What is a Computer Worm Virus?
A computer worm virus is a type of malware that can automatically propagate or make a copy of itself and spread from one device to another.
It is malicious software that self-replicates itself without requiring human intervention, making it one of the most impactful malware. It is like an infection that moves from computer to computer through a network to exploit vulnerabilities in a system or operating system.
How Does a Computer Worm Work?
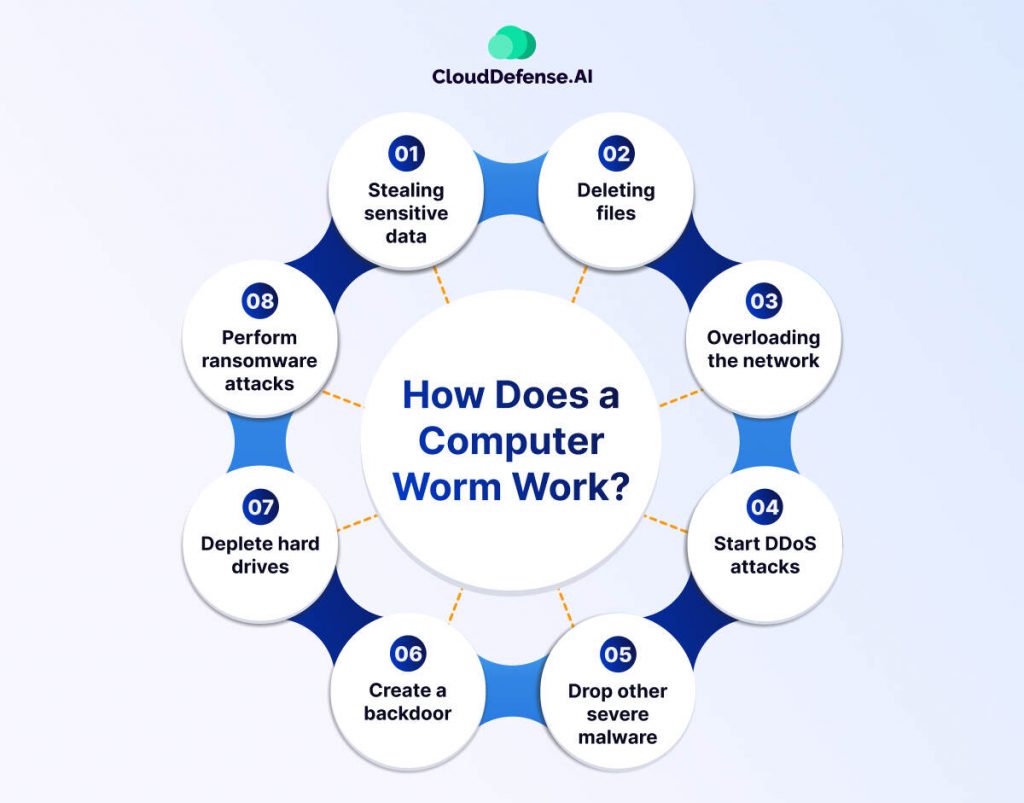
A computer worm virus operates with one primary goal: self-replication and spreading across networks or systems. Its design enables it to propagate autonomously, unlike other malware that often relies on human interaction. Here’s an in-depth look at how worms achieve their objectives:
Infiltration
The worm initiates its lifecycle by exploiting vulnerabilities in a system, such as outdated software, weak passwords, or unpatched security flaws. Attackers often use vectors like malicious email attachments, compromised websites, or infected files shared over a network to plant the worm on a target device.
Replication
Once inside a system, the worm creates multiple copies of itself without altering existing files or requiring user input. This self-replication process ensures its survival and prepares it to infect other devices in the network.
Propagation
A worm’s primary function is to spread to other systems. It scans for connected devices or networks and exploits their vulnerabilities to replicate itself. Worms can use multiple propagation methods, including:
- Email: Sending malicious attachments or links to contact lists.
- File Sharing: Planting itself in shared folders or P2P networks.
- Network Exploits: Using unpatched systems within the same network to infect multiple devices.
Payload Delivery
While some worms exist solely to propagate, others carry a payload that performs malicious actions. These can include:
- Installing backdoors for remote access.
- Encrypting files for ransom (ransomware worms).
- Stealing sensitive data.
- Overloading systems to cause crashes or service disruptions.
Evasion
Advanced worms often include techniques to avoid detection, such as encryption, code obfuscation, or disabling antivirus software. These techniques enable them to remain undetected for more extended periods, maximizing their impact.
Network Disruption
As worms replicate and spread, they consume network bandwidth and system resources, often leading to network slowdowns or crashes. In large-scale attacks, they can overwhelm infrastructure, causing significant operational disruptions.
Continued Propagation
Even after infecting initial targets, worms continue to search for new vulnerabilities and devices to infect. Their autonomous nature ensures ongoing propagation, making them difficult to contain without swift and comprehensive action.
Types of Computer Worms
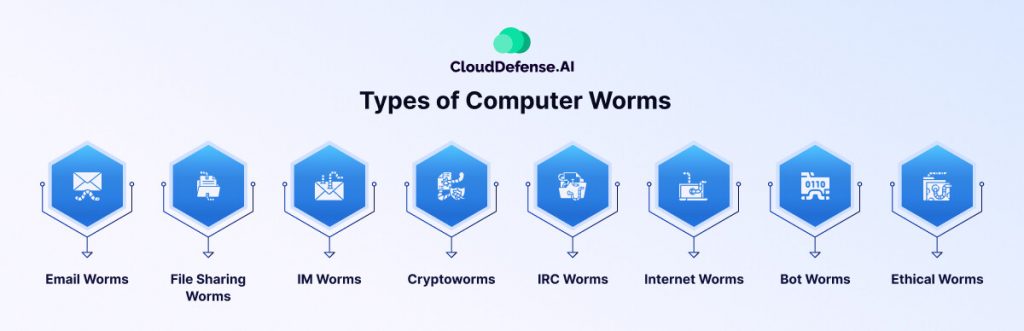
Computer worms are often mistaken as a single type of malware, but they vary based on their method of propagation. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types of computer worms that could threaten your organization:
- Email Worms: Email worms, also known as mass mailer worms, spread by sending malicious attachments or links via email. These worms replicate as executable files or links, tricking users into clicking through phishing or social engineering tactics.
- File-Sharing Worms: File-sharing worms proliferate via peer-to-peer (P2P) networks by creating copies in shared folders. They are often disguised as media files, deceiving users into downloading them. Notable examples include Stuxnet and Phatbot, which have disrupted industries like power utilities and water supplies.
- Instant Messaging (IM) Worms: IM worms target social media platforms and messaging apps by posing as legitimate attachments or links. Once a user clicks, the worm installs itself and spreads through the victim’s contact list, further infecting the network.
- Cryptoworms: Cryptoworms encrypt data on infected systems, rendering files and operations inaccessible. These are often used in ransomware attacks, where attackers demand cryptocurrency payments in exchange for a decryption key.
- IRC Worms: IRC worms specifically target Internet Relay Chat (IRC) networks. They propagate by sending malicious messages within chat rooms or forums, infecting users who interact with them.
- Internet Worms: Internet worms exploit vulnerabilities in poorly secured websites, targeting their servers or organizations. They can also infect users accessing the compromised sites by exploiting web browser flaws.
- Bot Worms: Bot worms are designed to convert infected systems into bots, creating botnets for large-scale DDoS attacks. Conficker, a bot worm, caused widespread damage by infecting thousands of systems in 2003.
- Ethical Worms: Ethical worms are used by security teams to deploy patches across networks. They exploit vulnerabilities listed in CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) to strengthen security proactively.
Each worm type poses unique risks to organizational networks, emphasizing the need for security measures to detect and mitigate these threats.
Most Common Ways a Worm Spreads
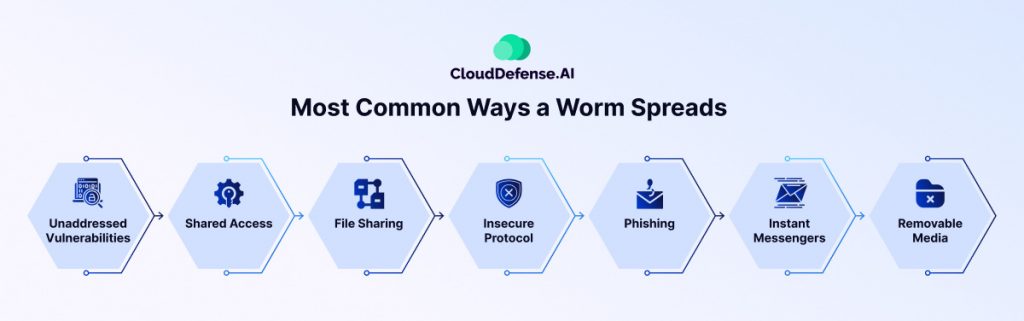
Computer worms are highly adaptable malware designed to propagate autonomously. While their primary objective is self-replication, the methods they use to spread depend on their design and purpose. Here are the most common ways worms infiltrate systems and networks:
Exploiting Unaddressed Vulnerabilities
Worms often target unpatched vulnerabilities in operating systems or applications. These weaknesses allow worms to infiltrate a system and propagate across networks without detection, making unpatched software an open invitation for malicious activity.
Using Shared Access
In many organizations, shared drives and network components create an ideal environment for worms. By exploiting these shared resources, worms spread rapidly to connected devices, capitalizing on network trust and permissions.
File Sharing via P2P Networks
Peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing platforms provide another vector for worm propagation. Worms can embed themselves in shared files and spread to every device that downloads or accesses the infected file.
Abusing Insecure Protocols
Protocols like Telnet or TFTP often use default or no credentials, making them vulnerable. Worms exploit these insecure protocols to move between systems, particularly in poorly secured networks.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing emails remain a popular method for spreading worms. Attackers craft emails with malicious links or attachments, disguising them to appear legitimate. Spear phishing, a targeted version of phishing, is particularly effective, especially in ransomware-based worm attacks.
Using Instant Messengers
Modern attackers increasingly use instant messaging platforms to distribute worms. Links or attachments sent via these platforms can lead to widespread infections as the worm exploits trust among network users.
Infecting via Removable Media
USB drives and external hard drives are common carriers for worms. When connected to an infected system, the worm replicates itself onto the removable media, which can then transfer the infection to any device it is subsequently plugged into.
Why are Worms Dangerous?
Computer worms are among the most destructive forms of malware. They can launch ransomware, DDoS attacks, self-replicate, or install backdoors. Even with efficient antivirus solutions, worms are notoriously difficult to eliminate because they feed on system resources and remain hidden.
Their rapid spread across networks can weaken organizations, consuming significant time and resources during incident response. Even worms without malicious payloads can disrupt operations, requiring extensive efforts to contain and remove them.
Computer Worm vs. Virus
While both worms and viruses replicate, their methods differ. A virus requires human interaction, such as installing or activating a malicious file, to infect a system. On the other hand, worms spread autonomously, needing no host or user action to propagate. This independence makes worms far more efficient and dangerous in infiltrating networks.
Examples of Computer Worms

Computer worms have been present on the internet for decades. The first worm was created in 1971 and was named Creeper. After its introduction, there have been many notable computer worm cases that have caused significant disruptions to businesses and networks. Here are examples of such computer worms:
Morris Worm
Created by Robert Morris in 1988, an MIT graduate, the Morris worm is considered to be the first computer worm introduced that was widely propagated on the internet. This worm targeted vulnerabilities in several UNIX programs, causing them to overload, and it crashed over 60,000 UNIX machines connected to the ARPANET at that time.
Even though Morris didn’t create it with malicious intention, the worm caused heavy financial damage, and it resulted in the first felony conviction under the 1986 Computer Fraud and Abuse Act.
SQL Slammer
Another widespread computer worm that surfaced on the Internet was SQL Slammer, which caused havoc on many devices and networks. In 2003, this worm crashed thousands of routers around the world, launched DoS attacks on different internet hosts and disrupted internet traffic. It spread quickly to 75,000 victim devices and affected them within 10 minutes.
ILOVEYOU Worm
The ILOVEYOU worm is considered one of the most dangerous computer worms. It was created in May 2000 and propagated through emails as a love letter attachment. The attachment was a waste file or script run in instant messaging chat sessions.
Once the victim opened the attachment, the worm sent itself to all the targeted victim’s contacts in Microsoft Outlook. It is estimated that the worm affected more than 50 million PCs within ten days and caused around $15 billion in cost to eliminate them from the PC. The spread wrecked so much havoc that Ford Motor Company had to shut their email service for a brief period.
Mydoom
Released in 2004, Mydoom is one of the fastest-spreading computer worms in history. It mainly targets Windows computers. After it was released on the Internet, it infected millions of systems operating in Windows OS, leading to a probable damage of $38 billion at that time. Mydoom is still an active computer worm that accounts for 1% of the total email worm types present on the Internet.
Stuxnet
Stuxnet is a unique computer worm that was introduced via USB drives around 2010. According to security researchers, it was created by Israel and US intelligence agencies to jeopardize Iranian nuclear weapon production.
Stuxnet exploited vulnerabilities in the Windows operating system of nuclear labs, which caused the nuclear centrifuges to malfunction.
Storm Worm
Storm Worm entered the Internet in 2007 and infected millions of systems through email. It baited millions of users by providing the subject line “230 dead as storm batters Europe,” and users clicked on the link to learn about the cause of the European weather disaster.
WannaCry
WannaCry is a deadly ransomware attack that started in May 2017 and used computer worms to infect Windows systems by encrypting files on the user’s drive. It was a widespread attack that targeted millions of computers throughout the world. This worm also targets systems of large organizations that belong to banks, hospitals, logistics, and others.
The worm encrypts the system’s files and then contacts the owner to pay a ransom to obtain the keys to decrypt them. The Lazarus Group from North Korea is estimated to have initiated the attack, which caused massive financial loss.
Signs of a Worm Virus Infection
Detecting worm infections can be tricky since they often blend in, but these key signs can help:
- Sluggish Performance: Increased CPU usage or reduced bandwidth without explanation.
- Missing Files: Files or folders disappearing unexpectedly.
- System Instability: Frequent crashes, freezing, or erratic program behavior.
- Unauthorized Actions: Emails are sent automatically, or apps/websites launch by themselves.
- Unfamiliar Files: Unknown programs or files appearing on your device.
- Strange Behavior: Odd messages, images, or sounds from your system.
- Browser Irregularities: Slow performance or unexpected sites in your history.
- Security Alerts: Warnings from antivirus software or the operating system.
How to Remove Computer Worms?
Eliminating worms, especially in networked systems, requires swift action:
- Deep Scan: Use additional malware removal tools to ensure no remnants are left behind.
- Prepare Tools: Use external storage to download necessary updates and tools.
- Detect Worms: Identify infected systems through signs or scanning tools.
- Contain the Worm: Disconnect infected devices from the network and internet.
- Scan and Clean: Update antivirus software and scan all connected systems to isolate and remove worms.
Best Practices to Prevent Worm Virus Infections
Computer worms are among the most destructive types of malware, capable of wreaking havoc on individual devices and entire networks. Prevention is crucial to avoid the significant damage they can cause. Here are practical and essential steps to secure your systems:
Use Endpoint Protection Solutions
An advanced endpoint protection solution, such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), is your first line of defense. It actively monitors for unusual activities, quickly identifies threats like worms, and eliminates them before they can spread.
Secure Your Email
Email is one of the primary ways worms infiltrate systems. Attackers often use malicious attachments or links to trick you into unknowingly spreading malware. By implementing email security tools, you can block harmful emails before they even reach your inbox.
Use DNS Filtering
DNS filtering works like a gatekeeper, blocking access to malicious websites and preventing you from clicking harmful links. It adds an extra layer of protection, ensuring that one wrong click doesn’t compromise your system.
Strengthen Firewall Rules
Firewalls are essential for managing what comes in and out of your network. Worms often exploit open ports or unused protocols to sneak in. Setting up strict firewall rules helps block these entry points and keeps unauthorized traffic out.
Disable Insecure Protocols
Protocols like Telnet and TFTP are outdated and easy targets for attackers. Turn off or close these vulnerabilities, disable them and replace default credentials with strong, unique passwords.
Implement Patch Management
Outdated software is a worm’s playground. Regularly updating your systems and applying patches ensures that known vulnerabilities are fixed before attackers can exploit them. Effective patch management identifies high-priority updates and applies them quickly.
Use Strong Passwords
Weak or default passwords make it easy for worms to spread across your network. Always use complex, unique passwords for routers and devices. Avoid using the factory-default credentials during setup, as these are widely known and easily exploited.
Be Cautious with File Sharing
Peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing networks are a hotspot for malware. Avoid downloading files from unverified or free sites unless you are confident in their safety. Stick to trusted sources to minimize the risk of downloading infected files.
How CloudDefense.AI Can Help?
Attackers often exploit system vulnerabilities or infect endpoint devices to launch and spread computer worms. Once inside, these worms self-replicate and rapidly spread across networks, posing a significant threat to your security posture.
CloudDefense.AI provides a suite of solutions designed to protect against computer worms and other forms of malware. With tools like threat detection, data protection powered by AI-SPM, and ransomware defense, you can fortify your systems against attacks before they occur.
These solutions offer advanced security features that precisely identify worms and prevent data encryption or unauthorized modifications. Whether you’re protecting individual systems or entire networks, CloudDefense.AI ensures reliable defense.
Take control of your cybersecurity. Sign up for a free live demo to see how CloudDefense.AI can transform your protection strategy and keep your systems safe.







