What is Cyber Reconnaissance?
Cybersecurity reconnaissance is the process of gathering detailed information about a target system, network, or organization to uncover vulnerabilities or weak points that could be exploited.
Often, the initial phase of a cyberattack enables attackers to map out a target’s infrastructure, defenses, and potential entry points. However, it is also a critical tool for security professionals to identify and address risks, strengthen defenses, and minimize the organization’s external attack surface.
How Does Reconnaissance Work?

Cybersecurity Reconnaissance is the critical first phase of a cyberattack, where attackers meticulously gather intelligence about their target to identify vulnerabilities. This phase often starts with passive methods, such as analyzing open ports and running network services, progressing to active techniques aimed at breaching systems not connected to the public Internet.
Cybersecurity Reconnaissance can span weeks or even months as attackers carefully build a comprehensive profile of the target while evading detection. Ethical hackers and attackers alike follow a systematic approach during reconnaissance, typically involving these seven key steps:
- Gathering preliminary information about the target.
- Mapping the network range to understand its boundaries.
- Identifying active machines within the network.
- Scanning for open ports and access points.
- OS fingerprinting is used to determine the operating system.
- Detecting running services on ports to uncover vulnerabilities.
- Building a detailed network map for future exploitation or defense planning.
When targeting a network, attackers focus on critical aspects, including:
- Operating system platforms to identify potential exploits.
- Active network services that can act as entry points.
- File permissions and configurations that may expose sensitive data.
- User account details to exploit credentials.
- Trust relationships between systems to expand access laterally.
This methodical process enables attackers to craft a precise strategy for intrusion, maximizing their chances of success. Conversely, security professionals can use the same approach to identify weaknesses and strengthen defenses, making reconnaissance a double-edged sword in cybersecurity.
Types of Reconnaissance in Cybersecurity
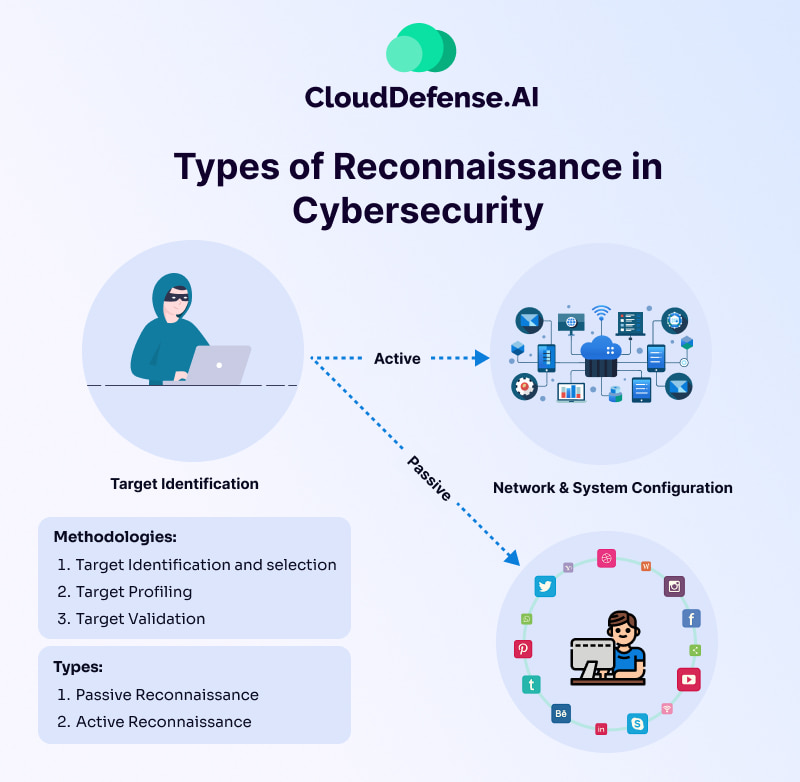
Cybersecurity reconnaissance is carried out in two main types, these are:
- Active Reconnaissance
- Passive Reconnaissance.
Let’s take a deeper look at these two topics and what they mean.
Active Reconnaissance
Active reconnaissance in cybersecurity is the deliberate attempt to gather information on a target by interacting with it actively. Cybercriminals using active reconnaissance employ tools such as automated scanning, manual testing, ping, and netcat to gather info about computer systems. While active reconnaissance is faster and more precise, it also makes more noise and is likelier to be detected within the system.
Port scanning is one of the widely used tactics attackers employ to identify open ports on a computer. These ports serve as entry points for data going in and out. By scanning and analyzing these ports, attackers can identify visible services and potential vulnerabilities.
This process allows them to strategize and pinpoint areas for potential attacks. Active reconnaissance enables threat actors to gather crucial information about a target system, laying the groundwork for further exploitation.
Passive Reconnaissance
Unlike active reconnaissance, passive reconnaissance involves gathering information on a target passively without directly interacting with the system. It employs nonintrusive methods like Wireshark and Shodan to collect information without directly interacting with target systems.
By utilizing tools such as OS fingerprinting, data is harvested discreetly from web searches and free reports, ensuring the target remains unaware. This approach enables the extraction of valuable details, including IP addresses, domain names, email addresses, and software vulnerabilities, through open-source intelligence.
Wireshark, a tool renowned for network traffic analysis, is a potent method used for passive reconnaissance. If a hacker infiltrates a company’s Wi-Fi network, they can discreetly eavesdrop on employee traffic. By analyzing this captured data in Wireshark, the attacker gains invaluable insights, posing a serious threat to the compromised network’s security.
What Is the Difference Between Reconnaissance and Scanning?
Cybersecurity Reconnaissance and scanning are both crucial steps in the early stages of a cyberattack or security assessment, but they serve distinct purposes and involve different techniques.
Reconnaissance
Cybersecurity Reconnaissance is the broader, overarching phase where attackers or ethical hackers collect as much information as possible about the target. This phase can involve both passive and active methods to map out the target’s environment without directly interacting with it (in passive reconnaissance) or by engaging directly with the system (in active reconnaissance). The primary objective is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the target’s infrastructure, defenses, and potential vulnerabilities before deciding on the next steps.
Key activities during reconnaissance may include:
- Gathering domain and IP address information.
- Researching publicly available details through open-source intelligence (OSINT).
- Identifying operating systems, network configurations, and running services.
- Analyzing email addresses, subdomains, and trust relationships.
Cybersecurity Reconnaissance is a preparatory phase that lays the groundwork for further action, such as exploitation or deeper analysis. It often spans a significant timeframe as attackers aim to gather details stealthily and avoid detection.
Scanning
Scanning, on the other hand, is a more focused and technical subset of reconnaissance. This phase involves actively probing the target’s systems to identify open ports, running services, vulnerabilities, and network configurations. Scanning often employs automated tools and scripts to uncover potential entry points or weaknesses that can be exploited.
Unlike cybersecurity reconnaissance, which can be passive or active, scanning is inherently active because it interacts directly with the target system. This makes scanning faster, more precise, and more likely to be detected by security systems.
Key activities during scanning may include:
- Port scanning to identify open or filtered ports.
- Network mapping to understand the architecture and connected devices.
- Service enumeration to detect software and applications running on the system.
- Vulnerability scanning to locate exploitable flaws in software, configurations, or services.
The Relationship Between Reconnaissance and Scanning
Scanning is typically considered part of the active reconnaissance phase but does not encompass the entire effort. While cybersecurity reconnaissance is a broader information-gathering effort, scanning represents a specific technical action focused on uncovering actionable data.
Cybersecurity Reconnaissance is about gathering a complete picture of the target, and scanning is one tool used to fill in the finer details. Together, these processes provide attackers or defenders with the insights needed to launch or thwart an attack.
7 Fundamentals of Reconnaissance
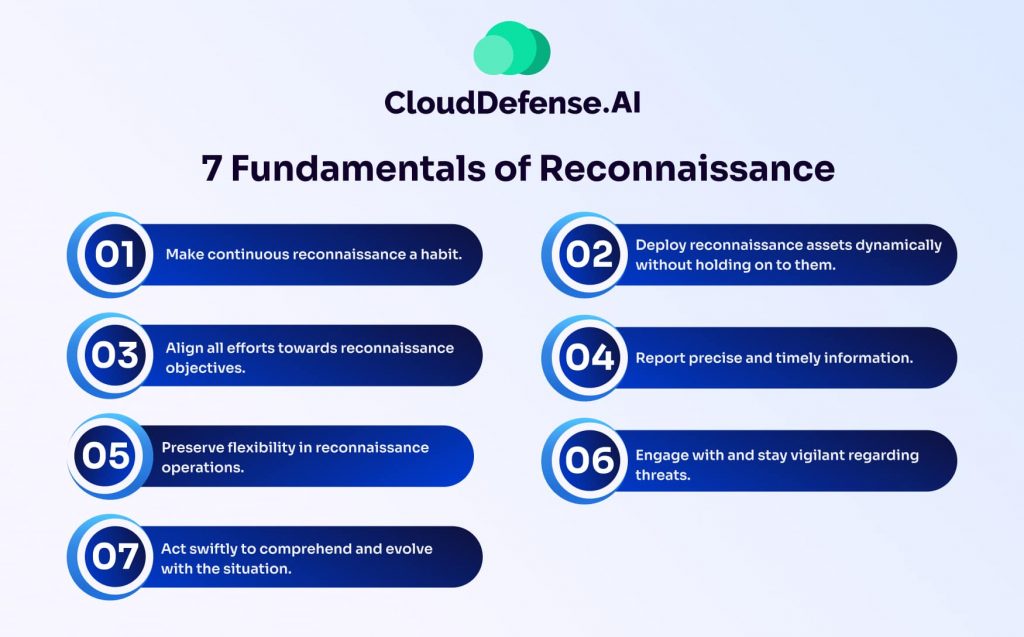
Effective cybersecurity reconnaissance is a cornerstone of both offensive and defensive cybersecurity operations. By following these seven fundamentals, organizations or ethical hackers can ensure a well-structured and effective reconnaissance process:
Make Continuous Reconnaissance a Habit
Cybersecurity Reconnaissance isn’t a one-time activity but an ongoing effort. Continuously gathering information about systems, networks, and environments ensures that any changes or new vulnerabilities are identified in real-time. This proactive approach minimizes blind spots and enhances situational awareness, especially in dynamic threat landscapes.
Deploy Reconnaissance Assets Dynamically
Instead of using static tools or methods, cybersecurity reconnaissance should leverage dynamic assets that adapt to the situation. Tools, strategies, and resources should be deployed strategically and in alignment with the target’s complexity. Retaining flexibility in asset deployment prevents predictable patterns and reduces the likelihood of detection.
Align All Efforts Toward Reconnaissance Objectives
Every reconnaissance effort should have a clear and measurable objective. Whether identifying vulnerabilities, understanding the security posture, or mapping a network, all actions must align with the defined goals. This focus ensures resources aren’t wasted on irrelevant data and that the gathered information directly contributes to the broader mission.
Report Precise and Timely Information
Timeliness is critical in cybersecurity reconnaissance operations. Gathering precise data and reporting it promptly allows decision-makers to act effectively. Delays or inaccuracies can compromise the next steps, whether it’s launching an attack (in offensive operations) or strengthening defenses (in defensive strategies).
Preserve Flexibility in Reconnaissance Operations
The cybersecurity reconnaissance process must remain adaptable. Unexpected challenges, changes in the target’s behavior, or emerging threats may require strategy shifts. Maintaining flexibility ensures that reconnaissance efforts can pivot and respond to evolving situations without compromising the overall mission.
Engage With and Stay Vigilant Regarding Threats
Cybersecurity reconnaissance requires active engagement with the threat landscape. Understanding potential adversaries, monitoring emerging attack vectors, and staying updated on industry trends ensure that reconnaissance operations are relevant and effective. Vigilance is key to detecting subtle changes in the target environment and preventing missed opportunities.
Act Swiftly to Comprehend and Evolve With the Situation
Speed is often a decisive factor in cybersecurity reconnaissance. Rapidly analyzing and interpreting gathered information allows for quicker decision-making and action. Whether defending against an attack or planning one, the ability to evolve with the situation ensures that reconnaissance efforts remain one step ahead of potential threats.
How Businesses Can Protect Themselves From Cybersecurity Reconnaissance?
Cybersecurity reconnaissance is the foundation for many cyberattacks, making it imperative for businesses to guard against them. By adopting a combination of advanced technologies, strict security policies, and proactive monitoring, organizations can effectively mitigate the risks associated with reconnaissance attacks.
Perform Regular Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Assessments
One of the most effective ways businesses can protect themselves is through regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments. Hiring certified security professionals allows organizations to simulate potential reconnaissance activities and uncover weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them. These tests can identify open ports, misconfigured services, and other vulnerabilities, ensuring organizations stay one step ahead.
Use Advanced Scanning Tools
To counter reconnaissance efforts, businesses can deploy passive scanning tools to identify online hosts and detect vulnerabilities. Unlike active scanning tools, passive scanners do not alert attackers, allowing organizations to assess their security posture discreetly. Vulnerability scanners further help in identifying exploitable flaws, which can then be promptly addressed to secure the network.
Use SIEM Solutions
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools are invaluable in detecting and responding to reconnaissance attempts. By analyzing network logs and detecting suspicious patterns, such as repeated connection attempts from the same source IP, SIEM systems provide real-time alerts that help security teams act swiftly to mitigate threats.
Implement Stateful Firewalls
Deploying stateful firewalls is critical for maintaining network security. Stateful firewalls monitor and log traffic connections over time, making it easier to identify and block malicious activities, such as unauthorized port scans or suspicious traffic patterns. Setting rules to log or block multiple connection attempts from the same IP ensures the network remains protected.
Enforce Strong Access Controls
Limiting access to sensitive systems and networks is another crucial step in protecting against reconnaissance attacks. Organizations should enforce strict user authentication protocols, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), to ensure only authorized personnel can access critical assets. Additionally, implementing least privilege policies reduces the risk of attackers gaining unnecessary access.
Monitor DNS and Network Traffic
DNS monitoring can help identify unusual queries or domain lookups, which may indicate an attacker’s reconnaissance efforts. Network traffic monitoring tools can detect anomalies, such as unexpected spikes in requests or connections to suspicious IPs, allowing organizations to respond proactively.
Educate and Train Employees
Employee awareness plays a significant role in safeguarding businesses from reconnaissance attacks. Regular training programs on identifying phishing attempts, suspicious activities, and proper cybersecurity hygiene empower employees to act as the first line of defense against reconnaissance and other forms of attacks.
Align Security Measures With Industry Frameworks
Adopting recognized cybersecurity frameworks like the MITRE ATT&CK Framework helps organizations implement best practices for detecting and mitigating reconnaissance activities. These frameworks provide detailed guidelines on identifying attacker tactics and techniques, allowing businesses to build a robust defense strategy.
Conclusion
Cyber reconnaissance is an essential part of an attacker’s arsenal. It is widely used as the initial step in gathering critical information on a target network that can be used for both defensive and offensive purposes.
As a cybersecurity expert, you can use cyber reconnaissance to your advantage to spot vulnerabilities and other open points in your infrastructure that could harm your company. Reconnaissance in cybersecurity can be a game-changer, allowing us to defend ourselves against cyber attacks by using one of the most widely used offensive tools.







