What is Vulnerability Management? — Definition
Vulnerability Management is all about finding and fixing security vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and software. It involves identifying potential risks and taking steps to keep them from becoming real problems. Some of its key capabilities include:
- Identifies weak points across networks, applications, and devices.
- Assesses how serious each issue is, based on potential impact.
- Prioritizes which vulnerabilities to address first, focusing on the most critical.
- Remediates by applying patches, updates, or other security fixes.
- Continuously monitors for new risks to stay ahead of threats.
By taking a proactive approach, organizations can better protect their data and maintain compliance with security standards. It’s not a one-time effort but an ongoing strategy that keeps evolving with the changing threat landscape, ensuring systems stay secure over time.
What Are the Differences Between a Vulnerability, a Risk, and a Threat?
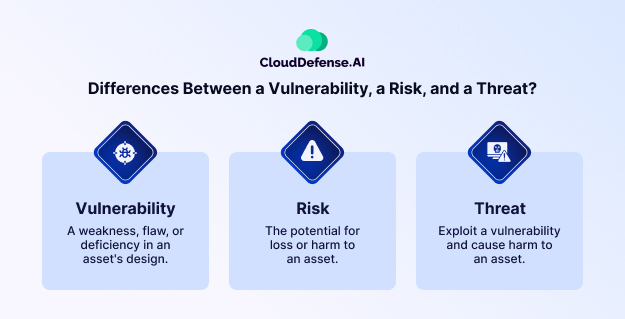
Before we move ahead, let’s clarify the differences between a vulnerability, a risk, and a threat, as it’s essential to understand these terms for effective vulnerability management.
- Vulnerability: A weakness or flaw in a system, software, or network that can be exploited.
- Threat: Anything that could exploit a vulnerability and cause harm, such as malware, hackers, or insider threats.
- Risk: The potential impact or damage that could occur if a vulnerability is exploited by a threat.
In essence, a vulnerability is the weak spot, a threat is what could take advantage of it, and risk is the possible outcome if nothing is done to address the issue.
| Read more: If you are interested in exploring more about Risk vs Threat vs Vulnerability, do read our exclusive article that explains the differences in details. |
What are Some Common Vulnerabilities that Businesses Face?
Businesses face various common vulnerabilities that can compromise their security. Here are some key examples:
- Unpatched software: Outdated software with known security flaws.
- Unsecured APIs: Interfaces lacking proper security measures.
- Weak credentials: Easy-to-guess passwords or poor authentication practices.
- Programming bugs: Code errors that create security gaps.
- Misconfigurations: Incorrect system settings that expose data.
- URL redirection: Redirects to malicious sites, often used in phishing attacks.
- Unsafe file uploads: Uploading files without proper security checks.
- Insider threats: Employees or contractors who misuse their access.
| Did You Know? The Log4j zero-day vulnerability, discovered in late 2021, exposed millions of systems worldwide to potential attacks! This serious flaw in a widely used logging library put countless organizations at risk, highlighting the importance of timely vulnerability management. Stay vigilant and protect your systems! |
How are Vulnerabilities Ranked and Categorized?
Ranking and categorizing vulnerabilities is essential for any organization looking to strengthen its security. It helps teams prioritize their efforts and manage resources effectively. Let’s break down how this process works in a more relatable way.
1. Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
One of the most popular methods used for this is the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). Think of CVSS as a grading system for vulnerabilities that helps teams understand how serious a problem is.
- Base Score: This is like the initial grade a vulnerability gets. It assesses how easily it can be exploited and the potential damage it could cause if someone takes advantage of it. A higher score means it’s more dangerous.
- Temporal Score: This adjusts the base score based on real-time factors. For instance, if a hacker has developed an easy exploit for that vulnerability or if a patch has become available, the score might change. It keeps things relevant to the current situation.
- Environmental Score: This part tailors the score to the specific context of an organization. It considers how critical the affected systems are for the organization and adjusts the score accordingly.
2. Risk Assessment
Next up is risk assessment, which is all about figuring out what could go wrong if a vulnerability is exploited. Here’s how it breaks down:
- Likelihood: This measures how likely it is that someone will exploit the vulnerability. It considers things like whether there are known exploits available or how active the threat landscape is.
- Impact: This looks at what would happen if the vulnerability were exploited. Would sensitive data be at risk? Could there be a significant operational disruption? Understanding this helps prioritize which vulnerabilities need immediate attention.
3. Severity Categorization
Finally, vulnerabilities are categorized based on their severity. Here’s how it usually looks:
- Critical: These are the “red flags” that require immediate action. They might allow attackers to take control of systems or access sensitive data quickly.
- High: Significant issues that should be addressed quickly but might not be an immediate crisis. They still need prompt action to avoid potential exploitation.
- Medium: These are moderate vulnerabilities that are less urgent but should be on the radar. Organizations can schedule time to address these without panic.
- Low: Minor vulnerabilities that pose minimal risk. While they should be tracked, they can be dealt with later on.
Vulnerability Management vs. Vulnerability Assessment
When discussing cybersecurity, terms like Vulnerability Management and Vulnerability Assessment often come up. While they might sound similar, they serve distinct purposes in protecting an organization’s digital assets. Here’s a breakdown of the differences in a clear and relatable way.
Vulnerability Management: Continuous Risk Mitigation
Vulnerability Management is all about the ongoing process of identifying and fixing security weaknesses in an organization’s systems and applications. It’s a proactive approach aimed at reducing risks over time. This involves everything from regularly scanning for vulnerabilities to patching them and ensuring systems are configured securely.
Vulnerability Assessment: Identifying Potential Weaknesses
On the flip side, Vulnerability Assessment is a snapshot in time. It involves checking systems to identify vulnerabilities at a particular moment. While it’s an essential part of understanding your security landscape, it doesn’t include the ongoing management or remediation of those vulnerabilities. Essentially, it tells you where your weaknesses are, but it’s up to you to take action.
Here’s a table that summarizes the difference between vulnerability management and vulnerability assessment in detail:
| Aspect | Vulnerability Management | Vulnerability Assessment |
| Definition | Ongoing process to find, prioritize, and fix vulnerabilities. | Snapshot analysis to identify vulnerabilities. |
| Objective | Minimize security risks through continuous management. | Provides a clear view of security posture. |
| Scope | Comprehensive; includes remediation and monitoring efforts. | Focused on scanning and reporting vulnerabilities. |
| Frequency | Continuous and ongoing. | Done periodically (like quarterly or biannually). |
| Tools Used | Utilizes various tools for scanning, patching, and ongoing monitoring. | Primarily relies on scanning tools for assessments. |
| Action Taken | Involves fixing vulnerabilities through patches and configuration changes. | Reports vulnerabilities but remediation is a separate step. |
| Outcome | A stronger security posture over time. | Identification of weaknesses at a specific point in time. |
| Responsibility | Managed by security teams with a focus on ongoing vigilance. | Can be conducted by internal teams or third-party vendors. |
Benefits of Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management is essential for keeping your organization’s digital assets secure. It’s not just about finding weaknesses—it’s about building a stronger defense against potential threats. Here’s a closer look at the key benefits:
1. Stronger Security Posture
By regularly scanning for vulnerabilities and addressing them, you can significantly improve your organization’s security. This proactive approach means you’re identifying and fixing issues before attackers have a chance to exploit them.
2. Effective Risk Mitigation
Not all vulnerabilities are created equal. Vulnerability management helps you prioritize based on the severity and potential impact of each weakness. This way, you can focus your resources on what matters most, reducing the chances of a successful attack.
3. Compliance Made Easier
Many industries have strict regulations around cybersecurity. Implementing a solid vulnerability management program helps you meet these compliance requirements, whether it’s GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. Keeping your vulnerabilities in check demonstrates that you’re serious about protecting sensitive data.
4. Faster Incident Response
When a security incident occurs, time is of the essence. With a robust vulnerability management process, your team can quickly identify if any known vulnerabilities contributed to the breach and take corrective action. This leads to a more effective response and helps prevent similar issues in the future.
5. Cost Savings
Addressing vulnerabilities early can save you a lot of money in the long run. The financial fallout from a data breach can be staggering—think remediation costs, legal fees, fines, and damage to your reputation. By investing in vulnerability management, you’re likely to avoid these costly consequences.
6. Increased Security Awareness
Vulnerability management isn’t just a tech issue; it’s about creating a culture of security within your organization. Regular training and awareness initiatives help employees understand the importance of cybersecurity, encouraging them to follow best practices and report potential issues.
7. Continuous Improvement
Vulnerability management is an ongoing journey, not a one-time task. Regular assessments and updates keep you aligned with the ever-changing threat landscape. This continuous improvement means you’re always ready to tackle new vulnerabilities and threats as they emerge.
8. Better Resource Allocation
Knowing where your vulnerabilities lie allows you to allocate resources more effectively. You can prioritize investments in security tools, training, and personnel based on the vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk, ensuring that your efforts are both efficient and impactful.
9. Incident Response Readiness
With a solid vulnerability management strategy, you’ll be better prepared to respond to incidents. Understanding existing vulnerabilities means you can develop effective response plans for any breaches or attacks.
Steps in Vulnerability Management Process
Managing vulnerabilities effectively is like keeping a close eye on your home’s security. You need to know what you have, what could go wrong, and how to fix things before trouble hits. Here’s a breakdown of the essential phases in the vulnerability management lifecycle, written in a relatable way to help you grasp these concepts easily.
Step 1: Identify Your Assets
First things first: you can’t protect what you don’t know you have. Start by creating a detailed list of your assets. Ask yourself:
- What physical devices do we have, like servers or routers?
Think of everything from your computers to networking devices. Knowing what hardware is in play helps you figure out where the risks might lie. - Which web applications are we using?
Make a note of all the web apps your team relies on. Understanding these gives you insight into potential vulnerabilities in your digital space. - What sensitive information do we need to protect?
Identify any sensitive data, like customer records or financial info. Knowing what needs extra care helps prioritize your security efforts.
By keeping an updated inventory of both hardware and software, you’ll set a solid foundation for everything that follows.
Step 2: Assess Vulnerabilities
Once you’ve identified your assets, it’s time to assess potential vulnerabilities. Consider these questions:
- What tools can help us find vulnerabilities?
Use vulnerability scanning tools tailored to your systems. They can help uncover weaknesses in your software, operating systems, and network setups that attackers might exploit. - How do we determine the severity of these vulnerabilities?
Create a system to evaluate how serious each vulnerability is. Prioritize them so you can focus on the ones that could do the most damage. - Are there any known vulnerabilities in our software or hardware?
Stay in the loop about the latest vulnerabilities affecting the tools you use. Regularly check security advisories from software vendors for any updates or patches.
Utilizing a range of scanning tools will help you keep your systems in check and reveal where you need to strengthen your defenses.
Step 3: Prioritize Threats
With vulnerabilities assessed, it’s time to figure out which ones to tackle first. Reflect on:
- Which vulnerabilities could be the most damaging to our operations?
Look at each vulnerability and assess its potential impact on your business. Some may have severe consequences if exploited, while others might be less critical. - What’s the likelihood that these vulnerabilities will be targeted?
Consider how easy it is for an attacker to exploit each vulnerability. This understanding helps you focus on the ones that pose the biggest threat. - What could happen if a vulnerability were to be exploited?
Think about the possible fallout, like financial losses or reputational harm. This assessment helps you prioritize your remediation efforts.
This phase is about focusing your resources effectively to protect your organization from the most significant threats.
Step 4: Mitigate Risks
Now that you know which vulnerabilities to address, it’s time to take action. Think about:
- What patches or updates are available for our systems?
Keep an eye out for security patches from software vendors and apply them promptly. Regular updates help close known vulnerabilities and keep your systems secure. - Do we need to tweak any existing configurations for better security?
Review the settings of your devices and applications to spot any insecure configurations. Adjusting default settings or tightening access controls can significantly enhance your security posture. - Should we consider replacing outdated software or hardware?
Sometimes, older systems may pose risks because they are no longer supported. Evaluate whether upgrading to newer solutions is necessary to maintain a strong security stance.
Taking action on high-priority vulnerabilities helps reduce your organization’s overall risk.
Step 5: Document and Learn
Once you’ve implemented fixes, make sure to document your findings. Ask yourself:
- How can we improve our reporting for future vulnerabilities?
Create clear reports that outline identified vulnerabilities, remediation steps taken, and their current status. This practice fosters communication within your team and provides a useful record for future reference. - What strategies worked well, and what could be improved?
Take a moment to reflect on what you learned during the process. Understanding what approaches were effective and which weren’t can help refine your strategies moving forward. - How do we ensure compliance with industry regulations in the future?
Stay updated on regulatory requirements related to data protection and security. Documenting your processes and findings can assist in meeting compliance obligations.
Proper documentation not only helps with compliance but also strengthens your organization’s overall security strategy.
Step 6: Continuous Monitoring
The final phase involves ongoing monitoring of your systems to catch any new vulnerabilities. Consider:
- How can we automate monitoring to spot threats in real time?
Implement automated tools that continuously scan your environment for new vulnerabilities. These tools can help detect changes and potential risks without needing constant manual oversight. - Are our current tools effective in identifying new vulnerabilities?
Regularly assess the performance of your monitoring tools to ensure they are up to date with the evolving threat landscape. They should be capable of detecting vulnerabilities across all your assets. - What processes can we implement for swift responses to detected threats?
Establish clear incident response protocols that outline steps to take when a vulnerability is identified. Quick reactions can help minimize potential damage.
Continuous monitoring is key to maintaining a strong security posture and addressing vulnerabilities promptly as they arise.
What to look for in a Vulnerability Management Solution?
When it comes to choosing a vulnerability management solution, it’s not just about ticking boxes. You need something that genuinely fits your organization and can keep up with the evolving security landscape. Here’s what you should look for:
1. Comprehensive Asset Discovery
- Can it identify all assets across your environment?
A good solution should give you a complete view of all your assets, whether it’s physical devices, cloud instances, or applications. After all, you can’t protect what you don’t know about. - Does it automatically update your asset inventory?
You’ll want a tool that refreshes your asset inventory in real-time, accounting for any new additions or changes without you having to lift a finger.
2. Reliable Vulnerability Detection
- Does it use a variety of methods to find vulnerabilities?
The more ways it can spot risks—like vulnerability scans, risk priortization, and automated remediation—the better protected you’ll be. - How frequently does it update its threat database? Threats are constantly changing, so your solution should update frequently with the latest vulnerabilities, keeping you ahead of the curve.
3. Accurate Risk Scoring and Prioritization
- How does it rank or prioritize vulnerabilities?
The right tool won’t just give you a generic score. It should factor in what really matters to your business—like the potential impact on operations or compliance requirements. - Can it tell you what to fix first?
Prioritization should go beyond severity scores. It’s about understanding which risks are more likely to be exploited and could cause the most damage, so you’re not wasting time chasing minor issues.
4. Auto Remediation Options
- Does it help you fix problems quickly?
Look for features like automated patching, configuration guides, or easy-to-follow instructions that make it simple to address issues right away. - Can it fit into your current workflow without disrupting everything?
Make sure the tool integrates with your existing processes, like ticketing or DevOps pipelines, so it becomes a part of your daily routine, not a headache.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Alerts
- Does it support ongoing monitoring for new vulnerabilities?
Vulnerabilities can pop up anytime. Continuous scanning ensures you’re alerted the moment something changes, not after it’s too late. - Can it detect changes in your environment that may introduce risks?
Look for solutions that can spot not just new vulnerabilities but also changes in configurations or permissions that could create security gaps.
6. Strong Compliance and Reporting Features
- Does it align with industry compliance standards?
If you’re dealing with strict standards like GDPR or HIPAA, the tool should help you stay compliant and make audits smoother with built-in reports. - Are the reports user-friendly and customizable?
The ability to create custom reports for different audiences (like execs or tech teams) will save you time and make security easier to communicate.
7. Seamless Integration with Other Tools
- Can it work with your current security setup?
Check if it integrates with other tools you’re using, such as SIEMs or firewalls, to build a cohesive security system. - Does it allow custom automations?
Look for solutions with good integration capabilities that let you create tailored workflows, making your vulnerability management more efficient and less manual.
CloudDefense.AI’s Approach to Vulnerability Management
If you want a solution that satisfies all the criteria we discussed above, then CloudDefense.AI might be exactly what you’re looking for.
Here’s how we go beyond the basics to deliver unmatched vulnerability management:
1. Comprehensive, Agentless Assessment
CloudDefense.AI offers continuous, agentless monitoring, ensuring that your entire environment is thoroughly assessed without burdening system performance. This allows for complete visibility across all assets, whether in the cloud or on-premises.
2. Smart Prioritization with Context-Driven Insights
Vulnerabilities aren’t just ranked by severity; they’re assessed in context. CloudDefense.AI prioritizes based on the potential impact, allowing your team to focus on the most critical threats first. This context-driven approach helps you understand how a specific vulnerability might affect your operations, enabling smarter, quicker decision-making.
3. Seamless Integration into CI/CD Pipelines
Security shouldn’t come as an afterthought. With built-in integration for CI/CD workflows, CloudDefense.AI catches vulnerabilities early in the development lifecycle. Automated scans ensure that security issues are identified and resolved before your applications even reach production.
4. Advanced Attack Path Analysis
Go beyond surface-level detection. CloudDefense.AI uses attack path analysis to understand how different vulnerabilities might be exploited together, providing a more comprehensive view of potential risks and offering more effective remediation strategies.
5. Real-Time CVE Intelligence and Threat Insights
Get up-to-the-minute data on emerging threats with real-time updates on new CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures). CloudDefense.AI keeps you informed with the latest risk assessments, so you’re never caught off guard.
6. Customized Compliance and Reporting
Meeting compliance standards is a easy process with built-in support for regulations like ISO 27001, SOC II, and GDPR. CloudDefense.AI helps maintain continuous compliance through automated checks and user-friendly reporting, making it easy to demonstrate adherence during audits.
7. Automated Remediation Powered by AI
Don’t just detect issues—resolve them quickly with AI-driven remediation suggestions. CloudDefense.AI guides your security team through each step to fix vulnerabilities, helping to patch, reconfigure, or mitigate as needed with precision and speed.
8. Complete Asset Inventory and Continuous Monitoring
Maintain a detailed inventory of all assets, with continuous monitoring that tracks any changes in your environment. By identifying and securing every asset, CloudDefense.AI ensures that nothing slips through the cracks, giving you full control over your security posture.
Wrapping up!
CloudDefense.AI delivers all the essential tools and more to keep your organization safe from threats. If you’re ready to take a proactive approach to vulnerability management and see what CloudDefense.AI can do for you, consider booking a free demo today. Get hands-on experience with a powerful solution that not only meets but exceeds modern security demands.







