What is Ransomware-as-a-Service?
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) is a cybercrime business model where ransomware developers provide their malicious software to other cybercriminals, known as affiliates.
These affiliates use the ransomware to execute their own attacks, often targeting organizations to extort money by encrypting their data and demanding payment for decryption.
RaaS has gained considerable popularity among cybercriminals because it lowers the technical barrier to entry, enabling even individuals with minimal hacking expertise to launch complex attacks.
This model benefits both parties: affiliates can profit from their extortion campaigns without needing to develop their own malware, while ransomware developers earn a share of the profits without directly engaging in the attacks.
The rise of RaaS has fueled the spread of infamous ransomware strains like LockBit and BlackBasta, making ransomware a persistent and a major threat for everyone!
How does RaaS work?
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) functions like a dark mirror to legitimate software services, offering a business model that makes ransomware attacks accessible even to those with little to no technical expertise. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Sign-Up and Payment
Just like subscribing to any software service, potential attackers sign up on RaaS platforms. These platforms often operate on the dark web and offer a variety of pricing options, including:
- One-time licensing fees: A single payment for access to specific ransomware tools.
- Subscription plans: Monthly or annual memberships, commonly paid in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to ensure anonymity.
After payment, the user gains access to a dashboard where they can customize and deploy their ransomware.
Selecting and Customizing Ransomware
Once registered, users can choose from a range of pre-developed ransomware strains. These strains often come with customizable options, such as:
- Setting the ransom amount.
- Personalizing messages to victims.
- Selecting encryption strength or adding timers to increase urgency.
This plug-and-play approach lowers the barrier to entry for would-be attackers.
Launching the Attack
With ransomware selected and configured, attackers distribute it through common methods like:
- Phishing emails: Fraudulent messages designed to trick recipients into downloading the malware.
- Malicious links or attachments: Embedded in emails, social media posts, or websites.
- Exploiting vulnerabilities: Targeting unpatched systems or weak passwords.
Once the malware infects a system, it locks or encrypts the victim’s files, rendering them inaccessible.
Demanding Payment
After encryption, victims receive a ransom note, typically displayed as a pop-up message on their screens. This message includes:
- Instructions on how to pay the ransom (usually in cryptocurrency).
- A deadline to pay before data is permanently destroyed.
- Threats to expose sensitive data if the ransom is not paid.
Support and Troubleshooting
RaaS platforms provide an astonishing level of “customer service” to their affiliates:
- 24/7 support: Help desks and forums where attackers can get advice on deploying attacks.
- Guides and tutorials: Detailed instructions that enable even novices to launch effective ransomware campaigns.
This robust support ecosystem is a key reason why RaaS has become so popular among cybercriminals.
Revenue Sharing
In many cases, RaaS providers operate on a revenue-sharing model:
- The affiliate keeps a percentage of the ransom paid by victims (e.g., 70-80%).
- The remaining portion goes to the RaaS provider as a commission for supplying the tools.
This model incentivizes providers to develop ever more effective ransomware strains.
Why RaaS is So Dangerous?
RaaS’s ease of use and accessibility have democratized ransomware attacks, allowing even low-skill attackers to launch sophisticated cyber threats. The comprehensive support system, combined with lucrative profit-sharing arrangements, has fueled the proliferation of ransomware, making it a dominant and evolving threat in cybersecurity.
By understanding how RaaS works, organizations can better prepare to defend against this growing menace.
Is Ransomware-as-a-Service Legal?
RaaS is unequivocally illegal. Participating in any activities involving ransomware attacks, such as purchasing RaaS kits from the dark web, hacking into networks, stealing, encrypting, and downloading system files, and demanding ransom payments, is strictly forbidden by law.
These actions constitute serious cybercrimes and are punishable by severe legal consequences. Engaging in RaaS facilitates illegal activities and contributes to the growing threat of cybercrime globally, making it a major concern for law enforcement and cybersecurity agencies.
Examples of RaaS
RaaS has become a popular and effective business model for cybercriminals, with some of the most notorious ransomware strains adopting this framework. Here are some prominent examples:
1. Egregor/Maze
Maze was a pioneer in using “double extortion,” stealing data and threatening to release it if the ransom wasn’t paid. Although Maze has ceased operations, its legacy continues through similar strains like Egregor, which also follow the RaaS affiliate model. These strains capitalize on the fear of data exposure to pressure victims into paying ransoms.
2. LockBit
Launched in September 2019, LockBit has quickly established itself in the RaaS market. It targets large enterprises, rapidly encrypting their systems and making it challenging for IT teams to detect and remove the malware before significant damage is done.
3. REvil/Sodinokibi
Known for its virulence, REvil competes with other severe ransomware strains like Ryuk. REvil affiliates often exploit unpatched Citrix and Pulse Secure VPNs to infect systems, using common networking tools that enable data sharing within organizations. Its effectiveness and destructiveness have made REvil a leading name in the ransomware world.
Cybersecurity Challenges of RaaS Attacks
RaaS has significantly lowered the barrier to entry for cybercriminals and increased the volume and sophistication of attacks. Here are some of the primary cybersecurity challenges posed by RaaS.
Fuzzy Attribution of Ransomware Incidents
One of the most significant challenges in combating RaaS is the difficulty in attributing attacks to specific attackers. Under the RaaS model, the developers of the ransomware are often separate from those who carry out the attacks. This separation means that multiple groups can use the same ransomware, leading to a murky attribution landscape. Cybersecurity professionals struggle to definitively link attacks to particular groups, making it harder to profile and apprehend the criminals involved.
Specialization of Cybercriminals
RaaS has facilitated a division of labour within the cybercriminal ecosystem, mirroring trends in the legitimate economy. This specialization allows threat actors to refine their skills and operate more efficiently. Developers can focus on creating increasingly sophisticated malware, while affiliates concentrate on devising effective attack strategies. A third group, known as “access brokers,” also infiltrates networks and sells access points to other attackers. This specialization accelerates the pace of attacks and increases their frequency.
More Resilient Ransomware Threats
RaaS models create a resilient and adaptable threat landscape. By distributing the risk among operators and affiliates, the RaaS ecosystem becomes more strong. Capturing affiliates does not necessarily disrupt the core operators, and affiliates can quickly switch to different ransomware kits if an operator is apprehended. This flexibility makes it challenging to shut down RaaS operations entirely. Additionally, cybercriminals have shown a capacity to reorganize and rebrand to evade law enforcement.
Protecting against RaaS
Preventing RaaS attacks involves an iron-fist approach that targets the root causes and common vectors of ransomware in general. Here are key steps to protect against these pervasive threats.
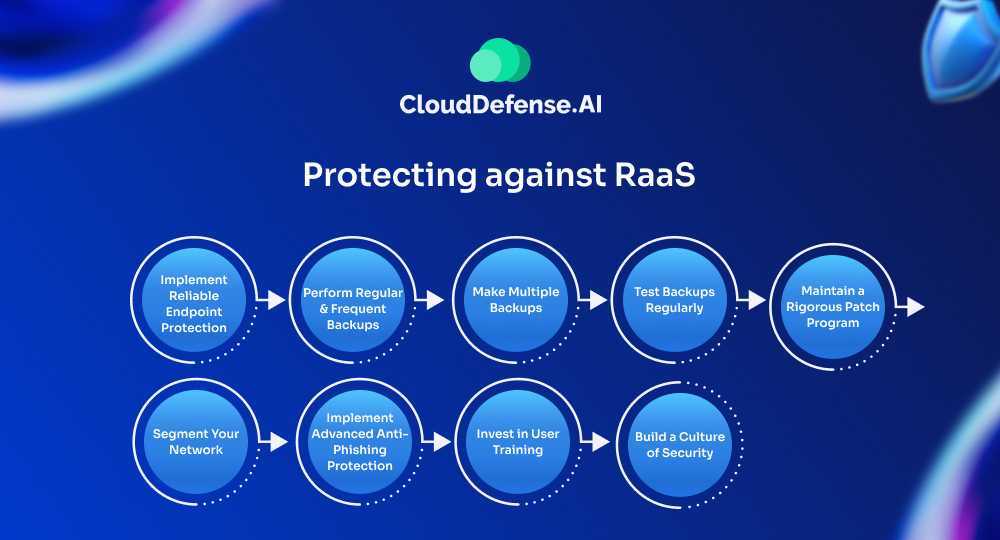
1. Implement Reliable Endpoint Protection
Use modern endpoint protection solutions that use advanced algorithms to detect and neutralize threats automatically. These solutions should work around the clock to provide continuous protection.
2. Perform Regular and Frequent Backups
Regularly back up your data to minimize potential losses. Ideally, backups should occur more frequently than once a week to ensure minimal data loss in the event of an attack. Daily backups can significantly reduce the impact of a ransomware incident.
3. Make Multiple Backups
Store backups on separate devices and in different locations. This redundancy ensures that even if one backup is compromised, others remain secure and accessible.
4. Test Backups Regularly
Regularly test your backups to confirm that data can be successfully retrieved and restored. This step is crucial to ensure your backups are functional and reliable in an emergency.
5. Maintain a Rigorous Patch Program
Apply patches and updates promptly to protect against known and unknown vulnerabilities. A well-maintained patching schedule reduces the risk of exploitation through unpatched software.
6. Segment Your Network
Network segmentation can limit the spread of ransomware within your environment. By isolating critical systems and data, you can prevent the malware from proliferating across your entire network.
7. Implement Advanced Anti-Phishing Protection
Invest in advanced anti-phishing solutions to detect and block phishing attempts, which are a common method for delivering ransomware. These solutions can prevent malicious emails from reaching end users.
8. Invest in User Training
Educate your employees about the dangers of ransomware and the importance of cybersecurity. Regular training sessions can help build a culture of security awareness, making users less likely to fall for phishing scams and other social engineering tactics.
9. Build a Culture of Security
Create an organizational culture that prioritizes security. Encourage employees to report suspicious activities and reinforce the importance of following security protocols.
Utilize CloudDefense.AI for Protection Against RaaS
CloudDefense.AI protects companies from Ransomware-as-a-Service attacks with its cutting-edge threat detection and response solution. By using advanced AI and ML-driven technology, it swiftly identifies and minimizes cyber threats, protecting critical assets.
With unified threat visibility and rapid investigation capabilities, CloudDefense.AI keeps companies ahead of attackers. Its risk-based prioritization and end-to-end visibility features ensure effective incident mitigation. Additionally, advanced attack simulation and API configuration auditing fortify defenses against ransomware.
Companies can rely on CloudDefense.AI to completely protect their data and infrastructure. Book a free demo to experience the platform’s powerful capabilities firsthand.







