With the growing complexity of securing both cloud and on-premises environments, organizations face a challenging decision when choosing between security solutions like CIEM and PAM.
CIEM vs PAM each address critical aspects of access control but focus on different areas. CIEM specializes in managing cloud identities and entitlements to secure cloud resources, while PAM focuses on securing privileged accounts and access across all IT systems.
This blog will explore the differences between CIEM vs PAM, their key capabilities, and how they complement an organization’s security infrastructure.
What is CIEM?
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) is a security solution designed to manage and secure cloud identities and their corresponding entitlements or permissions.
In cloud environments, identity and access management (IAM) plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive resources. CIEM specifically focuses on ensuring that the right users and services have the appropriate access to cloud infrastructure resources.
The core purpose of CIEM is to mitigate risks associated with over-permissioned identities, prevent privilege escalation, and reduce the chances of misconfigurations in the cloud environment that could lead to security breaches or data loss.
Key Features of CIEM
- Granular Policy Control: CIEM tools provide the ability to define and manage entitlements and access at a granular level, allowing organizations to establish permissions and roles with precision.
- Comprehensive Visibility: Offering visibility into all entities and their entitlements across the cloud environment, CIEM solutions help in proper access management by providing insights into users, devices, clients, services, and applications accessing cloud resources.
- Automated Compliance Checks: CIEM solutions automate the process of checking cloud configurations against industry regulatory requirements, ensuring that organizations remain compliant with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
- Continuous Monitoring and Reporting: CIEM tools continuously monitor user access and entitlements, offering real-time adjustments to permissions to ensure compliance with the principle of least privilege.
- Recommendations for Security Best Practices: CIEM tools offer tailored recommendations to help organizations implement security best practices specific to their cloud setups, enhancing overall security posture.
Benefits of CIEM
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) offers several advantages for organizations managing cloud environments:
- Enhanced Security Posture: By enforcing the principle of least privilege, CIEM ensures that digital identities have only the necessary access to critical cloud resources, reducing potential attack surfaces.
- Reduced Risk of Over-Permission: CIEM continuously monitors cloud entitlements to identify and eliminate unnecessary or excessive access permissions, mitigating the risk of insider threats and privilege misuse.
- Improved Visibility and Control: CIEM provides comprehensive visibility into identities, resources, and permissions across cloud environments, enabling organizations to manage and secure their cloud infrastructure effectively.
- Automated Entitlement Reviews and Continuous Monitoring: CIEM automates the process of reviewing and adjusting entitlements, ensuring that access permissions remain appropriate over time and continuously monitoring for potential vulnerabilities.
What is PAM?
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a cybersecurity strategy focused on securing and managing access to critical systems and resources by users with elevated privileges, such as administrators and superusers.
The core purpose of PAM is to reduce the risk of insider threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access by providing organizations with the means to control, monitor, and secure the access of privileged accounts across the IT infrastructure.
PAM is essential in environments where privileged users have access to sensitive systems, data, and configurations that could potentially be exploited if not properly controlled.
Key Features of PAM
- Credential Vaulting: PAM solutions securely store privileged credentials, such as administrator passwords or API keys, in an encrypted vault. This eliminates manual credential management, reducing the risk of accidental exposure or unauthorized access. Vaults are access-controlled, ensuring only authorized users can retrieve credentials.
- Session Recording and Monitoring: PAM tools record and monitor privileged user activities during sessions, enabling organizations to track any malicious or inappropriate actions. This provides a forensic trail for auditing, compliance, and investigation purposes. Real-time monitoring allows security teams to detect suspicious behavior instantly.
- Access Controls for Privileged Users: Strict access controls ensure that only authorized users can access critical systems. PAM solutions implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), time-based access restrictions, and role-based access controls (RBAC), enforcing the principle of least privilege. Users are granted only the permissions necessary for their role.
- Password Rotation and Management: PAM automates privileged password rotation, ensuring regular updates and reducing the risk of credential theft or misuse. This helps maintain secure password hygiene and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
- Audit and Compliance Reporting: PAM provides detailed logs of privileged user activity, which is crucial for auditing and compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS, ensuring accountability and transparency in privileged access management.
Benefits of PAM
PAM offers several key benefits for organizations:
- Minimized Risk of Insider Threats and Data Breaches: PAM helps control and monitor privileged accounts, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
- Tightened Control Over Privileged Accounts: PAM solutions enforce strict access controls, ensuring that only authorized users can access critical systems and sensitive data.
- Secure and Auditable Access for Admin Users: PAM provides secure access to privileged accounts and maintains detailed logs of user activities, facilitating auditing and compliance efforts.
- Simplified Compliance with Security Regulations: By managing and monitoring privileged access, PAM assists organizations in meeting regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
Key Differences Between CIEM and PAM
When comparing Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) and Privileged Access Management (PAM), it’s important to recognize that while both tools address security concerns related to access control, they serve different purposes and focus on distinct aspects of an organization’s infrastructure. Below are the key differences between CIEM vs PAM:
Scope of Access Control
- CIEM: Focuses on cloud-specific environments, managing cloud identities, permissions, and entitlements to prevent unintended privileged access through complex interrelationships across cloud resources.
- PAM: Manages privileged access across both cloud and on-premise environments, focusing on securing admin accounts and credentials but lacks the ability to analyze cloud-specific permissions or connections.
Types of Entitlements/Permissions Managed
- CIEM: Manages cloud-related entitlements, roles, and permissions to ensure proper access control and prevent privilege escalation in cloud environments.
- PAM: Secures privileged accounts, admin credentials, and sensitive system access, focusing on controlling elevated access across all IT resources.
Target Audience
- CIEM: Aimed at cloud architects, cloud security teams, and DevOps professionals responsible for managing cloud infrastructure and entitlements.
- PAM: Designed for IT security teams, system administrators, and compliance officers tasked with securing privileged accounts across the IT infrastructure.
Comparison Table
Here’s a comparison table for CIEM vs PAM:
| Feature | CIEM (Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management) | PAM (Privileged Access Management) |
| Primary Focus | Manages cloud-specific identities, permissions, and entitlements | Manages privileged accounts and credentials across all environments |
| Scope | Cloud resources and infrastructure | On-premise and cloud systems |
| Access Control | Prevents unauthorized access by managing cloud entitlements and roles | Controls access to critical systems and resources for privileged users |
| Type of Permissions Managed | Cloud entitlements, roles, and permissions | Privileged account credentials (e.g., admin passwords) |
| Target Audience | Cloud architects, cloud security teams, DevOps | IT security teams, system admins, compliance officers |
| Entitlement Reviews | Automated reviews of cloud entitlements | Manual or automated management of privileged access |
| Visibility | Provides detailed visibility into cloud access and permissions | Monitors privileged user activities and sessions |
| Session Monitoring | Limited to cloud configurations and permissions | Records and monitors sessions of privileged users in real-time |
| Password Management | Focused on cloud entitlements rather than password management | Manages password rotation and vaulting for privileged accounts |
| Compliance | Ensures compliance with cloud-specific security practices | Ensures compliance with industry regulations for privileged access |
Both CIEM and PAM play important roles in security but serve distinct purposes: CIEM focuses on cloud entitlements and preventing cloud-specific privilege escalation, while PAM secures privileged access across the entire IT infrastructure, including on-premise and cloud environments.
When to Use CIEM vs PAM
Both CIEM and PAM are essential security tools, but their applications differ based on an organization’s infrastructure and risk profile.
CIEM Use Cases: Securing Cloud-Native Environments
CIEM is designed for organizations operating in cloud-first or multi-cloud environments that need deep visibility and control over identities, roles, and entitlements across cloud platforms. It is beneficial when:
- Managing Cloud Access Complexity: Cloud environments operate with thousands of identities—human and machine—each with different permissions. CIEM continuously monitors and governs these entitlements to prevent excessive or unnecessary privileges.
- Preventing Privilege Escalation Risks: Attackers often exploit misconfigured cloud permissions to escalate privileges and gain unauthorized access. CIEM proactively identifies risky access paths, helping security teams eliminate unintended privilege chains.
- Ensuring Least-Privilege Access: CIEM enforces just-in-time (JIT) and least-privilege access policies, automatically adjusting permissions as needed while ensuring no unnecessary access lingers.
- Achieving Cloud Compliance & Security Governance: For organizations needing to comply with SOC 2, NIST, ISO 27001, or cloud security best practices, CIEM helps maintain continuous complianoptimizing cloud entitlements.
PAM Use Cases: Protecting Privileged Accounts
PAM is essential for organizations that need to secure privileged access to critical systems, sensitive data, and administrative accounts across on-premise, hybrid, and cloud environments. PAM is the right solution when:
- Controlling Administrative and High-Risk Accounts: Enterprises need to secure admin, root, and service accounts, ensuring that only authorized personnel access these credentials. PAM enforces multi-factor authentication (MFA) and session controls for these privileged users.
- Securing Credential Storage & Preventing Theft: PAM solutions provide secure vaulting, automated password rotation, and just-in-time access to privileged credentials, reducing the risk of credential-based attacks.
- Auditing Privileged Sessions: Organizations with strict compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR) use PAM to record, monitor, and audit privileged user activities, ensuring accountability and detecting unauthorized actions.
- Reducing Insider Threat Risks: PAM prevents excessive access by limiting privileged users to only what they need, mitigating risks posed by insider threats or compromised admin credentials.
Choosing the Right Solution
- Use CIEM if your primary challenge is securing cloud entitlements, enforcing least privilege, and preventing lateral movement in cloud environments.
- Use PAM if your focus is securing privileged accounts, managing credentials, and ensuring only authorized users access sensitive systems.
For a comprehensive access security strategy, organizations should integrate CIEM for cloud security and PAM for privileged access control, ensuring complete protection across their IT infrastructure.
Integrating CIEM and PAM for a One-Stop Security Solution
Integrating CIEM and PAM creates a strong, multi-layered security framework that addresses both cloud-specific entitlements and overarching privileged access controls. This integration ensures oversight and protection of an organization’s critical assets.
Benefits of Integration
By integrating CIEM and PAM, organizations can achieve:
- Unified Access Management: A cohesive system that manages both cloud-specific entitlements and traditional privileged accounts, reducing administrative silos and enhancing security posture.
- Enhanced Security Monitoring: Correlating data from CIEM and PAM provides a comprehensive view of user activities, enabling the detection of anomalous behaviors that may indicate security threats.
- Simplified Compliance: Consolidated reporting and auditing capabilities simplify adherence to regulatory requirements by providing a holistic view of access controls and user activities.
Integrating Third-Party PAM with CloudDefense.AI
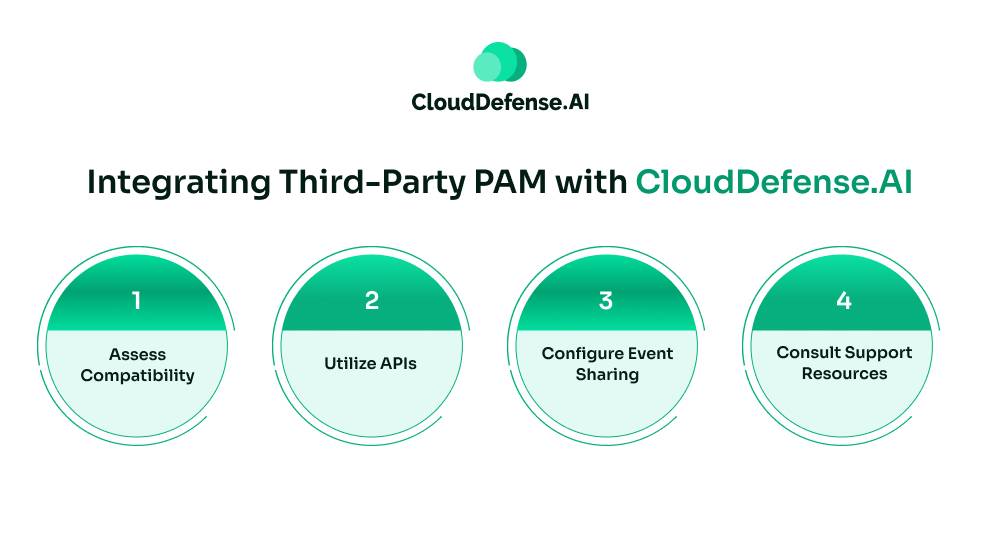
CloudDefense.AI offers a suite of security solutions, including CIEM, designed to integrate smoothly with various platforms. Even though the platform is designed to seamlessly integrate with all the existing security and infrastructure tools, the third-party PAM integration requires a systematic approach.
To achieve integration between a third-party PAM solution and CloudDefense.AI:
- Assess Compatibility: Review the PAM solution’s integration capabilities, such as API support or webhook functionalities, to ensure it can communicate effectively with CloudDefense.AI.
- Utilize APIs: Use CloudDefense.AI’s APIs to facilitate data exchange between the CIEM module and the PAM system, enabling synchronized access controls and unified monitoring.
- Configure Event Sharing: To enhance real-time threat detection and response, set up mechanisms for sharing security events and logs between both systems.
- Consult Support Resources: Engage with CloudDefense.AI’s support team or refer to their integration guides to obtain detailed instructions customized to your specific PAM solution.
By strategically integrating CIEM and PAM, organizations can establish a complete privileged access management system. It will defend both cloud-native and traditional IT resources, ensuring protection against more complex security threats. Book a free demo now to witness the power of CloudDefense.AI CIEM.







