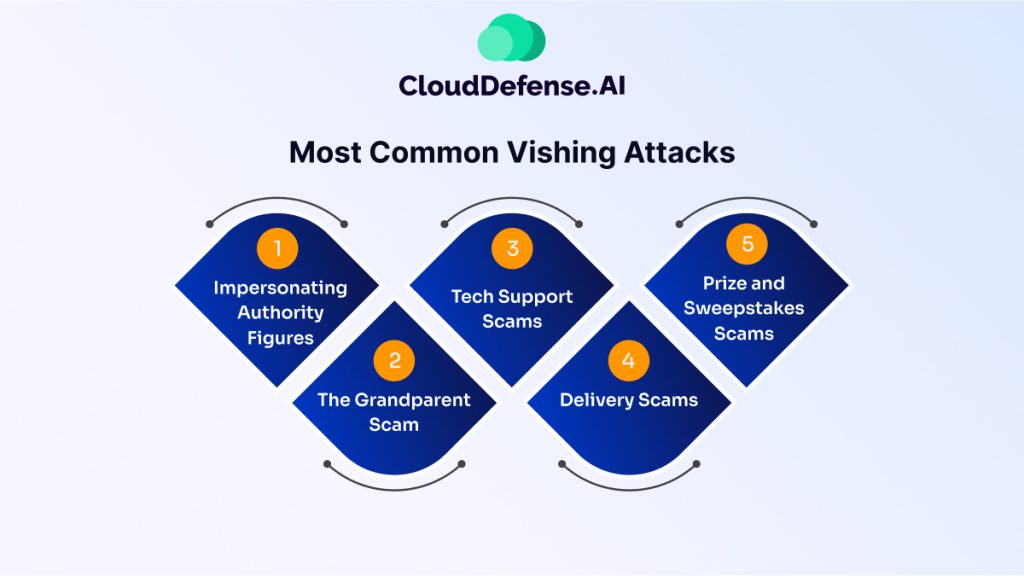
Vishing scams come in many flavors, but some themes pop up more frequently than others. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common vishing attacks:
- Impersonating Authority Figures: This is a classic tactic. Attackers might pretend to be from your bank, credit card company, the IRS, or even a tech support provider affiliated with a well-known company like Microsoft. They’ll claim there’s a problem with your account, suspicious activity, or an urgent issue requiring immediate attention.
- The Grandparent Scam: This preys on the emotions and vulnerabilities of elderly individuals. Scammers call, posing as a grandchild in trouble, often claiming to be arrested or needing money for an emergency. They pressure the victim to send money quickly, often through untraceable methods.
- Tech Support Scams: These attacks involve callers claiming to be from a tech support company, like Microsoft or Apple. They’ll warn you of a virus or security threat on your computer and offer to fix it remotely. However, their real goal is to trick you into downloading malware or granting them access to your device to steal personal information or financial data.
- Delivery Scams: Vishers might call pretending to be a delivery company informing you of a missed package or an issue with an upcoming delivery. They’ll often pressure you to confirm your address or verify payment details, which they can then misuse.
- Prize and Sweepstakes Scams: Be wary of unsolicited calls congratulating you on winning a prize or lottery. These are often attempts to get you to share personal information or pay “processing fees” for a non-existent reward.
Don’t Get Hooked! How to Identify and Prevent a Vishing Attack
Vishing scams can be tricky, but by staying alert and recognizing the warning signs, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim. Here are some key tips to help you identify a vishing attack:
1. Be Wary of Unsolicited Calls: Especially if the caller claims to represent a bank, government agency, or tech support company you haven’t recently contacted. Legitimate organizations rarely initiate contact through unexpected phone calls.
2. Question Caller ID: Don’t trust caller ID alone. Spoofing technology can make it appear as if the call is coming from a legitimate source.
3. Listen for Red Flags: Be cautious of callers who:
- Create a sense of urgency or panic.
- Use scare tactics or threats to pressure you into action.
- Offer “too-good-to-be-true” deals or solutions.
- Sounds unprofessional or has poor grammar.
4. Never Give Out Personal Information Over the Phone: Legitimate organizations won’t ask for sensitive information like passwords or Social Security numbers via phone.
5. Verify Information Independently: If the caller claims to be from your bank or another trusted entity, hang up and call them back using a publicly listed phone number, not the one provided by the caller.
6. Don’t Click on Links or Download Attachments: These could be attempts to install malware on your device.
7. Take Your Time: A legitimate company will understand if you need time to verify their identity or research the issue before taking any action.
8. If Unsure, End the Call: It’s always better to err on the side of caution. If the call feels suspicious, simply hang up and report it to the legitimate organization the caller claimed to represent.
Here are some additional tips to help you identify a vishing attack:
- Do not respond to the caller’s questions.
- Hang up the phone immediately.
- Verify the legitimacy of the call. If the caller claims to be from your bank or another organization, look up the company’s phone number on their official website and call them directly to inquire about the issue.
- Report the vishing attempt. You can report vishing attacks to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) at https://reportfraud.ftc.gov/
Being aware of these red flags and taking appropriate action, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to a vishing scam.
Damage Control: Steps to Recover from a Vishing Attack
Unfortunately, even the most cautious among us can fall victim to a vishing attack. If you suspect you’ve been tricked by a visher, here are some crucial steps to take to minimize the damage:
1. Stop the Bleeding: Immediately hang up the phone if you’re still in contact with the visher. Don’t engage with them further.
2. Assess the Situation: Take a moment to breathe and analyze what information you might have revealed. This could include passwords, account numbers, Social Security numbers, or one-time verification codes.
3. Secure Your Accounts: If you gave out any account login credentials, act swiftly:
- Change Passwords: For any accounts where you revealed passwords, change them immediately using a strong, unique password for each account. Don’t reuse old passwords. A password manager can be a helpful tool for creating and storing strong passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): If available, activate two-factor authentication (2FA) on your accounts. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification code in addition to your password when logging in.
4. Contact Your Financial Institutions: If you suspect your financial information has been compromised, contact your bank or credit card company immediately. Report the incident and inquire about any suspicious activity or unauthorized transactions. They might recommend freezing or canceling your accounts and issuing new ones.
5. Monitor Your Accounts: Keep a close eye on your bank statements and credit card reports for any unauthorized activity in the coming weeks and months. Report any suspicious transactions to your financial institution promptly.
6. Report the Vishing Attempt: Consider reporting the vishing attempt to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC)This helps authorities track vishing scams and potentially prevent others from falling victim.
7. Learn from the Experience: Reflect on how the vishing attack unfolded and what red flags you might have missed. This awareness will help you stay even more vigilant in the future.
Wrapping Up: Stay Secure, Stay Vigilant
Vishing attacks are a cunning threat, evolving alongside our increasing reliance on technology. But by understanding the tactics scammers employ, the red flags to watch out for, and the steps to take if you suspect a scam, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim.
While vishing scams target individuals, businesses are susceptible to cyberattacks as well. Cloud-based security solutions can play a vital role in protecting your organization’s data and applications across complex multi-cloud environments.
CloudDefense.AI offers robust cloud and application security solutions designed to safeguard your valuable information from ever reaching the wrong hands. We don’t analyze call patterns or personal information, but we focus on providing a comprehensive security shield for your cloud infrastructure.
Book a FREE demo with CloudDefense.AI today and see how our advanced solutions can empower your organization to stay ahead of cyber threats. With CloudDefense.AI on your side, you can have peace of mind knowing your valuable information is protected.







