What is a Trojan Horse?
A Trojan Horse (often called Trojan) is a malware program that is disguised as a legitimate program carrying malicious codes and functionality. These programs are designed in such a way that it might seem it will perform one function but once it gets entry it performs another, malicious function.
Usually, the Trojan Horse is disguised as free software, legitimate advertisement, free music, software patches, external updates or downloads in games and tools containing malicious code.
Besides, many modern Trojan attacks involve social engineering techniques like phishing where they trick users into performing desired actions and enable the program to gain entry. Trojan usually carries malicious code that after gaining access, takes over the system without raising any suspicion to the IT administrator.
Leveraging the Trojan, the attacker can perform a varied type of action: stealing data, exploring files, deleting specific data, monitoring activity and various other functions. Unlike other malware types, Trojan Horse doesn’t self-replicate and they mostly rely on user interaction or social engineering tactics for spreading.
To deliver future payloads to the infected network or system, attackers often use Trojan downloaders or rootkits and stay active to carry out their malicious actions. Unusual network activity or frequent changes in the system are some strong signs of the presence of a Trojan in your network or system.
History of the Trojan Horse
The original story of Trojan Horse stemmed from the Trojan War in Greek Mythology where Greeks used a large wooden horse to trick Troy’s people into getting their army inside the city. In the war, the people of Troy considered the horse as a gift but little did they know Greek Warriors were inside the horse.
Once the horse was pulled inside, the warrior came out at night and enabled the Greek army to get inside the city. Similarly in computing, the Trojan Horse malware came into existence and it was first mentioned in a US Air Force report in 1974 that highlighted vulnerability in systems.
However, it was Ken Thompson who made it popular among everyone while receiving the Turing Award in 1983. During the 1980s era, the use of BBS also boosted the spread of Trojan Horse attacks as BBS enabled users to gain entry into a system through phone lines.
The first Trojan Horse attack that was reported was known as Spy Sheriff and using it attackers infected around 1 million systems around the world. The malware came up as a pop-up ad where it looked like a warning about malicious software in the system. Antivirus and antimalware software weren’t able to detect the Trojan and remove it as it utilized a hidden file in the system to reinstall itself.
Many cybersecurity specialists also claim the Trojan named “Animal” made by computer programmer John Walker was the first of its kind in the computing world. During the 1980s and 1990s Trojan Horse attacks became widely popular due to the rising use of computing among enterprises.
In the late 1980s, PC-Write Trojan wreaked havoc as it entered the system by appearing in a specific program and deleting files on infected systems. In 1999, Remote Access Trojans or RATs came into existence and it allowed attackers to remote access the victim’s system without raising any suspicion.
With time, Trojans evolved into more sophisticated and it is now widely used to carry out advanced malware attacks. Recently in 2021, a banking Trojan called Emotet affected Chilean Bank Consorcio through email and led to the loss of around $2 million.
How do Trojans infect Devices?
Trojans mostly infect devices by impersonating genuine programs and tricking users into downloading or executing them on their devices. When the malicious code gets executed through executable (.exe) files, the malicious program infiltrates the devices and takes over everything.
While most of the Trojan attacks are intended towards PC and enterprise systems, nowadays many attacks are directed towards mobile devices especially endpoints like tablets and smartphones.
In recent times, Mac devices have seen a surge in attacks, especially Apple Macbooks. Trojan doesn’t rely on a particular way to infect a device, rather it utilizes many intuitive ways to gain entry. Here are some common ways:
- When a user downloads a video game, movies, music, paid content or any media file through a pirated site, the Trojan is transferred through the downloadable media.
- Accepting pop content from an untrusted site or without going through the content enables a gateway for a Trojan attack.
- Downloading any attachment, documents or photos without verifying the source or content inside the attachment.
- Opening emails with attachments from unknown sources or sometimes legitimate-looking sources allows Trojan to spread.
- Not verifying the source or without going through user agreement while downloading software.
- When a user doesn’t update or patch their browser, application, or OS, it allows attackers to launch Trojan attacks through social engineering techniques.
- When a user visits a website infected with malicious code, it often paves the path for an attacker to launch a Trojan attack.
- Attackers often exploit unknown software vulnerabilities to launch Trojan attacks and get access to the system.
Attack on Mobile Devices
Apart from desktops and laptops, Trojan attacks also focus on various mobile devices like smartphones, tablets or devices used in endpoints. Like traditional devices, Trojan attacks on mobile devices happen through impersonating legitimate apps or commonly downloaded items.
Users often download applications or files from unsolicited sources and these applications or files are mostly designed to launch Trojan attacks for stealing data.
Once the malware infects the device, it stays undetected until the particular action triggers its functionality. When the malicious code gets activated, the Trojan will carry out its malicious action and depending upon the Trojan type, it will stop its actions.
Common Types of Trojan Malware

The first Trojan Horse came out around the mid-1970s and since then millions of Trojans have come into existence. Trojan horses are designed to perform different types of functions and based on their functionality, they are segregated into different types and they are:
1. Backdoor Trojan
A backdoor Trojan has been designed to open a backdoor for an attacker to gain access and establish secret communication to the attacker’s Command and Control hub. Once the attacker takes control through the backdoor Trojan, the attacker can perform their desired action on the device. These types of Trojans are usually utilized to create a botnet.
2. Remote Access Trojan (RAT)
A remote access Trojan or RAT is a widely popular Trojan type whose main focus is to infiltrate a system and enable an attacker to gain remote access. In some cases, RATs are carried out to allow other malware to be downloaded and deployed on the system according to the intent.
3. Banker Trojan
Banker Trojan is a popular choice among cyber attackers as this type is designed to target banking accounts and information of enterprises and users.
Using various malicious means, banker Trojan gains entry into the system and extracts sensitive financial information about cards, e-payments, online banking, financial mandates, login credentials and various others. Using this information, they can steal money from the account or perform identity theft.
4. Downloader Trojan
Downloader Trojan is a unique Trojan type that acts as a medium and deploys other malicious code especially ransomware or rootkits on the target system. Using this type, different variants of ransomware are distributed by installing the Trojan on the target system and then deploying the desired ransomware.
A downloader Trojan often serves as the first phase of a multi-stage Trojan attack as it enables attackers to install other Trojan types in the system.
5. DDoS Trojan
To disrupt the network of an enterprise for malicious intent, attackers often launch distributed denial-of-service Trojans. Basically in this type, the attacker overwhelms the network or website of an enterprise by sending multiple requests from a network of computers, leading to denial of service.
6. Spyware
Spyware is a special type of Trojan that is mostly utilized by attackers to collect necessary information about users of an infected system. Once the Trojan takes over the system, it continuously monitors the user’s activity and collects information like login credentials, applications they use, keyboard actions and many more.
7. Exploit Trojan
It is designed to target specific programs where this Trojan carries specific code that exploits the vulnerabilities of an application or computer of the target user. The attacker usually takes the help of a phishing attack to deliver the package and then uses the malware to attack the application.
8. Rootkit Trojan
Unlike other types, rootkit Trojan after gaining access takes administrative access to the system and boots along with the OS. It is designed to hide their presence in the system and perform various tasks stealthily.
9. Fake Antivirus Trojan
This type of Trojan disguises itself as legitimate antivirus software that simulates antivirus software’s action and provides fake alerts regarding issues. It is generally used as a ransomware attack where it extorts money from users to remove those fake issues.
10. SMS Trojan
Designed specifically to target mobile devices, this Trojan type infiltrates mobile devices to intercept and send text messages. Cybercriminals often use this Trojan type to gain money by sending texts to premium-rate numbers.
11. Game-Thief Trojan
A game-thief Trojan is mainly used by attackers to steal the account information of online players playing varied types of online games. Once they get access to their gaming account, they use it to perform various other malicious activities.
12. Infostealer Trojan
Infostealer Trojans are deployed by cybercriminals on enterprises’ systems to only steal sensitive information like personal data and login credentials. Besides, it is also used to install other Trojans and prevent any program from detecting its existence.
13. Mailfinder Trojan
With the only motive to extract email addresses, mailfinder Trojan’s main motive is to enter a system through social engineering techniques and harvest all the email addresses stored in it.
14. Ransom Trojan
Ransom Trojan are similar to ransomware where the Trojan jeopardizes the system workflow or locks all the files in the system. The attacker then demands a ransom fee to unlock the access to files or undo the damage from the organization or users.
15. Instant Messaging Trojan
This type of Trojan is specifically designed to infect IM services like AOL instant messaging MSN messenger, Skype, Yahoo Pager and many more. The main motive of this Trojan is to steal the user’s login credentials and use it for malicious purposes.
16. Spy Trojan
Spy Trojan is a specialized type that stealthily hides in the system of a user or enterprise and spies all the activity. From taking screenshots of various instances and keeping track of keyboard actions to logging all the login data, spy Trojan tracks every move a user makes on the system.
17. Notifier Trojan
It is a modern Trojan that has been designed by cyber criminals to send the developer information and the status of the infected system. The information that is sent carries information regarding running services, software, open ports and many others.
18. Proxy Trojan
This type of Trojan enables attackers to get anonymous access to a particular website through a victim’s system. Cybercriminals mostly utilize this type of Trojan to generate and send spam by camouflaging under’s victim’s IP address.
How to Detect a Trojan Virus
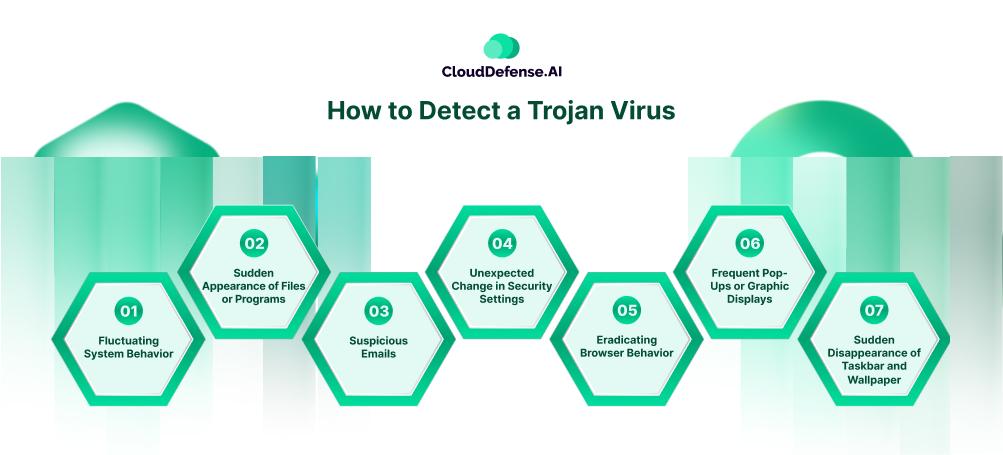
Trojan Horse malware serves as one of the major threats to the organization and it is widely used as a part of APTs. Detecting the Trojans is a challenging task since attackers are evolving with their techniques. Here are some practices and methodologies you can utilize to detect Trojan:
Fluctuating System Behavior
If you notice unexpected slowing down, frequent crashes or erratic behavior of your system, then it is a sign that your system is infected by Trojan. Even if the system is in an idle state, you will notice the hardware resource or network activity is unusually high.
Sudden Appearance of Files or Programs
While using the system, if you come across unfamiliar files or programs in your enterprise’s system, then it could be due to the presence of Trojan installation. Different types of Trojans might install new programs or download new files to carry out their malicious action.
Suspicious Emails
Unfamiliar emails from unknown senders often act as an indicator of a Trojan attack. These unfamiliar emails often come with malicious attachments containing code that when executed will infiltrate the system and networks connected to a device.
Importantly, if your email starts sending spam messages to all the content or specific email addresses with suspicious attachments, then it means that your email has been infected.
Unexpected Change in Security Settings
Once a Trojan gains entry into the system, it might attempt to change the security settings like disabling antivirus and firewall. While going through your system, if you notice such malicious changes that you didn’t authorize then you should take the necessary steps to eliminate the Trojan.
Eradicating Browser Behavior
If you notice any unfamiliar behavior like the browser might consistently redirect to an unknown website or the homepage changes every time you open the browser. The unknown website will usually have pop-ups requesting you download certain software or click on certain offers. Such a situation serves as an indication of a Trojan in the system.
Frequent Pop-Ups or Graphic Displays
While using the system, you might come across mysterious pop-up messages or unfamiliar graphic displays. These pop-up messages might usually contain cryptic messages or links that will redirect you to malicious websites. If you face such a situation, it could mean that there is a Trojan in your enterprise’s system.
Sudden Disappearance of Taskbar and Wallpaper
Another possible way to find out whether your system is infected by Trojan or not is by monitoring changes in the taskbar and wallpaper activity. If the taskbar of your endpoint device disappears or changes frequently, or wallpaper changes rapidly, then it could mean a Trojan infection. Along with the taskbar and wallpaper, the format of the desktop icons might also change due to the presence of Trojan.
How to Prevent Trojan Horse Attack

Trojan Horse attacks come in different manners and you can’t rely on one preventive measure to prevent such an attack. You need a comprehensive security approach to prevent such attacks. Here are some practices and technologies you can utilize to prevent Trojan Horse:
Safe Web Browsing
Trojan attacks often trick users into downloading malware programs from a fake site impersonating a legitimate website. You should avoid downloading any program from a site that doesn’t have HTTPS badging or has a peculiar web address.
You can also get help from a secure web browsing solution that assesses files before it is downloaded and helps in preventing such attacks.
Avoiding emails with attachments from Unknown Sources
Cybercriminals utilize phishing techniques by sending files through email attachments to inject Trojans into the enterprise’s computer. So the best defense against such an attack is to avoid opening email attachments or installing software from unknown sources.
Keeping All Software Updated
All the inbuilt system security software should be updated at regular intervals which mitigates the security flaws and vulnerabilities Attackers utilize various techniques to exploit security flaws that help Trojans in facilitating their actions.
Keep the Firewall Enabled
Firewalls of both the security software and hardware play an important role in an enterprise to prevent Trojans from infecting the system. IT administrators should always keep the firewall in an active state and utilize a firewall system that will prevent malicious from affecting endpoints and networks.
Avoiding Third-Party Downloads
Users using endpoints in a network should avoid visiting websites with shortened URLs and downloading any program from unknown publishers. You should always download programs from known sources having an HTTPS web address, known vendors or official websites.
Endpoints Security Solutions
Endpoints of an enterprise serve as an entry point for many Trojans so utilizing endpoint security solutions can not only help in detecting malware but also zero-day attacks. An effective endpoint security solution can create a robust security perimeter to prevent most of the Trojan Horse types.
Web Application Firewall
Web Application Firewall or WAF when deployed at network edges, plays a significant role in preventing Trojan infection by preventing execution of malicious software or attachments. Moreover, it also has the capability to identify and block any unusual behavior in network communication.
Anti-Phishing Solution
Utilizing anti-phishing solutions serves as one of the effective ways to prevent Trojan attacks. Phishing techniques serve as the primary technique to deliver Trojans to the system and trick users into executing them. Anti-phishing solutions can block such malware delivery by blocking malicious emails from reaching the user’s inbox.
Mobile Device Management
Users often download applications into their endpoint mobile devices from unofficial app stores and these applications often help in delivering Trojans. MDM solutions help assess all mobile applications for unusual functionality before they are installed and prevent the device from a Trojan attack.
Threat Hunting
Threat hunting is another preventive measure that can help enterprises to prevent Trojan attacks. IT administrators can utilize tools like XDR and SIEM to utilize their advanced threat detection and data analytics to identify and mitigate Trojan infection.
Conducting Security Awareness Training
Humans are the primary target of attackers to deliver Trojans into the endpoints or system of an enterprise. Users with minimal security awareness often download or execute attachments that inject Trojans into the system. Every enterprise should conduct security awareness training where they aware employees of various phishing techniques and all the aspects associated with Trojan Horse attacks.
How CloudDefense.AI can Help?
Modern enterprises are constantly in threat from Trojan Horse attacks and a single breach in one system can compromise the whole network. It has become essential for organizations to adopt an all-in-one solution that will not only help enterprises detect all types of Trojans but also prevent them from affecting the network.
Platforms like CloudDefense.AI can be your ideal choice as it will meet all your requirements. CloudDefense.AI is a leading CNAPP platform that offers a varied type of solutions to prevent Trojan attacks in various ways and they are:
Ransomware Protection: With capabilities like rapid incident response, advanced threat detection and real-time monitoring, CloudDefnese.AI provides robust protection against ransomware Trojans.
WebApp Security: Attackers often exploit web applications to get entry into the network and extract data. However, you can utilize WebApp security that will mitigate outdated AppSec risk and prevent Trojan breaches.
Vulnerability Management: Trojan often exploits vulnerability in a system or network to gain access. However, having effective vulnerability management can discover all the vulnerabilities and fix them across the multi-cloud environment.
Threat Detection: With its cutting-edge threat detection solution, you can easily find any Trojan presence in your system and mitigate them before they can make any major impact.
Conclusion
We are hopeful we have been able to answer your query “What is a Trojan Horse” and give you a broad idea regarding this malware attack. In this article, we have supplied all the necessary information you need to build an effective security shield against Trojan attacks and protect your system from getting infected. Dealing and eliminating with Trojan is not an easy task and you will have to be diligent with your security measures and practices.







