Cloud tech isn’t just running in the background anymore—it’s the backbone of modern business. But as we all know, with great capability comes an even greater need for security. Fast-forward to 2025, and you’ve got cyber threats evolving faster than software updates. Organizations face a relentless challenge: How do you outsmart the bad actors and keep your data, apps, and infrastructure locked down?
That’s where cloud vulnerability management comes in. This guide breaks down key strategies and best practices for spotting and handling vulnerabilities in the cloud. These steps will help make sure your cloud environment stays resilient, reliable, and ready for whatever comes next.
What is Vulnerability Management?
In cloud computing, vulnerability management is all about continuously identifying, analyzing, and addressing security issues across your cloud environment. It’s a proactive process that helps businesses protect their cloud infrastructure—whether on AWS, Azure, GCP, or any other public cloud—by finding and fixing weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Think of it as a framework for staying in control of your cloud security. Good vulnerability management does more than just “plug leaks.” It actively blocks every possible entry point, sealing off paths that attackers might use to breach your systems. This has become an essential pillar in defending against modern cloud security threats.
So how does it work? Effective cloud vulnerability management follows four steps:
- Identify Vulnerabilities: The process begins with scanning for potential weaknesses in the infrastructure.
- Assess Risks: After identifying vulnerabilities, the next step is to evaluate how severe each one is.
- Prioritize: Not all risks are equal, so you’ll need to determine which ones to tackle first.
- Remediate and Confirm: Finally, fix the issues and verify the solution through re-scanning and reporting.
By following these steps, cloud vulnerability management ensures that your cloud environment remains secure, resilient, and ready to handle whatever challenges come its way.
| Did You Know? Cloud vulnerabilities are rising fast! In 2023 alone, 26,447 new vulnerabilities were disclosed—1,500 more than the year before. That’s three new security risks discovered every three hours, with exploit code available for over 7,000 of them. |
Some Common Cloud-Based Vulnerabilities
When you employ cloud vulnerability management in your cloud workspace, it is best to know about the cloud-based vulnerabilities that need to be identified and managed.
Here are some common cloud-based vulnerabilities that need to be addressed to prevent any security breaches;
1. Misconfiguration in containers:
One of the common vulnerabilities is a misconfiguration in containers, and it has led to severe breaches in the cloud platform.
These misconfigurations are glitches that have arisen due to a lack of required secure settings or leaving the cloud platform with public access. Security group misconfiguration is another type of vulnerability that occurs in a security system and leads to direct access to the cloud platform.
2. Improper authentication:
Poor authentication process in the cloud security system is another common vulnerability that often leads to security breaches. Lack of multi-factor authentication and poor password strength are some serious cloud vulnerability management challenges.
Moreover, when there is no proper access control, any authorized user who shouldn’t be allowed to get access may be able to get into the cloud system.
3. Non-compliance:
Non-compliance with industry standards like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and SOC 2 is one leading cause of vulnerabilities in the cloud platform. These cloud vulnerability management policies ensure that your cloud workload is appropriately secured.
When the cloud security provider and customer improperly manage the security settings, it leads to glitches, and attackers take advantage of them to gain access to the server.
4. Bad network configuration:
It is essential that your cloud network should be configured appropriately; otherwise, it would risk data security. The security team should be careful with providing port access to private networks because if it is left open by default, then anyone can access the sensitive data.
The security team should provide access to specific ports that are needed to access, and all the other ports should be disabled for connection to private networks.
5. Poor access management to sensitive data:
Cloud platforms contain many specific applications that can help anyone to get access to many sensitive data. So it is vital that you should never create a group credential or ID for all the applications.
Instead, it would be best if you created specific credentials for specific applications, and only authorized personnel can get access to them. A marketing or network user shouldn’t have access to applications that contain sensitive financial data.
6. Improperly secured APIs:
Insecure APIs serve as one of the primary ways for attackers to gain access to cloud platforms and steal all the essential data. Not every cloud provider secures APIs properly, and these insecure APIs lead to providing pathways for attackers to get access to the cloud platform. Attackers always look for APIs that lack proper authorization and authentication and exploit them for illicit means.
7. DDoS attack:
DDoS attack or distributed denial of services is another common vulnerability that occurs in the cloud environment. In this vulnerability, the attackers flood the infrastructure with numerous requests and make servers unresponsive so that authorized requests can’t be processed.
This vulnerability mainly occurs when the cloud provider doesn’t have proper DDoS protection or DDoS security is kept off.
| Read More: For a deeper dive into the fundamentals of vulnerability management and how it fits into your cloud security strategy, check out our exclusive article on What is Vulnerability Management? |
Features of a Vulnerability Management Solution
When it comes to cloud vulnerability management solutions, there are certain features that make it vital for the cloud infrastructure as it ensures optimum protection.
So let’s take a look at those features that makes cloud vulnerability management important;
Optimum security protection:
Cloud vulnerability management is responsible for constant monitoring and detecting threats in your system. They ensure all the data and applications are completely protected; it identifies the threats and remediates them efficiently. By employing effective cloud vulnerability management techniques, the vendor ensures better security for your cloud infrastructure.
Effective prevention:
Another vital feature that makes cloud vulnerability management imperative for cloud applications and data is effective preventative measures. Whatever the attack intensity is directed at your cloud application and crucial data, cloud vulnerability remediation can easily prevent and block them.
Cost-effectiveness:
Manual monitoring, managing, and detecting threats in the cloud infrastructure is an expensive and cumbersome task. However, having cloud-vulnerable management for cloud security makes it very cost-effective to secure all the cloud applications and data stored in the system.
Through constant monitoring and quick remediation of threats, cloud vulnerability management saves you from colossal fixing costs and losses if the infrastructure is exploited.
Saves time:
Having cloud vulnerability management saves a lot of time by helping you to detect and solve vulnerabilities in the first place. When you don’t continuously monitor your cloud infrastructure, it can lead to glitches that can be exploited by attackers.
The time then you will have to spend to remediate the after-effect of the vulnerability will be a lot, and it will also incur a lot of resources and expenditure. But when your data and application in the cloud are monitored by cloud vulnerability management, you can save a lot of time.
Best Cloud Vulnerability Management Practices
You can’t expect to have a successful vulnerability management platform in your cloud environment without opting for best practices. These practices not only enhance perfection but also maximize the security of your infrastructure. Here are some best cloud vulnerability management practices:
1. Contextualizing Vulnerabilities
When it comes to cloud vulnerability management, context is everything. Common scoring systems like CVSS don’t account for the full business impact of a vulnerability, which is why it’s essential to go beyond basic metrics and consider the bigger picture.
Start by answering these critical questions for each vulnerability:
- Who can access the vulnerable system?
- Is the system exposed to the internet?
- What data could be compromised if breached?
- What would the impact be if this resource were compromised?
By focusing on these questions, you gain a clearer sense of each vulnerability’s potential impact, allowing you to prioritize more effectively. To build this context, consider other risk factors that could contribute to an attack path, such as:
- Misconfigurations in your cloud environment
- Exposed secrets or sensitive data
- Excessive permissions that may enable lateral movement
- Publicly exposed assets or services
How CloudDefense.AI Helps with Contextual Analysis
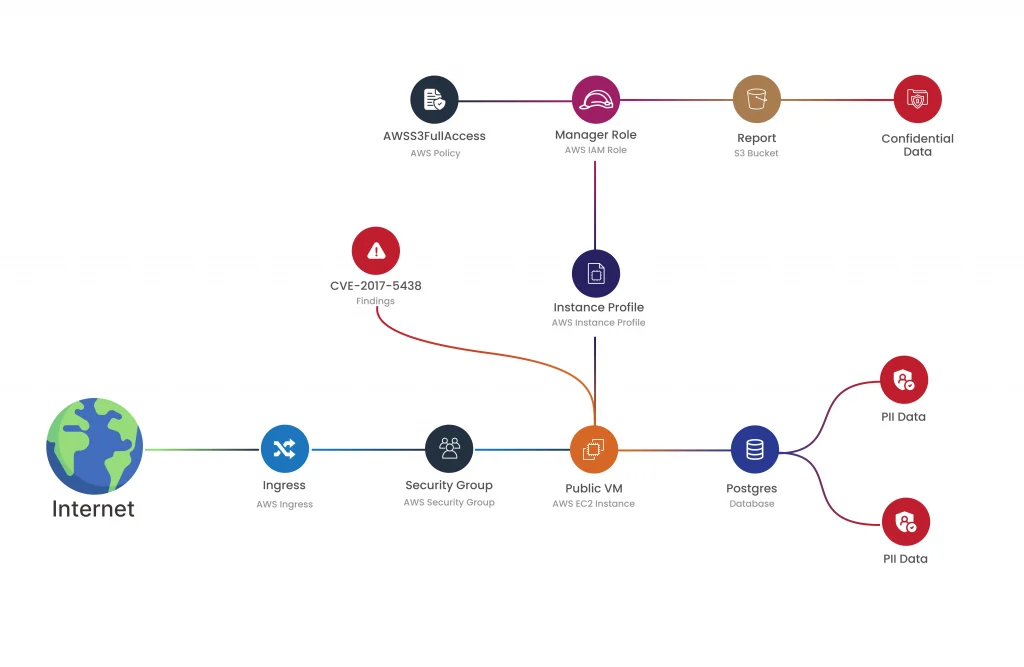
Tools like CloudDefense.AI take context-based vulnerability management to the next level. With CloudDefense.AI, you get insights into critical attack paths and risky combinations within your environment, helping you understand the real-world risk associated with each vulnerability.
CloudDefense.AI correlates vulnerabilities with related risks—like misconfigurations, public exposure, permissions, secrets, and even malware—so you can focus on vulnerabilities that pose the highest threat to your business.
When implementing context-aware vulnerability management, the goal is to prioritize issues that impact your business directly, from code deployment to runtime. CloudDefense.AI makes this easy by aggregating critical data in its Vulnerability Dashboard, providing your team with the information needed to tackle the most pressing issues. Our security Graph offers a deeper dive into each vulnerability’s context, along with tailored remediation guidance to help you address high-impact issues quickly.
2. Constant Cloud Vulnerability Scanning
To stay ahead of emerging threats, it’s crucial to have a system for continuous cloud vulnerability scanning. Early detection of vulnerabilities can prevent minor issues from turning into major security risks. Here’s how to make cloud vulnerability scanning effective and efficient:
- Use Updated Vulnerability Databases: Make sure your scanners rely on a comprehensive, up-to-date database of known vulnerabilities, so they’re equipped to catch threats at the earliest stage.
- Ensure Accurate Detection: Effective scanners should be able to:
- Identify any logic errors that could lead to security gaps.
- Filter out false positives, helping your team focus only on real threats.
- Conduct “behind the login” scans to catch vulnerabilities that might otherwise go undetected.
- Integrate Scanning in the Development Pipeline: To embed security into the development process, establish automated vulnerability checks within your CI/CD pipeline using tools like SAST, and IaC scanning solutions.
With continuous cloud vulnerability scanning in place, you create an added layer of protection, identifying and fixing potential issues before they have a chance to escalate.
How CloudDefense.AI Enhances Continuous Scanning
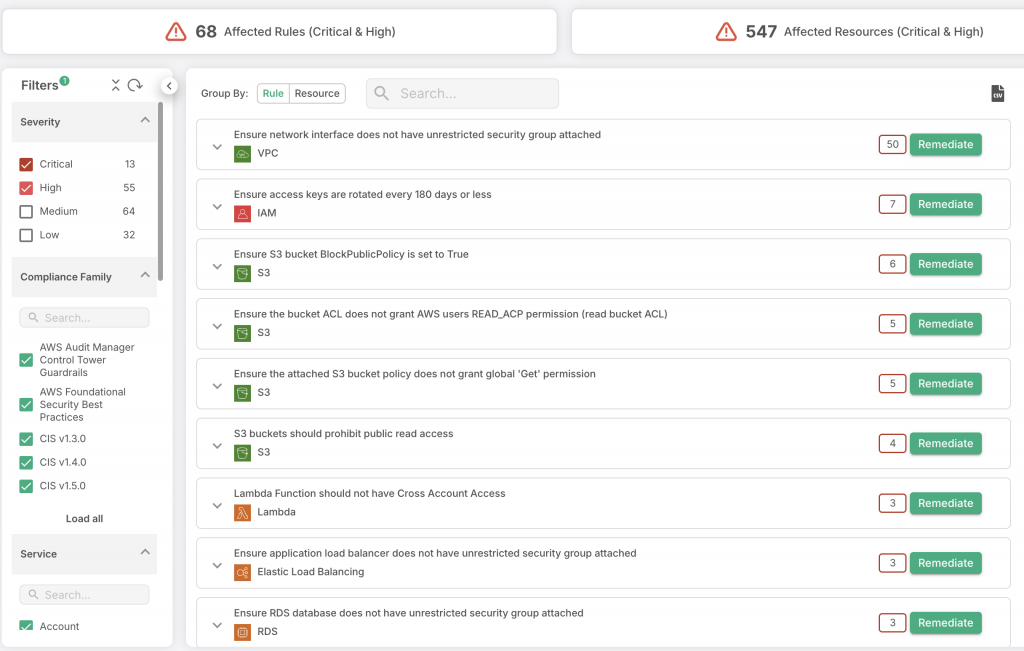
CloudDefense.AI enhances continuous vulnerability scanning by automating it across your entire cloud environment. Here’s how CloudDefense.AI strengthens cloud scanning:
- Real-Time Threat Detection: CloudDefense.AI continuously monitors your infrastructure, detecting vulnerabilities as soon as they appear. This enables your team to take action quickly, reducing exposure time.
- Comprehensive Coverage: By scanning for misconfigurations, malware, excessive permissions, and other risks, CloudDefense.AI provides a holistic view of your security posture.
- Seamless Integration: CloudDefense.AI integrates smoothly into your CI/CD pipeline, running scans automatically on new code and infrastructure changes to catch vulnerabilities before they go live.
3. Prioritizing the Vulnerabilities:
Once you have comprehensive visibility across your cloud environment, the next step is to focus on the vulnerabilities that present the highest risk. Not all vulnerabilities are equal—some are far more dangerous than others, depending on factors like your application, data sensitivity, and cloud configuration.
Why Prioritization Matters
Prioritizing vulnerabilities isn’t one-size-fits-all; each organization has its own risk landscape. To make prioritization effective, consider these factors:
- Vulnerability Severity: Evaluate each vulnerability based on its potential to impact critical systems or sensitive data.
- Business Impact: Consider how a vulnerability might affect your operations, customer trust, and compliance obligations.
- Environmental Context: Some vulnerabilities are more dangerous in specific cloud setups or configurations, so assess risk within your unique environment.
- Exposure Level: Prioritize issues with public exposure or those that allow lateral movement, as these have a greater chance of being exploited.
By focusing on these criteria, your team can target remediation efforts on the vulnerabilities that matter most, saving time and reducing risk where it counts.
How CloudDefense.AI Helps Prioritize Vulnerabilities
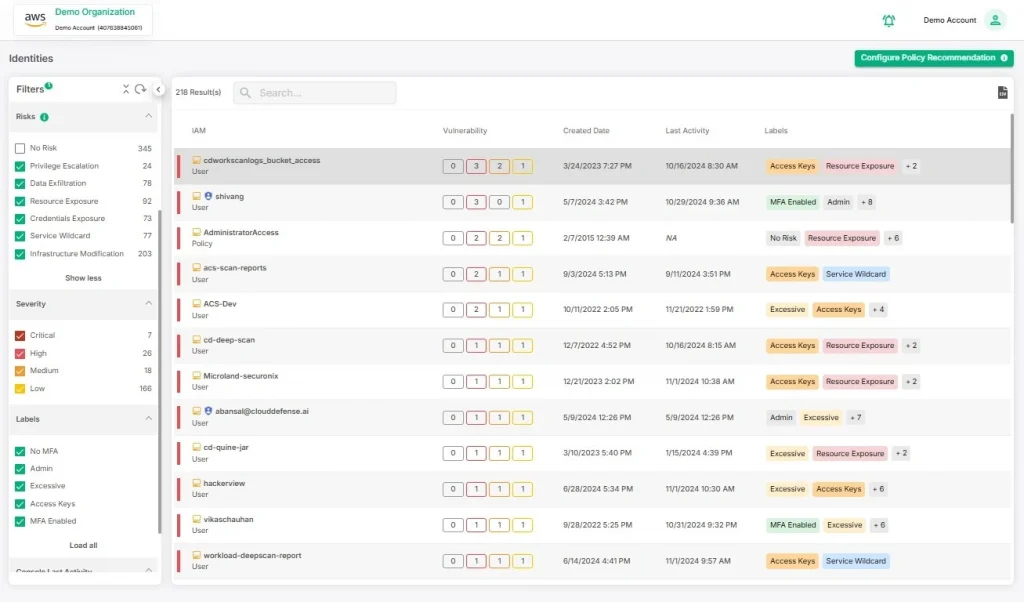
CloudDefense.AI makes it easy for organizations to prioritize vulnerabilities through a comprehensive analysis of each weakness in relation to the surrounding cloud environment. Below are some ways in which CloudDefense.AI improves vulnerability prioritization:
- Contextualized Insights: CloudDefense.AI correlates each vulnerability with misconfigurations, public exposure, and access privileges, helping your team understand which issues are most critical.
- Impact-Driven Alerts: Generates alerts for vulnerabilities that pose the highest risk to business operations and data security, allowing teams to focus on the areas that matter most.
- Customizable Prioritization: With CloudDefense.AI, you can adjust prioritization settings based on your organization’s risk profile and business needs, ensuring that your resources are used efficiently.
4. Full Visibility of the Cloud Infrastructure
It is important for security managers to see all over the cloud infrastructure so as to manage security properly. By conducting comprehensive assessment, security teams are able to see every asset that is in the cloud and therefore be in a position to detect any risk and its source. The following are reasons why it is important to have inclusive visibility:
- Early Detection: Total visibility enables security teams to identify emerging risks before they become serious enough and take appropriate measures.
- Root Cause Analysis: Understanding where risks come from enables teams to deal with fundamental problems and minimize their chances of occurrence in future.
- Efficient Monitoring: Visibility over every part of the cloud environment makes it possible for security teams to keep watching out for misconfigurations, unauthorized entries, abnormal activities so that everything is under control.
Here’s how CloudDefense.AI enhances Infrastructure Visibility
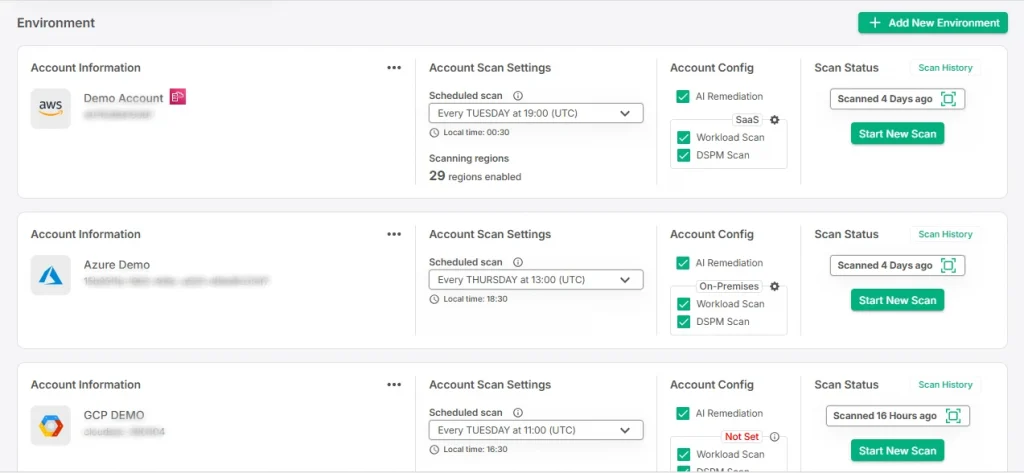
CloudDefense.AI ensures that companies have continuous and up-to-date visibility into their entire cloud environment through:
- Automated Asset Discovery: With CloudDefense.AI, all cloud assets are identified automatically so that no resource is left out.
- Detailed Context: CloudDefense.AI provides information on each asset such as configuration settings, access rights as well as its interplay with other resources thus aiding in decision making of security by the team.
- Continuous Monitoring: CloudDefense.AI carries out round-the-clock surveillance on assets for weaknesses, misconfigurations, exposure risks and offers immediate alerts on any identified issues.
5. Concentrate on Compliance
As part of vulnerability management, security teams must prioritize compliance to ensure all cloud workloads are secure and meet industry standards. An effective compliance strategy includes not only regular patching but also customized compliance measures that align with organizational needs.
- Ensure Patch Compliance: To keep system secure, it is important to apply patches which are updated version of security software that can be used to reduce risks associated with non-compliance of regulations.
- Tailor Compliance Practices: Different organizations have different requirements in relation to security and following certain laws. Customize compliance measures with respect to applicable laws (such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS) and internal rules of the organization.
- Follow Regulatory Requirements: Adherence to certain rules by industry reduces the risk of lawsuits and penalties, but at the same time contributes to an increased level of security within an organization.
- Document Compliance Efforts: Make sure to take notes on everything you do for compliance, like patch management, and show them when required by auditors who will want proof of adherence with rules.
How CloudDefense.AI Supports Customized Compliance
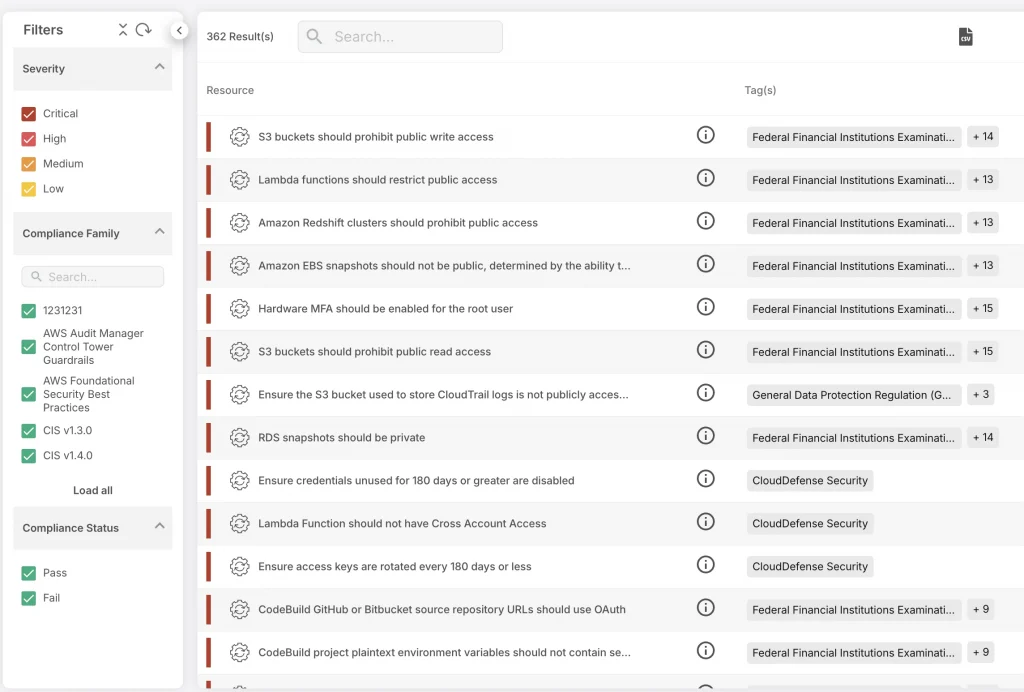
By providing tailored compliance solutions, CloudDefense.AI enhances the effectiveness of compliance management:
- Automated Tracking: For outdated components throughout your cloud environment, CloudDefense.AI identifies what they are so that proper measures can be taken to ensure system safety.
- Customized Compliance Templates: In order to simplify meeting your particular compliance requirements, CloudDefense.AI offers standardized templates for various industry standards.
- Compliance Reporting: CloudDefense.AI generates compliance-focused reports that demonstrate adherence to regulatory standards, streamlining audit processes.
- Continuous Monitoring: With continuous scanning, CloudDefense.AI is able to identify any non-compliance with configuration or assets and alert the team so that they can keep up a secure environment which complies with regulations
6. Attack Path Analysis and Auto remediation
The first step to making cloud environments secure is to trace out all the attack paths and use the auto remediation process to rectify vulnerabilities autonomously. Attack path analysis shows IT professionals where attackers could potentially intervene and exploit a weak point. Following this, auto remediation enables to respond immediately through automated repair mechanisms.
- Identify Attack Paths: The attack paths will reveal how an attacker would be able to move in your cloud environment to access sensitive data or disrupt services.
- Correlate Weak Points: Provide links between various vulnerabilities, misconfiguration issues, and exposure threats that the attacker could target consecutively.
- Visualize Attack Chains: The attack paths’ visual representation helps the security teams trace the potential flow of attacks and, hence, prioritize the protections in those high-risk areas.
Along with that, automating remediation processes allows teams to address issues immediately, reducing the time vulnerabilities remain exposed.
- Automated Response to Vulnerabilities: Set up workflows that automatically address known vulnerabilities or misconfigurations upon detection.
- Reduce Manual Intervention: By automating repetitive security tasks, teams can focus more on strategic analysis and response.
- Continuous Risk Mitigation: Auto remediation acts as a proactive measure, reducing the risk of exploitation without waiting for manual fixes.
How CloudDefense.AI Helps?
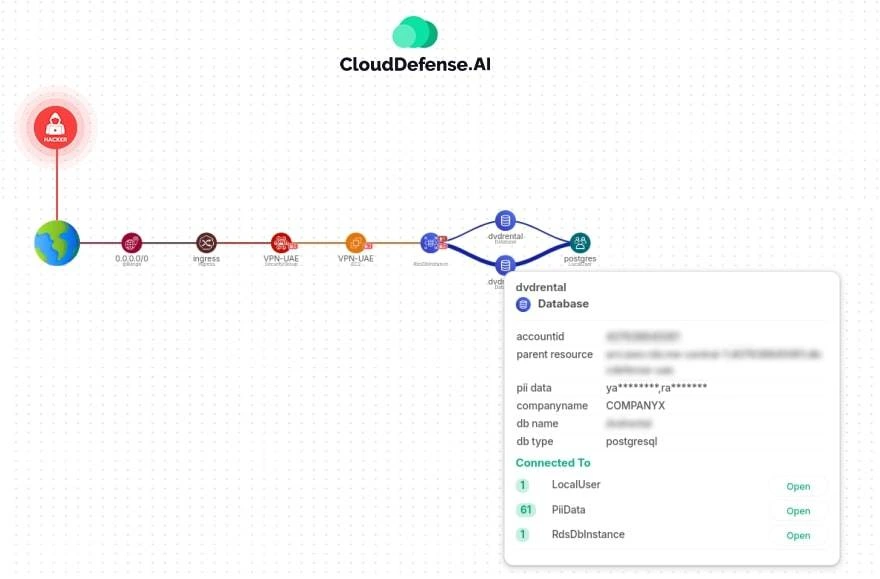
CloudDefense.AI empowers organizations to defend against complex attack paths and automate security responses:
- Comprehensive Attack Path Visualization: Our Security Graph maps potential attack paths across your cloud environment, highlighting vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and sensitive data exposure.
- Risk Correlation and Prioritization: CloudDefense.AI correlates risks across the environment, showing critical paths attackers might use and enabling prioritized protection.
- Auto remediation Workflows: Our platform offers built-in auto remediation features, automatically resolving common issues like misconfigurations and permission errors to keep your environment secure.
- Continuous Monitoring and Automated Fixes: CloudDefense.AI continuously monitors for new risks and initiates immediate remediation steps, ensuring minimal exposure time.
Upgrade Your Cloud Vulnerability Management with CloudDefense.AI
Managing cloud vulnerabilities requires precision, speed, and comprehensive visibility—and that’s where CloudDefense.AI excels. Our platform empowers organizations with proactive vulnerability management, real-time threat detection, and seamless auto remediation. With CloudDefense.AI, you gain end-to-end cloud protection, from uncovering hidden vulnerabilities to safeguarding critical assets with automated security solutions.
Ready to protect your cloud environment with a trusted, efficient, and scalable security platform? Join the countless organizations that rely on CloudDefense.AI for enhanced cloud resilience. Take the next step toward superior cloud security—Book a demo and discover how CloudDefense.AI can strengthen your defenses!







