Definition — What is a Cloud Security Framework?
A Cloud Security Framework is a set of policies, tools, and best practices designed to protect cloud environments from security risks and ensure compliance with regulations. It provides a structured approach to safeguarding data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud.
So, what does a Cloud Security Framework guarantee:
- Establishes clear guidelines to manage security risks in cloud-based systems.
- Defines access controls to prevent unauthorized data exposure or breaches.
- Ensures compliance with industry standards and government regulations.
- Facilitates monitoring and detection of suspicious activities in real-time.
- Simplifies the process of responding to and recovering from security incidents.
- Supports the secure integration of cloud services across hybrid environments.
A robust Cloud Security Framework isn’t just a checklist—it’s an operational necessity. It aligns security measures with your organization’s goals, making sure your cloud assets are resilient, reliable, and future-ready.
Cloud Compliance vs. Cloud Governance Frameworks
Let’s be clear: cloud compliance and cloud governance frameworks are not the same, but both are absolutely critical. They have different goals, different focuses, and if you don’t understand this, your cloud strategy is going to be a mess.
Cloud Compliance Frameworks are about following the rules—laws, regulations, standards. We’re talking about things like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001. These frameworks make sure your systems check every box, keep data safe, and avoid penalties. Compliance is about proving you’re doing the bare minimum required to stay legal. It’s basic but necessary.
Cloud Governance Frameworks, on the other hand, are a much bigger deal. Governance is about control. It’s about making sure your cloud operations run efficiently and align with what your business needs. Policies, responsibilities, resource allocation—it’s all about keeping things organized and focused. Governance isn’t reactive like compliance; it’s strategic, forward-thinking, and powerful.
Key Differences:
- Purpose: Compliance is about avoiding fines. Governance is about running your cloud environment like a winner.
- Focus: Compliance cares about meeting external requirements. Governance looks inward, focusing on how your business manages its resources and policies.
- Action: Compliance reacts to regulations. Governance takes charge, setting the rules and driving success.
Comparing both, you will need both. Compliance keeps you out of trouble, sure. But governance? Governance sets you apart. It’s the framework that drives efficiency, innovation, and dominance in the cloud.
Benefits of a Cloud Security Framework
A cloud security framework is not just another fancy set of guidelines—it’s the backbone of a strong and reliable cloud environment. Without it, your business is exposed, and let’s face it, no one wants that. Let’s break down why having a solid cloud security framework is a game-changer:
1. Data Protection
Your data is your business’s most valuable asset. A cloud security framework ensures your data is encrypted, backed up, and accessible only to the right people. It prevents unauthorized access, theft, and leaks. In today’s world, if you’re not protecting your data, you’re losing.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Governments and industries have rules—lots of them. Whether it’s GDPR, HIPAA, or something else, a good cloud security framework helps you meet these regulations. You avoid fines, lawsuits, and the negative press that comes with being caught off guard. Compliance isn’t optional; it’s mandatory, and a framework keeps you in check.
3. Improved Trust and Reputation
When customers know their data is secure with you, they trust you. Trust leads to loyalty, and loyalty leads to growth. A security framework doesn’t just protect; it builds confidence. Businesses that prioritize security always stand out.
4. Operational Efficiency
A well-structured framework simplifies security management. With clear policies, automated monitoring, and streamlined processes, your team spends less time putting out fires and more time focusing on what matters—growing your business.
5. Risk Mitigation
Cyberattacks are everywhere, but a strong cloud security framework helps you detect and neutralize threats before they cause damage. It’s about being prepared, staying ahead, and ensuring your operations run smoothly no matter what.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
As your business grows, so do your cloud needs. A robust security framework adapts to your growth, ensuring consistent protection. Whether you’re adding users, applications, or data, you can scale without worrying about vulnerabilities.
7. Cost Savings
Security breaches cost money—a lot of it. By preventing incidents, a cloud security framework saves you from expensive recovery efforts, legal fees, and downtime. It’s an investment that pays off big.
Common Elements of Cloud Security Frameworks
When you’re talking about cloud security, there are a few key areas that make or break your protection. These are the elements that any solid cloud security framework should have in place to keep things running smoothly, safely, and efficiently.
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
This is about control—who gets in and what they can do once they’re inside. IAM systems ensure that only authorized users can access your cloud services and sensitive data. It’s not just about usernames and passwords; it involves multi-factor authentication, role-based access, and strong authentication protocols. You need to keep track of who’s accessing what, when, and why. No exceptions.
2. Data Protection
Your data is everything. You can’t afford to leave it exposed. Data protection covers encryption, secure storage, and backup systems. Encryption ensures that data is unreadable to anyone who doesn’t have the decryption key, whether it’s in transit or stored. You also need secure storage solutions that protect data even if there’s a breach. Backup strategies are equally important—you need to be able to restore critical data if anything goes wrong.
3. Threat Detection and Response
You can’t just sit back and hope everything stays secure. Continuous monitoring for suspicious activities is key. This means real-time tracking of everything that happens in your cloud environment—whether it’s a small anomaly or something more serious. When a threat is detected, you need to respond immediately. That’s why having automated alerts, incident response plans, and a team ready to act fast is essential.
4. Compliance Management
Compliance isn’t just a box to check. It’s about making sure you follow the laws and regulations that apply to your industry. Whether it’s GDPR in Europe, HIPAA in healthcare, or ISO 27001 for information security, your cloud framework needs to keep track of these standards and ensure you meet them. Not doing so could lead to fines, lawsuits, or worse. A solid cloud security framework helps you stay compliant without the headache.
5. Shared Responsibility Model
This is where the cloud provider’s role and your role come into play. The shared responsibility model defines who is responsible for what. For example, the cloud provider might be responsible for securing the infrastructure, but you’re in charge of securing your data and how it’s used. This division of responsibilities needs to be crystal clear. You can’t just rely on the provider to handle everything, and they can’t do it all. The framework sets this out, so everyone knows what they’re responsible for.
7 Major Compliance Frameworks to Know in Cloud Security
Here’s an overview of seven major cloud security frameworks commonly used by organizations:
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS targets merchants handling card payments and establishes criteria to protect cardholder data. Compliance requires implementing antivirus software, firewalls, and regular vulnerability assessments. These measures ensure the security and integrity of sensitive payment information, shielding it from potential threats and unauthorized access.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA guarantees the security of sensitive health records overseen by healthcare entities. Compliance requires companies to regularly assess risks and implement risk management policies. These measures uphold the confidentiality and integrity of individuals’ health information, ensuring it remains protected from unauthorized access or breaches.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
GDPR prioritizes the protection of personal data gathered and handled by organizations within the European Union. It establishes fundamental rights, including access, rectification, erasure, and notification in the event of data breaches. Here is a breakdown of all the user rights highlighted under GDPR.
- Right to Access: Individuals have the right to obtain confirmation from organizations about whether their personal data is being processed. They can request access to their personal data and information about how it is being used by the organization.
- Right to Be Informed: Individuals have the right to be informed about the collection and use of their personal data. Organizations must provide clear and transparent information about the purposes of data processing, the categories of data being processed, and any third parties involved.
- Right to Modify: Users have the right to request the correction of inaccurate or incomplete personal data held by organizations. If the data is found to be incorrect or outdated, organizations must promptly update it to ensure its accuracy.
- Right to Erasure (Right to Be Forgotten): Individuals have the right to request the deletion or removal of their personal data when there is no compelling reason for its continued processing. This right enables individuals to have their data erased under specific circumstances, such as when the data is no longer necessary for the purposes for which it was collected.
- Right to Data Portability: Users have the right to receive their personal data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format. They can also request the transfer of their data from one organization to another, without hindrance from the original organization.
- Right to Object: Individuals have the right to object to the processing of their personal data in certain situations, such as direct marketing or processing for purposes of scientific or historical research. Organizations must respect these objections and cease processing the data unless they have legitimate reasons for continuing to do so.
- Right to Restriction of Processing: Users have the right to request the restriction of processing of their personal data under certain circumstances. This right allows individuals to limit the ways in which organizations can use their data while unresolved issues are being addressed.
- Right to Notification of Data Breach: Individuals have the right to be notified without undue delay if their personal data is involved in a data breach that poses a risk to their rights and freedoms. Organizations must inform affected individuals about the nature of the breach, the potential consequences, and any measures taken to mitigate its impact.
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 serves as a global benchmark for information security management systems, applicable across diverse cloud solutions. Emphasizing key aspects such as risk assessment, asset management, access control, incident response, and continuous monitoring, provides a systematic approach to ensuring strong security measures.
Other than ISO 27001, ISO has two other compliance frameworks which include:
- ISO/IEC 27002: Also known as ISO 27002, is a standard that complements ISO/IEC 27001 by providing guidance on implementing specific security controls outlined in ISO 27001. It details best practices for information security management and offers recommendations for protecting sensitive data and mitigating security risks.
- ISO/IEC Technical Report 22678: This technical report provides guidelines for cloud service providers and cloud customers on implementing cloud security policies. It offers insights into various aspects of cloud security, including access control, data protection, and compliance requirements.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework, developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), provides comprehensive guidelines for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity risks. Specifically tailored for cloud environments, it emphasizes the assessment, mitigation, and management of cybersecurity risks.
Here are a few other sub-categories other than the NIST Cybersecurity Framework:
- NIST Special Publication 800-53: NIST 800-53 helps organizations assess and manage security risks effectively, ensuring the protection of sensitive information in the cloud.
- NIST Special Publication 800-144: NIST 800-144 assists organizations in making informed decisions regarding the adoption and use of public cloud services.
- NIST Special Publication 800-171: While primarily focused on protecting controlled unclassified information (CUI) in non-federal systems and organizations, NIST 800-171 includes security requirements relevant to cloud service providers. It outlines specific security controls that organizations must implement to protect CUI stored or processed in cloud environments.
Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls
CIS Controls offer a set of consensus-based regulations aimed at bolstering cybersecurity posture, particularly focusing on securing databases. These controls are divided into two categories: Level 1 and Level 2, catering to organizations with different security requirements. By implementing these controls, organizations can strengthen their defense mechanisms, mitigate risks, and ensure the protection of sensitive data stored in cloud environments.
AWS Well-Architected Framework
The AWS Well-Architected Framework is tailored for AWS users, offering guidelines to design secure, reliable, and cost-effective cloud solutions. It covers five essential pillars:
- Operational excellence
- Security
- Reliability
- Performance Efficiency
- Cost optimization.
By adhering to these pillars, organizations can ensure that their cloud architectures are well-designed, efficiently managed, and resilient to potential threats or disruptions, while also optimizing costs and maximizing performance.
Cloud Security Framework Best Practices
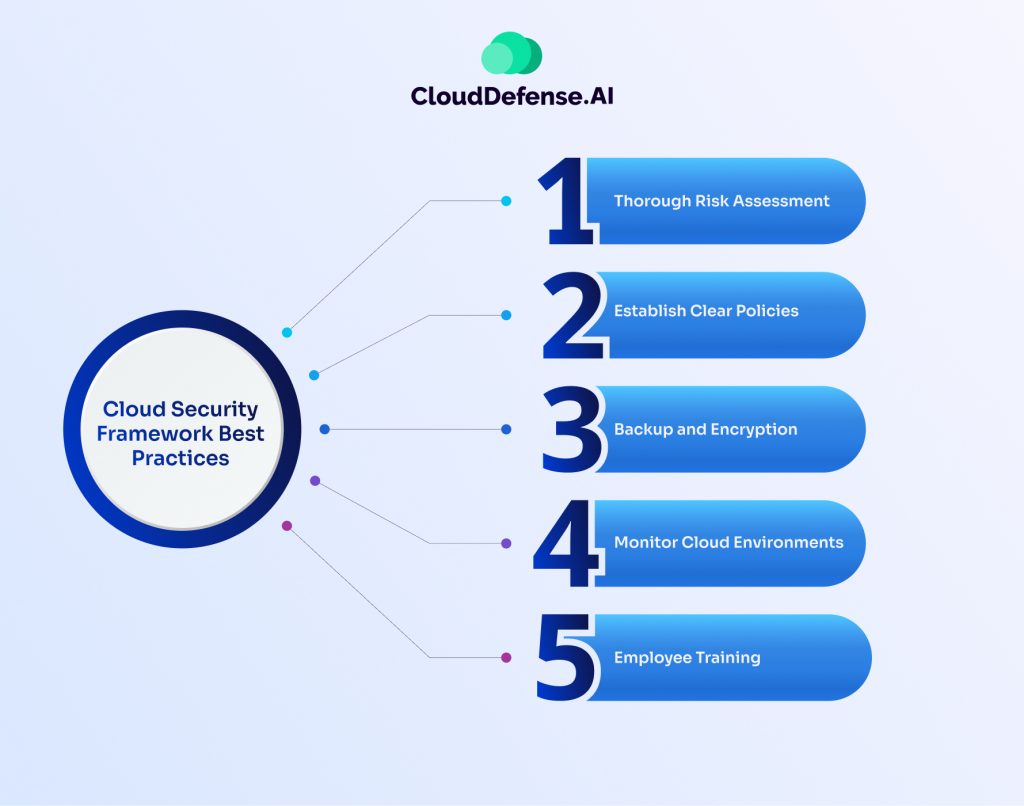
Best practices work as a blessing when it comes to effectively managing cloud frameworks. Here are five best practices for implementing cloud security frameworks:
Thorough Risk Assessment
Before migrating data or workloads to the cloud, conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential security risks. If any unacceptable risks are uncovered, consider adopting a hybrid cloud approach to segregate sensitive processes. This approach allows organizations to maintain control over critical data while leveraging the benefits of cloud services for less sensitive workloads.
Establish Clear Policies
Develop clear policies for sharing information in the cloud, including selecting suitable cloud providers, deployment models, and applications that align with organizational requirements. Perform due diligence on cloud service providers to understand their security practices and internal controls, ensuring compliance with relevant standards such as ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002.
Backup and Encryption
Implement strong backup and encryption mechanisms to protect data stored in the cloud. Ensure that cloud storage settings, such as replication and high availability, are configured appropriately to meet data protection obligations. Consider managing encryption keys independently to mitigate risks associated with relying solely on cloud providers for data security.
Monitor Cloud Environments
Implement cloud security monitoring solutions to collect real-time data from cloud platforms and infrastructure. This enables organizations to detect and respond to potential threats and vulnerabilities promptly. Utilize role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict user privileges and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive cloud resources.
Employee Training
Provide training and education programs to employees to raise awareness about cloud security best practices. Ensure that employees across all departments understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining cloud security. Training should cover topics such as identifying social engineering attempts, adhering to access control policies, and responding to security incidents effectively.
Challenges in Implementing a Cloud Security Framework
Implementing a cloud security framework is not as simple as it sounds. Let’s be honest, businesses face a lot of obstacles, and it’s important to address them head-on. Here are the key challenges organizations face when trying to secure their cloud environments:
1. Complexity of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Cloud environments today are all over the place. Some businesses are running hybrid setups, others are working with multiple cloud providers. Keeping everything secure across these environments is tough. Every platform has its own tools, policies, and requirements. Without proper coordination, you’re looking at a fragmented security system, which is bad—very bad.
2. Evolving Threats
Cyber threats are getting more sophisticated. Hackers are smart, very smart, and they’re always looking for new ways to break in. A static security framework just doesn’t cut it anymore. Businesses need to stay ahead of the game, constantly updating their frameworks to counter these evolving threats.
3. Limited Budgets and Resources
Here’s the truth: many companies don’t have the budget or the manpower to implement a comprehensive security framework. Small businesses, especially, struggle with this. They want top-notch security, but the costs can be overwhelming. Balancing affordability with effectiveness is a big challenge.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Pressure
Compliance is a huge factor. Governments and regulators keep coming up with new rules, and they expect companies to comply. If your security framework isn’t aligned with these requirements, you’re in trouble—big trouble. And staying compliant isn’t a one-time thing. It’s a continuous process, which can be exhausting for organizations.
5. Skill Gaps and Training Needs
Not every organization has a team of cloud security experts. Training employees and finding skilled professionals is a major hurdle. Without the right expertise, even the best framework can fail.
How Can CloudDefense.AI Help Manage Cloud Security Frameworks?
CloudDefense.AI offers a comprehensive solution for managing cloud security frameworks, making it easier for companies to comply with local and international standards. At its core, the platform provides a state-of-the-art multi-cloud compliance management system, enabling organizations to streamline their compliance efforts effectively.
Automatic Assessment Capability
One of the key features of CloudDefense.AI is its automatic assessment capability, which allows businesses to track their compliance progress against various industry standards effortlessly. By analyzing every business resource based on API metadata, the platform provides real-time insights, identifying non-compliant resources and areas that require attention.
Multiple Framework Support
CloudDefense.AI simplifies the compliance process by offering support for over 20 compliance frameworks, including SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, ISO, PCI, and more. This broad coverage ensures that organizations can address a wide range of regulatory requirements from a single platform, saving time and resources.
Custom Policy Creation
The platform also empowers users to create custom policies tailored to their organization’s specific security needs. Whether utilizing existing policy templates or designing custom frameworks from scratch, CloudDefense.AI provides the flexibility to align compliance objectives with internal standards.
Create Detailed Reports
Furthermore, CloudDefense.AI generates real-time reports for security teams and executive summaries for top-level management with just one click. These audit reports, available in PDF format, highlight any compliance violations and suggest improvements to help organizations achieve their goals more efficiently.
CloudDefense.AI offers a centralized solution for managing cloud security frameworks, enabling organizations to maintain compliance, minimize risks, and enhance their overall security posture from a single, user-friendly dashboard.
Want to get hands-on experience on the functionalities of CloudDefense.AI Cloud Security Framework management? Then book a free demo with us right now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the cloud security framework work in cloud computing?
A cloud security framework in cloud computing establishes guidelines and standards for securing data and applications in the cloud. It defines security controls, policies, and procedures to protect against cyber threats and ensure compliance with regulations.
What is the difference between the NIST and CSA cloud security framework?
The NIST cloud security framework, created by a US government agency, offers guidelines for assessing, mitigating, and managing cloud-related risks. In contrast, the CSA framework provides best practices and controls to enhance cloud security posture.
What are cloud security framework examples?
Examples of some common cloud security frameworks include ISO, NIST, GDPR, and PCI DSS. These frameworks offer guidelines and best practices for securing cloud environments and data.







