What is Firewall Configuration?
Firewall configuration is a critical aspect of network security, essential for protecting organizations against data breaches and cyberattacks. It involves setting up and managing firewall policies that control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
A well-configured firewall helps prevent unauthorized access to a network, ensuring that only legitimate traffic is allowed while blocking potential threats. This process typically involves specifying domain names and IP addresses to determine which sources and destinations are permissible.
Firewall policies are customized to the type of network—whether public or private—reflecting the varying security needs and risks associated with each environment. In a public network, stricter rules may be applied to prevent access from unknown sources, while a private network might allow more flexibility for trusted devices and users.
Importance of Basic Firewall Configuration
Basic firewall configuration is crucial for network security, as it determines which traffic can pass through a network boundary based on predefined rules. Properly configured rules are essential to block malicious connections while allowing legitimate business communications. Misconfigurations can either leave a network vulnerable to attacks or disrupt business operations by blocking valid traffic.
An improperly secured firewall can be exploited by cyber threat actors, who can use vulnerabilities to gain access to the protected network and compromise sensitive data. Establishing clear rules, regularly updating configurations, monitoring traffic, and implementing strict access controls are vital steps in maintaining an effective firewall. By prioritizing these practices, organizations can prevent unauthorized access, protect data, and ensure the smooth operation of their network.
Firewall Configuration Challenges
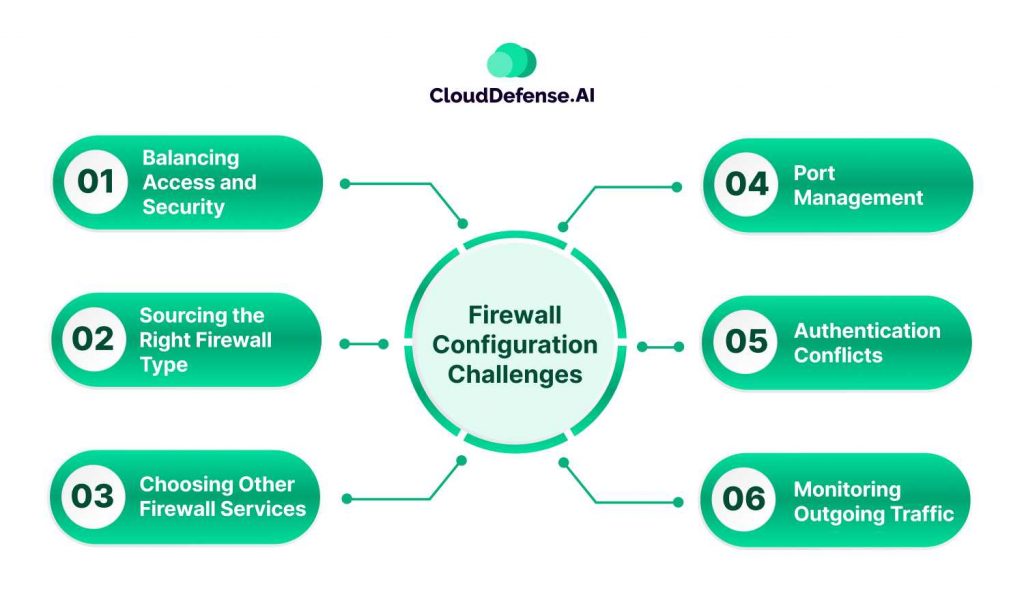
Setting up firewalls is a complex task that involves navigating various challenges to ensure both security and accessibility.
Balancing Access and Security
One significant challenge is balancing access and security. Overly broad firewall settings can leave the network vulnerable to attacks, while excessively tight controls can hinder legitimate users and disrupt business operations. Striking the right balance that aligns with business needs is crucial.
Sourcing the Right Firewall Type
Another challenge is sourcing the appropriate firewall type. Hardware firewalls are ideal for on-premises networks, whereas software firewalls are better suited for individual devices. Selecting a reliable firewall that matches the device mix and, if possible, covers both on-premises and cloud-hosted assets is essential for comprehensive protection.
Choosing Other Firewall Services
Incorporating additional firewall services, such as Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), Network Time Protocol, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), can add complexity. It’s advisable to focus on core firewall settings first and add extras only when they serve a clear security purpose.
Port Management
Port management is another critical area. Open ports can serve as entry points for cyber attackers, so assessing and configuring port settings before the firewall goes live is vital. Unnecessary ports should be disabled, and all active ports should be monitored for signs of intrusion.
Authentication Conflicts
Authentication conflicts pose additional risks. Some non-standard authentication systems can interfere with firewall operations, making even approved traffic risky. Ensuring that multi-factor authentication (MFA) or two-factor authentication (2FA) systems are compatible with firewall interfaces is essential for secure access.
Monitoring Outgoing Traffic
Monitoring outgoing traffic is crucial for total security. While firewalls often focus on incoming traffic, outgoing traffic must also be filtered to prevent data leaks. Regular monitoring for anomalies in outgoing traffic can help detect potential data exfiltration attempts, protecting sensitive information.
How to Configure Firewalls?
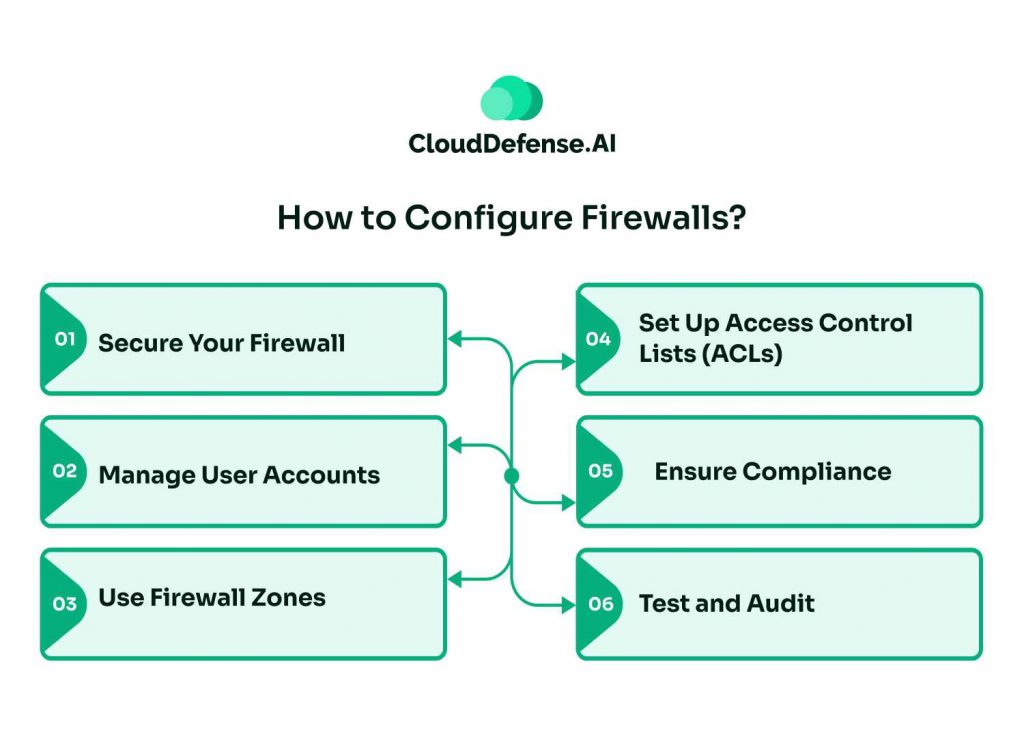
Configuring a firewall is essential for strong network security. This guide outlines key steps, from securing your firewall and managing user accounts to setting up zones and ACLs, ensuring compliance, and conducting thorough testing and auditing to protect against threats.
Secure Your Firewall
Securing your firewall is the first crucial step in the configuration process. Start by changing default passwords to strong, unique ones to prevent unauthorized access. Regularly updating your firewall’s firmware is essential, as outdated software can have vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
Disabling the Simple Network Management Protocol is also important because it lacks support for modern authentication systems, making it easier for attackers to spoof users and gain access. Regulating TCP traffic by restricting the number of open ports minimizes potential entry points for attackers. Finally, ensure all unused ports, such as FTP ports, are closed unless they are specifically needed.
Manage User Accounts
Proper management of user accounts is vital to maintaining firewall security. Avoid using shared accounts for multiple administrators, as they present a tempting target for attackers. Instead, assign individual accounts to each administrator.
Implement RBAC to distribute user privileges and create protection measures, limiting the potential damage if an admin account is compromised. Emphasize strict password hygiene for all admin users, requiring secure passwords that are regularly changed, and ensure that any default passwords are replaced.
Use Firewall Zones
Using firewall zones effectively secures high-value data and assets within your network. Define and group network assets into zones, ensuring that high-value areas are well-protected. Implement demilitarized zones for critical servers, such as email, web, and VPN servers, to allow in-depth monitoring while keeping core resources secure.
When designing your zone structure, balance the complexity of managing multiple zones with the need for security, particularly in smaller organizations. Each zone should have a distinct IP address structure that correctly connects with the appropriate firewall interface.
Set Up Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Access Control Lists are essential for specifying which types of traffic are allowed to enter or exit your network. When configuring ACLs, define rules for source and destination port numbers, allowed IP addresses, and permitted protocols.
Ensure each sub-interface within the firewall system has its own ACL, alongside the core firewall router. Including a “deny all” rule at the end of your ACL ensures that any unapproved traffic is blocked. Additionally, secure firewall administration interfaces by blocking public access and disabling unencrypted management protocols.
Ensure Compliance
Firewall configuration must align with regulatory standards such as PCI-DSS and HIPAA, which mandate strong protection around sensitive data. Ensure your firewall setup includes automated logging of access requests to meet compliance requirements.
Regularly review these logs to confirm that they are accurate and comprehensive. Building your configuration around relevant regulatory standards helps to ensure that all necessary security measures are in place and maintained.
Test and Audit
Testing and auditing are critical components of firewall configuration. Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability scans during the configuration process to identify and address potential weaknesses before the firewall goes live. After deployment, schedule regular audits to inspect firewall logs, review ACLs, and carry out further vulnerability scans.
Document any changes made and store audit information for easy regulatory reporting. Establish procedures for updating firewall firmware, utilizing automation where possible to ensure timely patching, but continue to perform regular security scans to maintain strong protection.
Final Word
Effective firewall configuration is crucial for protecting your network from threats. By securing your firewall, managing user accounts, using firewall zones, setting up ACLs, ensuring regulatory compliance, and conducting rigorous testing and auditing, you establish a strong defense. Consistent maintenance and vigilance are key to adapting to evolving threats and ensuring your firewall remains a strong barrier against cyber attacks.







