In today’s modern software development, where speed and security go hand-in-hand, application security (AppSec) is no longer just a feature. AppSec has become a necessary foundation of every organization’s security strategy.
As developers write code, especially through AI-code editors, it creates a possibility of introducing vulnerabilities in the codebase. To address these vulnerabilities, organizations have armed themselves with automated scanning tools like SAST, DAST, SCA, and others.
Despite being effective, these tools have overwhelmed the security and development team with a serious challenge: false positives. These false positives in AppSec scanning are more than just noise. It is a serious concern that not only wastes valuable time of teams but also leads to fatigue and delays response to real threats.
So, how does an organization reduce false positives in appsec scanning? A strategic approach can help an organization overcome this obstacle. This field guide will outline those approaches and how organizations can utilize advanced tools to get real alerts.
The High Impact of False Positives
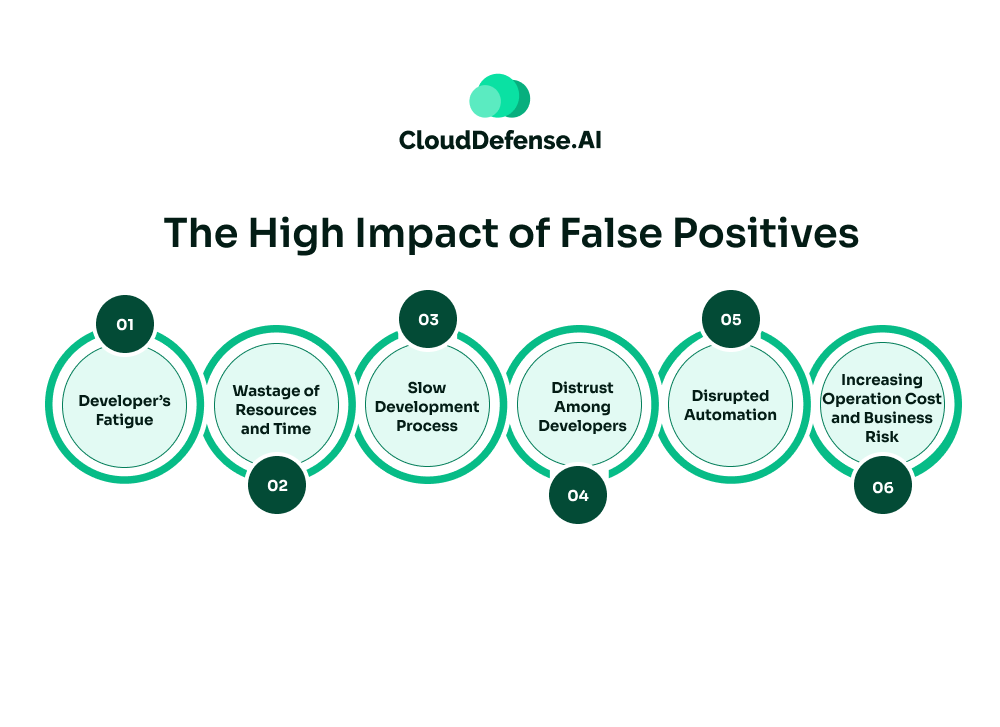
Organizations running AppSec scanning often consider false positives as harmless alerts. But in reality, they are the hidden tax.
False positives serve as a serious operational bottleneck that slowly drains the organization’s resources and lessens the incident response time of the AppSec team:
- Developer’s Fatigue: One of the biggest concerns of false positives is developer fatigue. Development teams are overwhelmed by hundreds of security alerts daily, and they have to sift through every one of them. It not only leads to burnout but also causes frustration and a culture of ignoring high-impact alerts. According to a study by Lokalise, 56% of employees are affected by tool fatigue, especially false alerts.
- Wastage of Resources and Time: Security teams have to spend hours reviewing and triaging security alerts, which ultimately turn out to be false positives. As a result, a lot of time is wasted, which could have been invested in fixing genuine vulnerabilities and building application features.
- Slow Development Process: When automated AppSec scanning generates a heap of false positives, security teams have to manually triage them. It creates a roadblock in the CI/CD pipeline, causing the development process to slow down and reduce agility. Most importantly, it also creates friction between the DevOps and AppSec teams.
- Distrust Among Developers: When the AppSec scanning consistently generates false positives daily, developers start distrusting the tool. It creates a dangerous habit where developers assume most of the alerts are false positives, causing them to overlook many critical vulnerabilities.
- Disrupted Automation: Excessive noise through automated AppSec scanning also disrupts the complete automation process. It forces the AppSec team to resort to manual, which ultimately leads to a delay in the release cycle.
- Increasing Operation Cost and Business Risk: High false positives also have a huge impact on the ROI of an organization’s security investment. Consistent manual triage causes additional work hours in the payroll system, affecting the ROI on the security tool. Moreover, delayed response to critical vulnerabilities also makes the business prone to compliance issues and regulatory fines.
Primary Causes Behind False Positives in AppSec Scanning
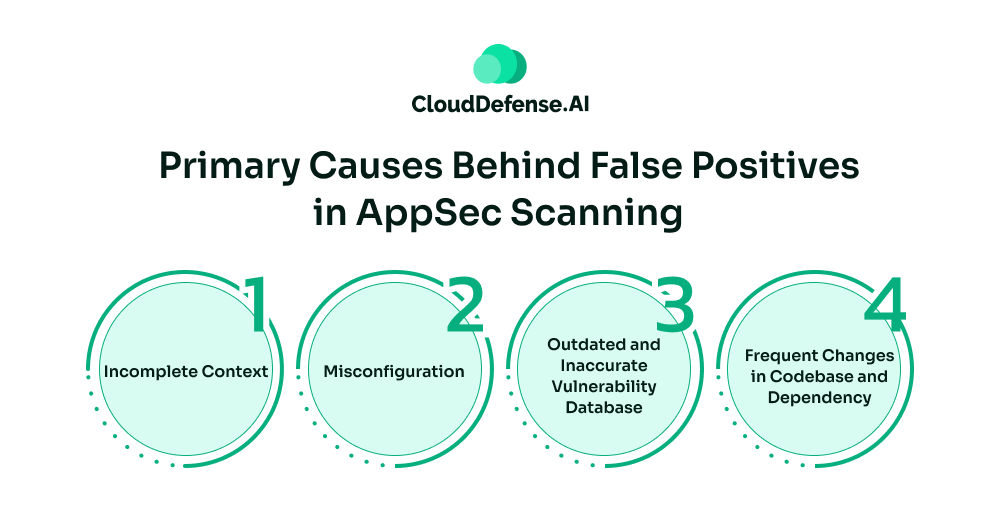
False positives are a bane to all developers’ productivity.
But why do they arise?
They arise due to a number of factors which include:
- Incomplete Context: Many AppSec scanning tools scan a code or any segment without understanding the context in the application. It causes the scanning tool to falsely identify a vulnerable code. When the scanner does not have full access to the application, the lack of context makes it misidentify safe code segments as a threat.
- Misconfiguration: When the tool is poorly calibrated or misconfigured, it generates a huge amount of false positives. Another reason that causes the scanner to generate false alarms is when they are set to high sensitivity or a generic ruleset.
- Outdated and Inaccurate Vulnerability Database: If the scanner is not updated with the recent changes in the database, it can cause the scanner to create alerts for previously fixed vulnerable code. Inaccurate vulnerability databases often stem from late patches.
- Frequent Changes in Codebase and Dependency: When developers frequently change the codebases and dependencies, it increases the number of false alarms. Since the scanner doesn’t have real-time knowledge of the changes, it causes the tool to falsely identify a code as a security threat.
A Field Guide to Reduce False Positives in Security Scanning
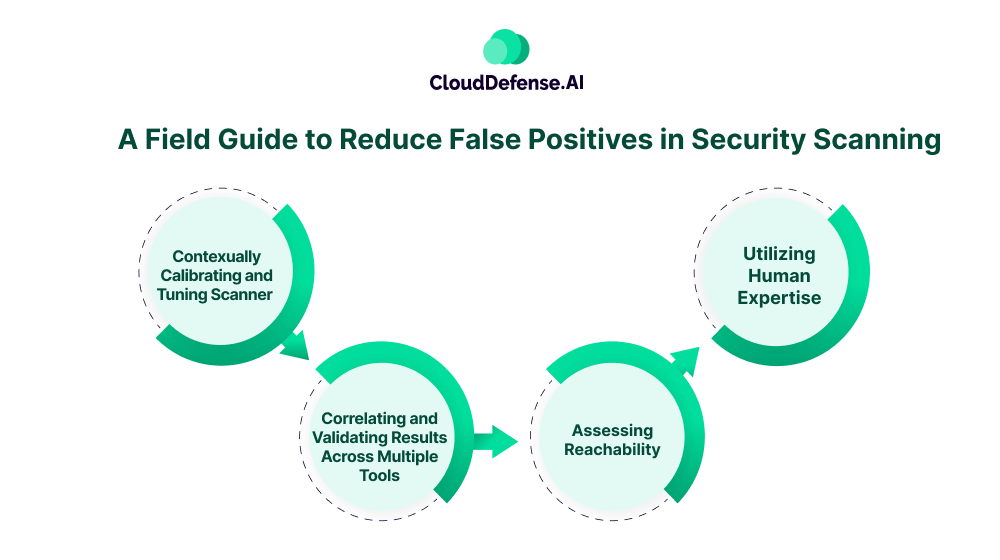
Reducing false positives during is not a straightforward task. Organisations need a comprehensive strategy that combines security scanning with modern technology to reduce SAST false positives. Here is a comprehensive guide that can help organizations:
Contexually Calibrating and Tuning Scanner
All AppSec scanning tools come with a default configuration that covers all the possible scenarios in the application, causing high false positives. Organizations need to calibrate and tune the scanner according to their application. To optimize it, security teams need to:
- Contextually Configure the Tool: When using a security scanning tool, an organization should calibrate and tune it according to the framework and security context of the application. It should be optimized meticulously so that it involves vulnerability scans that matches the application’s configuration.
- Customized Rule Set: It is vital that teams work on implementing a customized rule set that is relevant to the tech stack, safe coding standards, regulatory requirements, and native functions. The rules should also consider the acceptable deviations that will ensure SAST noise reduction.
- Tuning the Target: Organizations should work on tuning their AppSec scanning process on vital parts of the application. For example, security teams can tune the focus of scanning towards code changes, code embedded with sensitive data, and others.
Correlating and Validating Results Across Multiple Tools
When it comes to application scanning, teams utilize multiple tools to scan different aspects of the application. Organizations must leverage an orchestration platform to integrate findings from different tools to correlate and validate the results.
- Correlating SAST and DAST: SAST provides security professionals with findings regarding source code flaws, while DAST identifies runtime exploitability. By correlating the findings of both the AppSec tool, the team can validate whether a particular vulnerability is exploitable or not.
- Utilizing IAST for Real-Time Context: Interactive Application Security Testing or IAST serves as a great tool to uncover vulnerabilities. It introduces agents to monitor behavior and data flow, providing real-time feedback on vulnerabilities. It can be utilized to validate AppSec scanning findings in real-time and reduce false positives in security scanning.
- Discarding Duplicates: Using an orchestration platform, AppSec teams can discard all the duplicate findings to minimize the false positives. After discarding all the findings can be cross-referenced with an updated threat intelligence, ensuring minimum false positives.
Assessing Reachability
All the vulnerabilities that are uncovered during AppSec scanning have different reachability. Security professionals need to assess the reachability of each finding to identify which vulnerabilities attackers can exploit.
- Reachability Analysis: It is vital to perform reachability analysis of all the findings from SAST and DAST. Based on the reachability aspect of each finding, AppSec teams can focus their effort on vulnerabilities that have reachability from malicious sources. It can drastically reduce the false positives and highlight true flaws.
- Dead Code Expulsion:Dead code serves as one of the key reasons behind high false as these findings are no longer executable. Organizations can leverage specialized tools that can detect and eliminate dead code segments like non-executable code or functions.
Utilizing Human Expertise
Although automation has taken over AppSec scanning, human expertise is indispensable. Human intervention during AppSec scanning will help the organization to uncover high-risk issues that an automated scan can miss.
- Manual Code Assessment: In conjunction with AppSec scanning, it is vital for an organization to assign the responsibility of manual code review to DevSec teams. Even though development and security teams are the most expensive resources, they can help an organization identify complex and nuanced vulnerabilities.
Instead of using security experts as filters, they can be leveraged for building a robust AppSec program and reducing false positives in security scanning. Developers can provide actionable context on all the security findings to improve accuracy. - Integrating Feedback: While implementing manual code review, organizations need to integrate the feedback of developers and security teams. It will be helpful for future references when the team comes across similar vulnerabilities. Moreover, automating the feedback loop will help in improving the detection capability of scanning and refining the AI engine.
QINA Clarity: AI-Driven Approach to Reduce SAST False Positives
AI-driven tools have brought a revolution in how organizations perform AppSec scanning while minimizing false positives. AI-powered SAST tools like QINA Clarity AI have been the key driver that enables organizations to go past traditional pattern-matching approaches.
Being an AI-driven SAST, it utilizes contextual analysis, behavioural analysis, and adaptive learning to accurately identify all types of threats. Most importantly, it is powered by Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Large Language Models. This enables the tool to understand the intent and flow of the code.
QINA Clarity 4-Stage AI SAST Pipeline
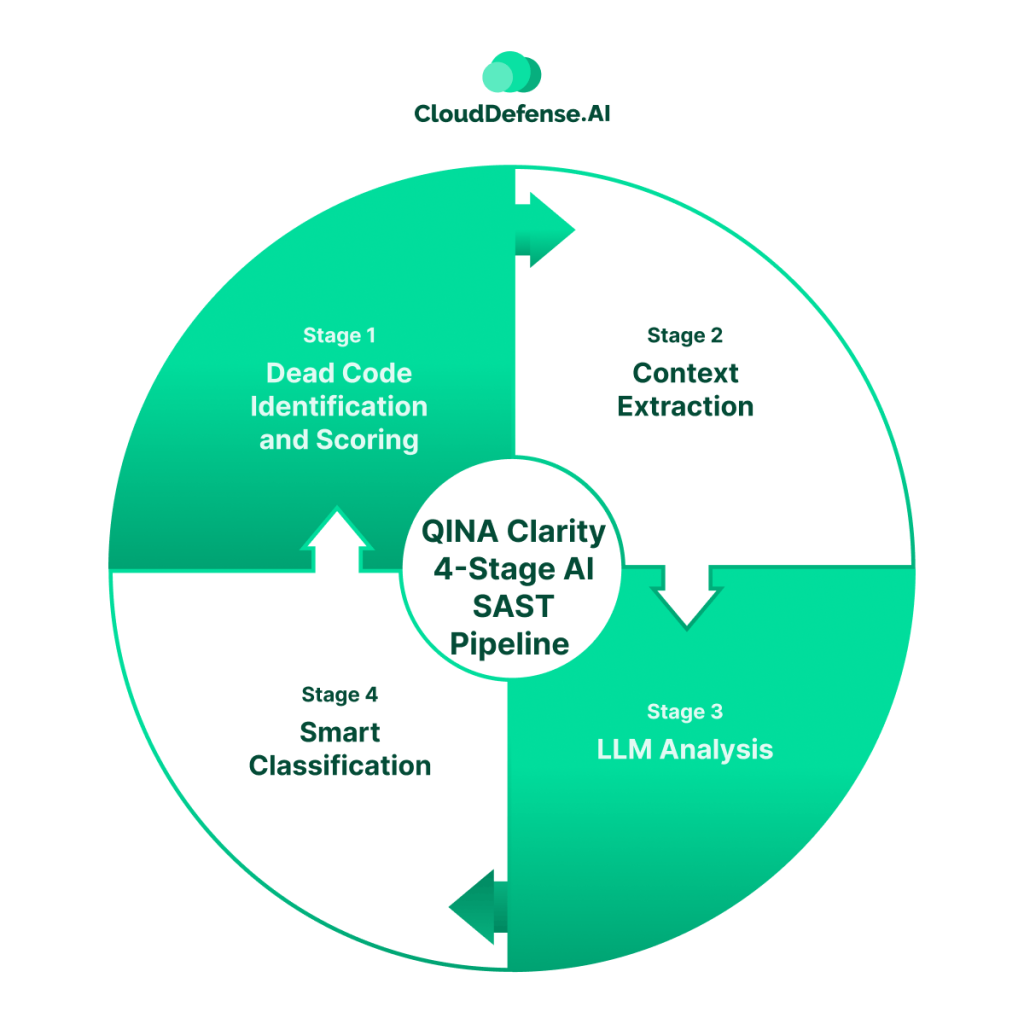
QINA Clarity takes an intelligent approach that analyzes code changes and provides feedback in real-time. This process utilizes intelligent 4-stage analysis to ensure SAST noise reduction:
- Stage 1: Dead Code Identification and Scoring: QINA Clarity puts all the security findings for dead code identification. It performs static analysis for code reachability and scores them accordingly.
- Stage 2: Context Extraction: Then, it puts all the reachable findings along with the surrounding code to understand the context. All the findings are put through data and control flow analysis to extract contextual data.
- Stage 3: LLM Analysis: In this stage, all the contextual data, reachable codes, and known vulnerability patterns are put to the test. The LLM reasoning process takes place that helps in estimating the business impact of the and exploitable path of the security findings. It provides a detailed vulnerability assessment along with reasons and a remediation guide.
- Stage 4: Smart Classification: It takes all the LLM reasoning detailing and reachable codes into context in this stage. An intelligent triage is carried out, where it segregates security findings in Must Fix, Good to Fix, and False Positives categories.
In this way, it reduces false positives in security scanning while providing teams with actionable and prioritised vulnerability reports.
Bottom Line
The issue with false positives might not fade out easily during AppSec scanning. However, by moving rigid-rule-based scanning and taking a comprehensive approach, organizations can reduce false positives in security scanning.
Modern organization requires a robust AppSec scanning strategy where they need to find the right and high-impact flaws and remediate them quickly. AI-driven tools like QINA Clarity are helping organizations to achieve it and reduce SAST false positives.
The main goal of every organisation is to adopt a context-aware and intelligent AppSec program that will provide clear and actionable alerts to developers. Leaders, by adopting AI-powered tools, can eliminate all the noise and help teams focus on alerts that really matter.







